A team of scientists at Harvard’s Wyss Institute has just presented its latest creation in the field of robotic exoskeletons, a fully wearable soft exosuit that automatically tweaks its level of assistance on the fly.



Over its 60-year history, DARPA has played a leading role in the creation and advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies that have produced game-changing capabilities for the Department of Defense. Starting in the 1960s, DARPA research shaped the first wave of AI technologies, which focused on handcrafted knowledge, or rule-based systems capable of narrowly defined tasks. While a critical step forward for the field, these systems were fragile and limited. Starting in the 1990s, DARPA helped usher in a second wave of AI machine learning technologies that created statistical pattern recognizers from large amounts of data. The agency’s funding of natural language understanding, problem solving, navigation and perception technologies has led to the creation of self-driving cars, personal assistants, and near-natural prosthetics, in addition to a myriad of critical and valuable military and commercial applications. However, these second wave AI technologies are dependent on large amounts of high quality training data, do not adapt to changing conditions, offer limited performance guarantees, and are unable to provide users with explanations of their results.
To address the limitations of these first and second wave AI technologies, DARPA seeks to explore new theories and applications that could make it possible for machines to adapt to changing situations. DARPA sees this next generation of AI as a third wave of technological advance, one of contextual adaptation. To better define a path forward, DARPA is announcing today a multi-year investment of more than $2 billion in new and existing programs called the “AI Next” campaign. Agency director, Dr. Steven Walker, officially unveiled the large-scale effort during closing remarks today at DARPA’s D60 Symposium taking place Wednesday through Friday at the Gaylord Resort and Convention Center in National Harbor, Maryland.
“With AI Next, we are making multiple research investments aimed at transforming computers from specialized tools to partners in problem-solving,” said Dr. Walker. “Today, machines lack contextual reasoning capabilities, and their training must cover every eventuality, which is not only costly, but ultimately impossible. We want to explore how machines can acquire human-like communication and reasoning capabilities, with the ability to recognize new situations and environments and adapt to them.”

