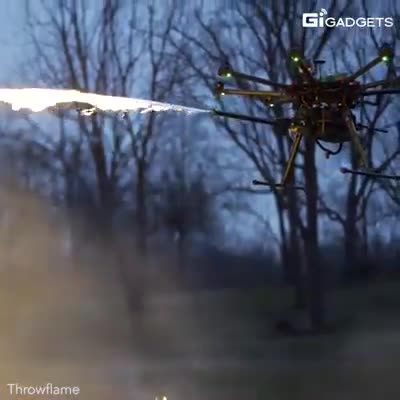
Drones with flamethrowers! 😃 They seem to be using it to burn hornets nests and debris.
This flamethrower drone can shoot a 23-foot-long stream of fire.
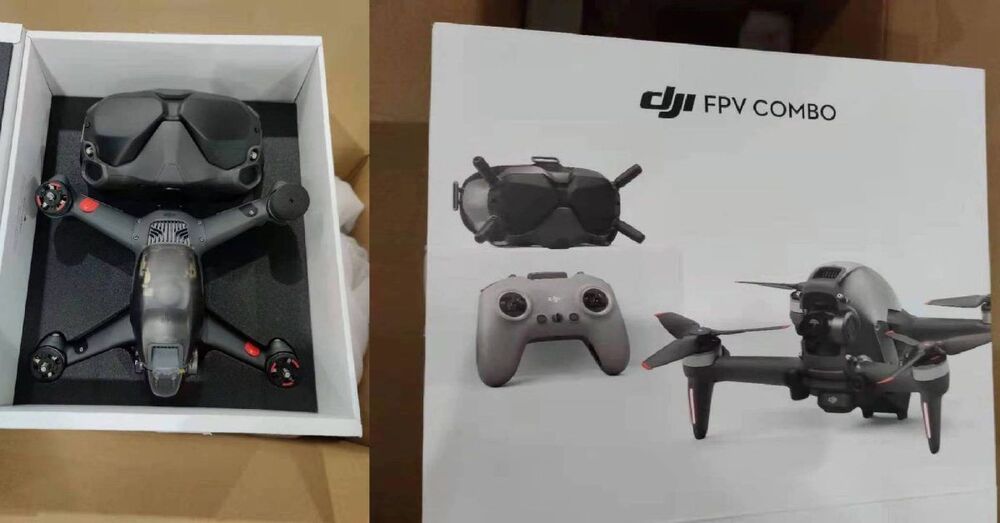



There’s a lot of buzz right now about DJI’s impending FPV drone. We have some thoughts on why there’s so much interest and why this product will likely be a winner for the company.
It’s pretty clear that people are champing at the bit for the release of the new DJI FPV drone. We can say that because we’ve seen the page views on those posts, as well as the many comments and questions posted to our YouTube channel or sent as DMs on our Facebook page. Many people seem to be super keen to see this new drone in person. We are, too. And all this has us thinking this product has the potential to be huge. Huge.
Let’s have a look at why we say that.
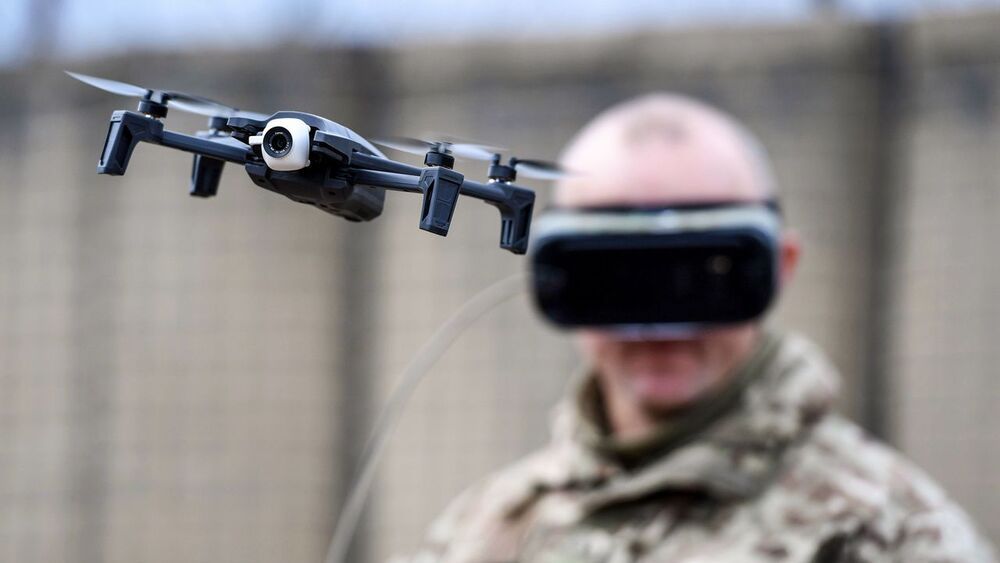


