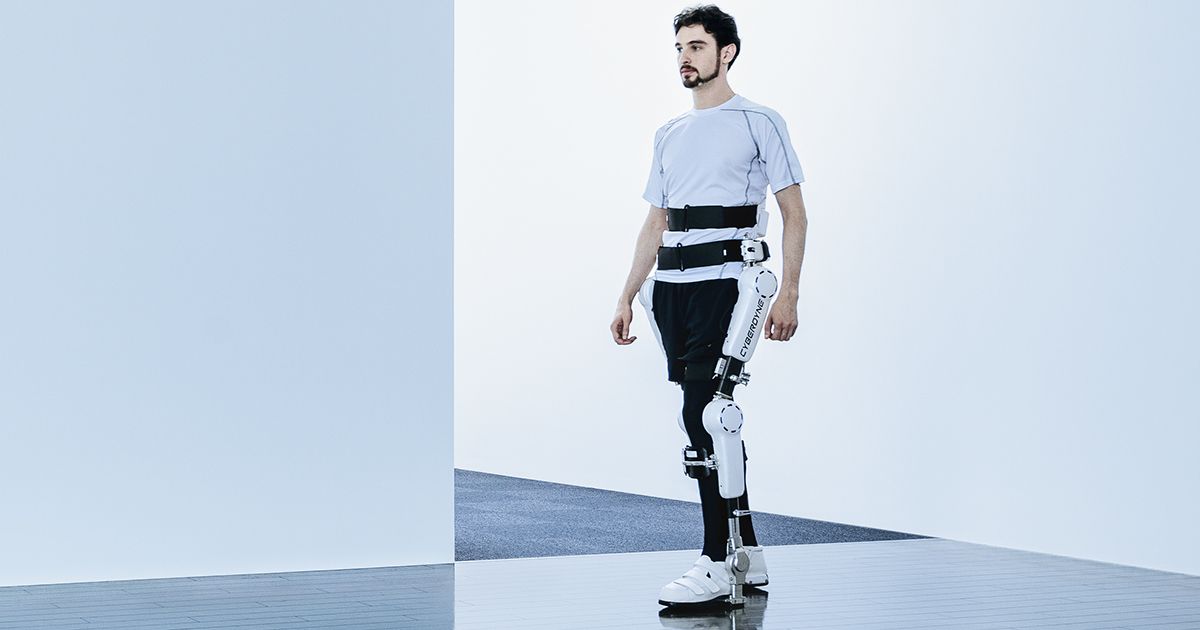
In the basement of the Engineering Center at the University of Colorado Boulder, a group of researchers is working to create the next generation of robots. Instead of the metallic droids you may be imagining, they are developing robots made from soft materials that are more similar to biological systems. Such soft robots contain tremendous potential for future applications as they adapt to dynamic environments and are well-suited to closely interact with humans.
A central challenge in this field known as “soft robotics” is a lack of actuators or “artificial muscles” that can replicate the versatility and performance of the real thing. However, the Keplinger Research Group in the College of Engineering and Applied Science has now developed a new class of soft, electrically activated devices capable of mimicking the expansion and contraction of natural muscles. These devices, which can be constructed from a wide range of low-cost materials, are able to self-sense their movements and self-heal from electrical damage, representing a major advance in soft robotics.
