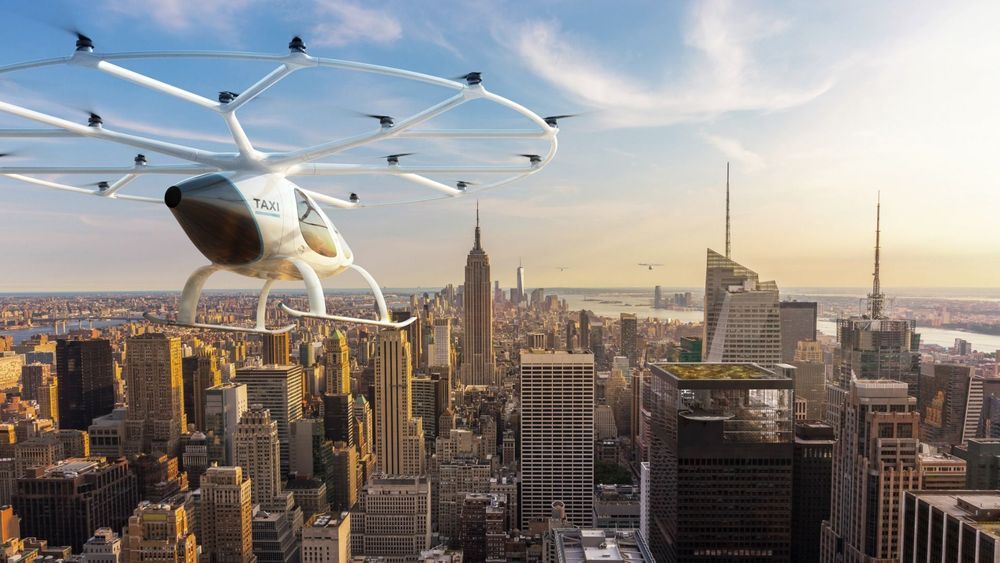
Electric VTOL air taxis are one of the great emerging technologies of our time, promising to unlock the skies as traffic-free, high-speed, 3D commuting routes. Much quieter and cheaper than helicopter travel, they’ll also run on zero-local-emission electric power, and many models suggest they’ll cost around the same per mile as a ride share.
Eventually, the market seems to agree, they’ll be pilotless automatons, even cheaper and more reliable than the earliest piloted versions. Should the onboard autopilot computers get confused, remote operators will take over and save the day as if they’re flying a Mavic drone, and every pilot gone will be an extra passenger seat in the sky.
Large numbers of eVTOL air taxis will change the way cities and lifestyles are designed. Skyports atop office buildings, train stations and last-mile transport depots will encourage multi-mode commuting. Real estate in scenic coastal areas might boom as people swap 45 minutes crawling along in suburban traffic for 45 minutes of 120 mph (200 km/h) air travel, and decide to live further from the office.