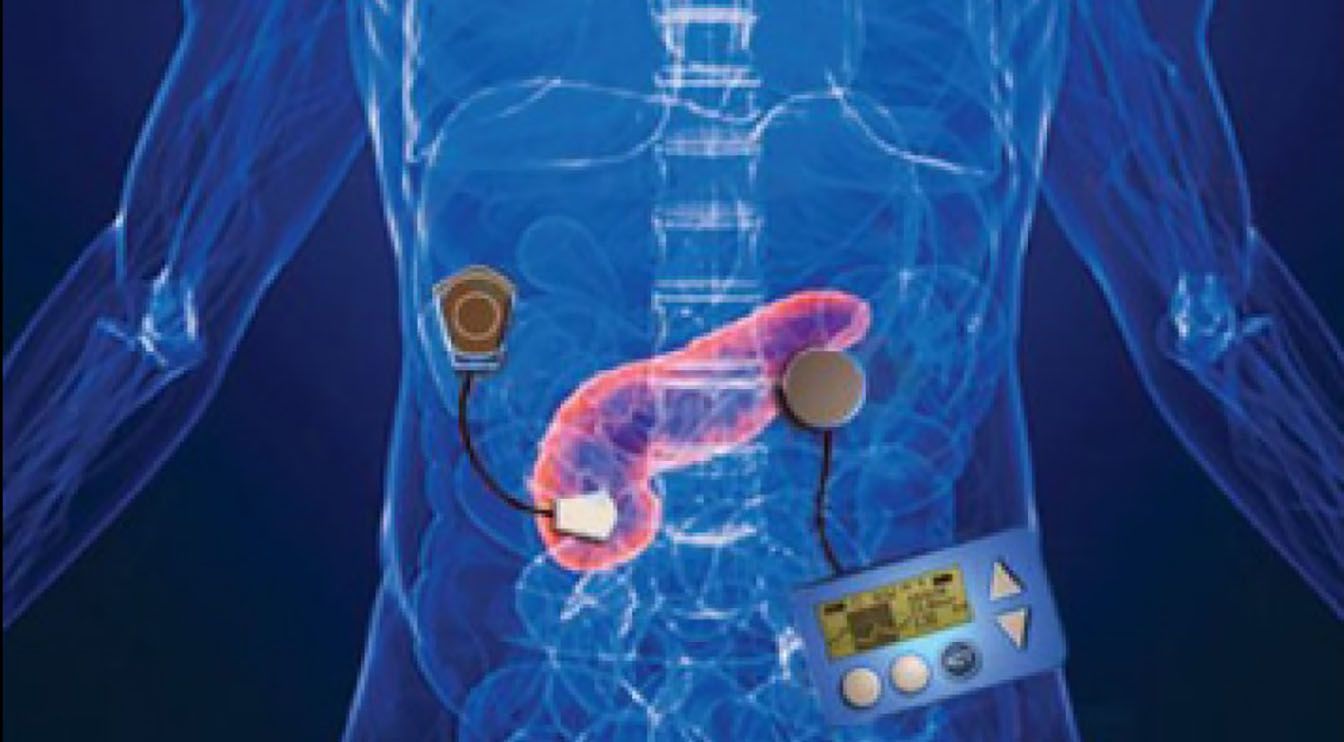
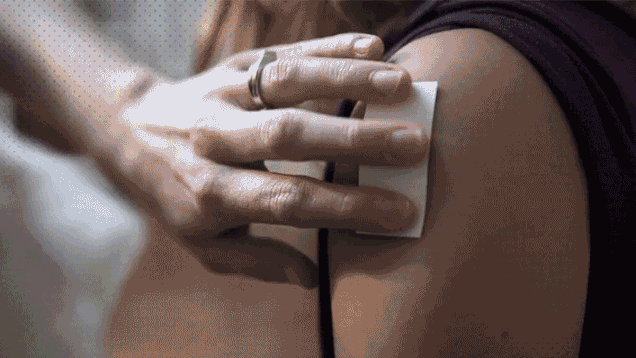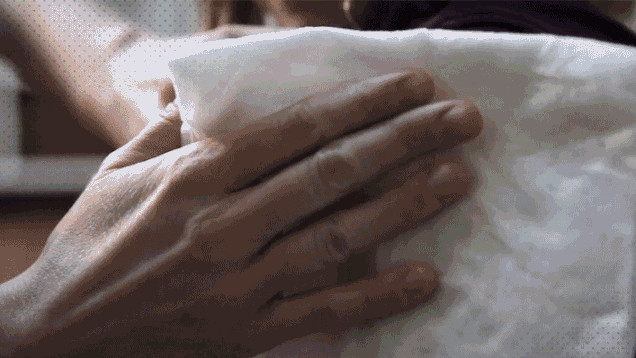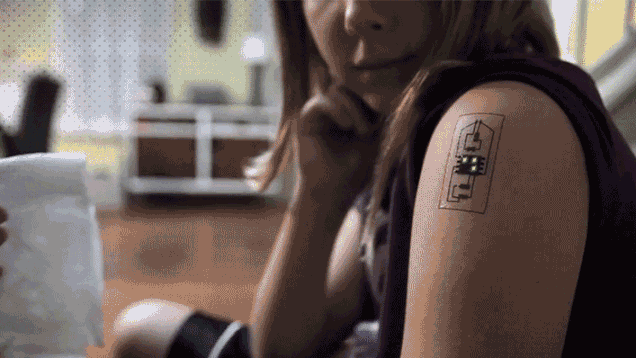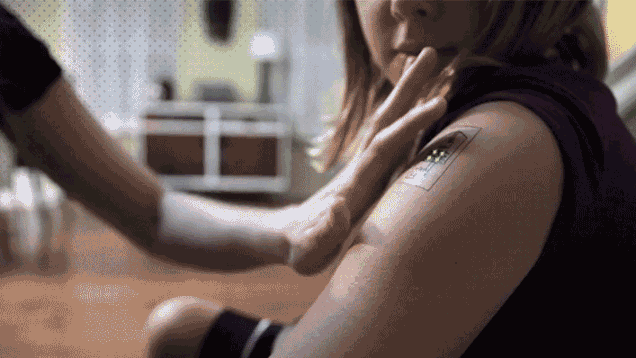
If you haven’t heard of the bionic pancreas, it’s likely you soon will. With diabetes on the rise and the demand for insulin therapies becoming a real pain point for the medical establishment, the need for innovative solutions has spiked. Back in April, we reported on the Do-It-Yourself Pancreas system, a closed-loop artificial pancreas scavenged from a Medtronic pump, Dexcom CGM, a Raspberry Pi, and CareLink USB. Now a fully bionic pancreas similar in design to the Do-It-Yourself model is being developed by doctors at Massachusetts General Hospital and Boston University, with the goal of winning FDA approval. If it succeeds, this will likely be the first bionic organ to see widespread adoption.
Let’s examine some of the previous attempts at bionic organs to see if we can catch a glimpse of where things are heading and some of the societal repercussions that lay in wait. The holy grail of bionic organs is without question the human heart. Coronary artery disease being one of the principal causes of the death worldwide, a fully functioning bionic heart could radically change life expectancy and alter the demographic landscape.
The first bionic hearts, designed over 70 years ago, were plagued by problems that often resulted in thromboembolism and hemorrhage, and made this even more of a gamble than donor transplants. Recent technological advances, however — specifically the advent of bio-prosthetic materials that fool the human immune system into believing the bionic heart is an organic part of the body — could indicate a new era of artificial organs is upon us.