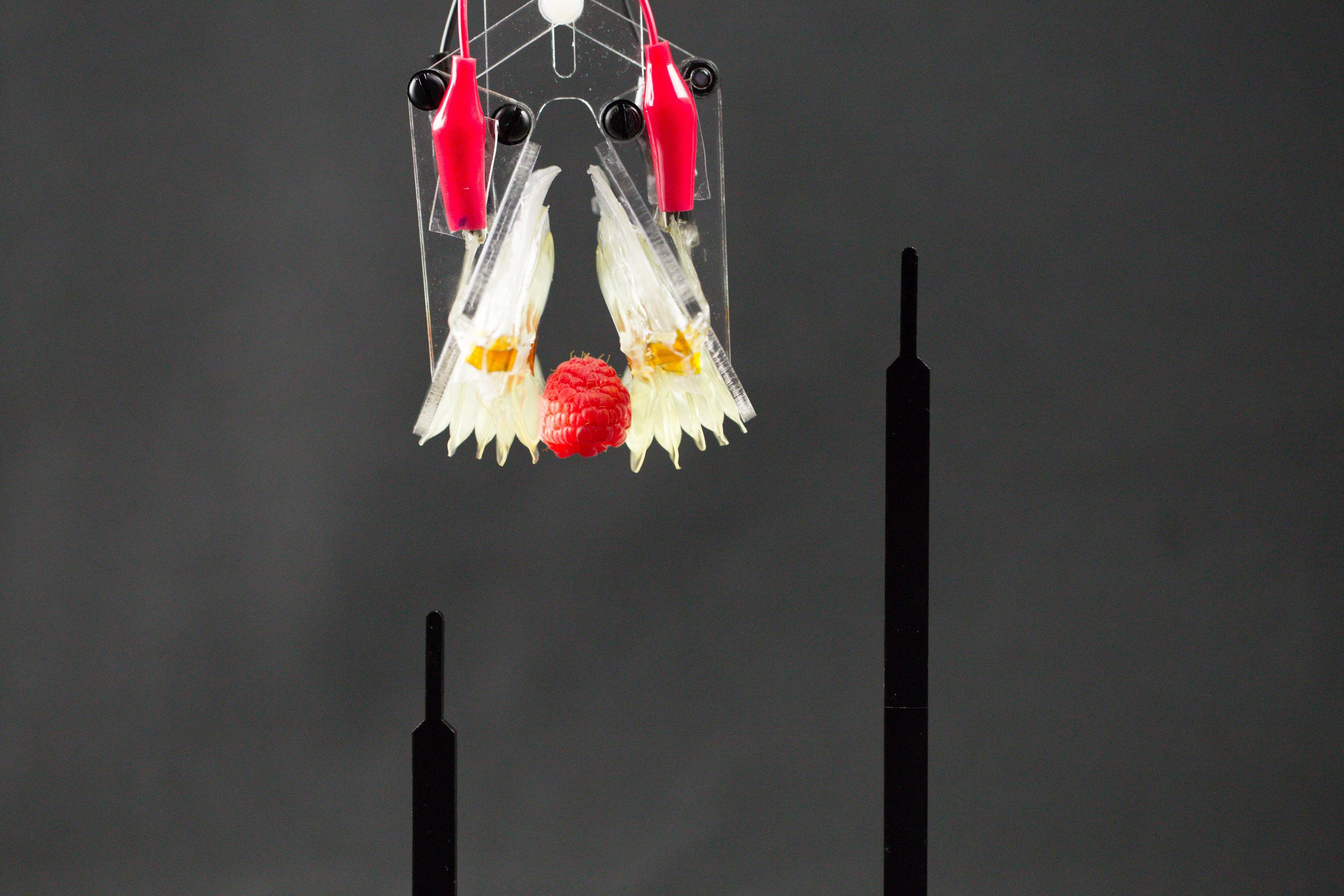
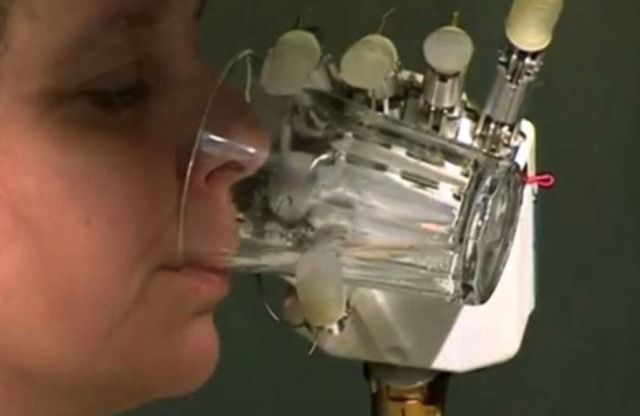
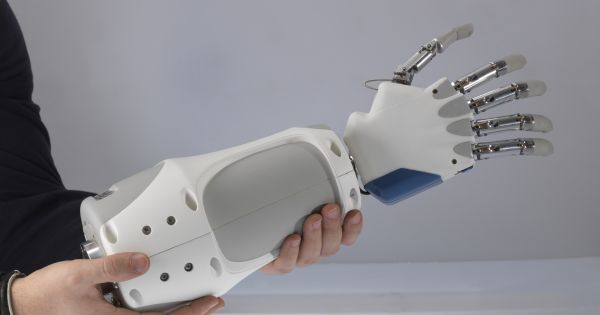
The newly developed hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic (HASEL) actuators eschew the bulky, rigid pistons and motors of conventional robots for soft structures that react to applied voltage with a wide range of motions. The soft devices can perform a variety of tasks, including grasping delicate objects such as a raspberry and a raw egg, as well as lifting heavy objects. HASEL actuators exceed or match the strength, speed and efficiency of biological muscle and their versatility may enable artificial muscles for human-like robots and a next generation of prosthetic limbs.
Read more