Future EDF research topics will be specified in annual calls run by the European Commission, the EU executive branch, and approved by a committee of national delegates. AI will be a big topic, Ripoche says. He says EDF funding will also go to new materials, such as discreet metamaterial antennas that can be engineered into the surfaces of vehicles and weapons. Muravska says she expects “a healthy take-up” in the EDF by European academic researchers, “provided they are aware of it.”
With no military of its own, European Union funds work on camouflage, drones, and laser weapons.



We all have images in our mind of rocket launches from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station hurtling astronauts into space and satellites into orbit.
But those launches may be a thing of the past as a new generation of drones that can do the same job cheaper, safer and better steps into play.
Alabama-Based Aevum unveiled its Ravn X Autonomous Launch Vehicle Wednesday that it says is the world’s largest unmanned aircraft system.

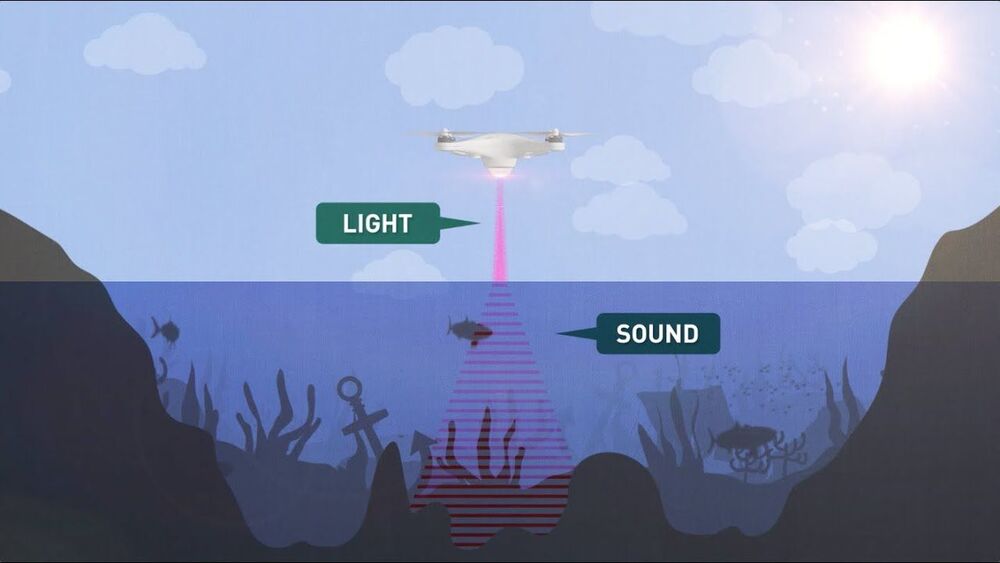
Stanford University engineers have developed an airborne method for imaging underwater objects by combining light and sound to break through the seemingly impassable barrier at the interface of air and water.
The researchers envision their hybrid optical-acoustic system one day being used to conduct drone-based biological marine surveys from the air, carry out large-scale aerial searches of sunken ships and planes, and map the ocean depths with a similar speed and level of detail as Earth’s landscapes. Their “Photoacoustic Airborne Sonar System” is detailed in a recent study published in the journal IEEE Access.
“Airborne and spaceborne radar and laser-based, or LIDAR, systems have been able to map Earth’s landscapes for decades. Radar signals are even able to penetrate cloud coverage and canopy coverage. However, seawater is much too absorptive for imaging into the water,” said study leader Amin Arbabian, an associate professor of electrical engineering in Stanford’s School of Engineering. “Our goal is to develop a more robust system which can image even through murky water.”