The German start-up company ELiSE creates the DNA of a technical part. Based on the DNA, automated design processes are used to find the best solution which considers all predefined constraints and which is produced by additive manufacturing. Meet ELiSE at ESA’s Start-ups Zone powered by ESA space solutions at IAC 2018.
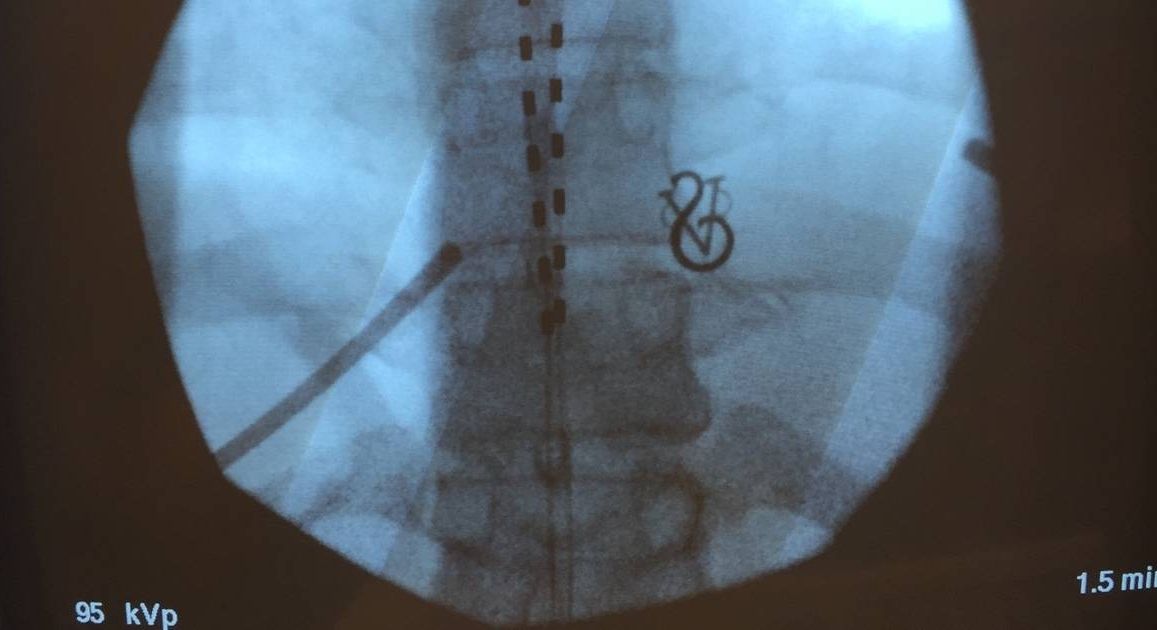
I don’t remember what it feels like to live without pain. At 15, I began feeling aching, stabbing, and burning sensations in my lower back and down my legs. Swallowing a few Aleve didn’t help—in fact, nothing did. If I sit or stand for any period of time, or lift something heavy or fall, I pay for it, sometimes for weeks or months. I’ve slept on the kitchen linoleum, because the carpet felt too soft to stand.
For 17 years, I went to doctor after doctor, undergoing scans, physical therapy, and just about every “alternative” treatment that promised relief. Despite some amazing doctors and the expensive tests at their disposal, they could never see anything wrong, so I never got a diagnosis.
That is, until a couple of years ago, when a routine CAT scan finally caught a structural problem with my spine. Because of that, I qualified to have a spinal cord stimulator, an electronic device used to treat chronic pain, implanted into my back. Although I was scared to go under the knife, I was more than willing to become a cyborg in order to find even partial relief. And this type of therapy might also be able to help some of the 100 million Americans who suffer from chronic pain.
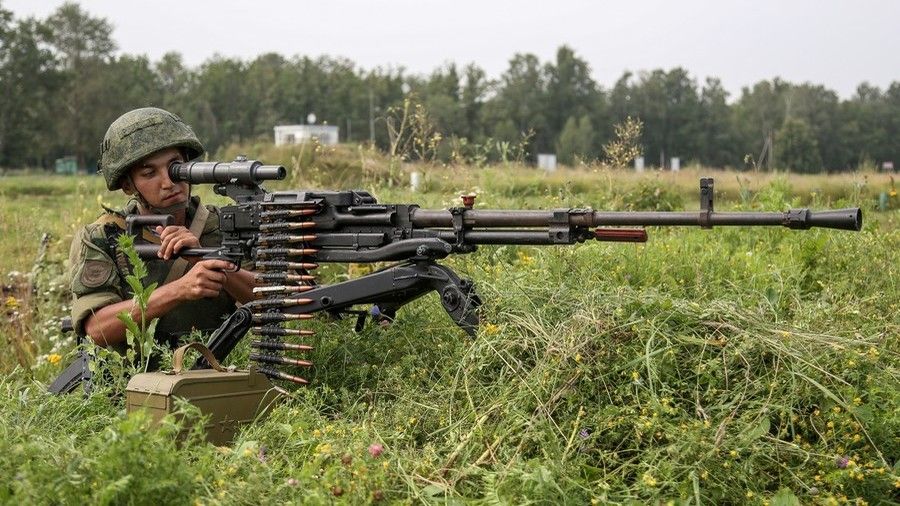

The passive exoskeleton is already part of the Russian Army’s Ratnik (warrior), or ‘future combat system’, which also includes a range of surveillance, communications, and defensive equipment. The active exoskeleton may become part of Ratnik by 2025, according to Military-Scientific Committee Chair of the Ground Forces Aleksandr Romanyuta.
Russia has tested a battery-powered electric motor exoskeleton. The ‘Iron Man’ suit enables the wearer to accurately hit a target with a machine gun one-handed.
Soldiers wearing the high-tech exosuit can run faster and wield heavier equipment and weapons, Oleg Faustov – the chief designer of military industry company TsNIITochMash, which developed the exoskeleton – told TASS.
“We have already tested a prototype of an active exoskeleton, it increases physical capabilities of a serviceman,” Faustov said. A soldier will be able “to shoot a machine gun with only one hand” and accurately hit the target, he added.


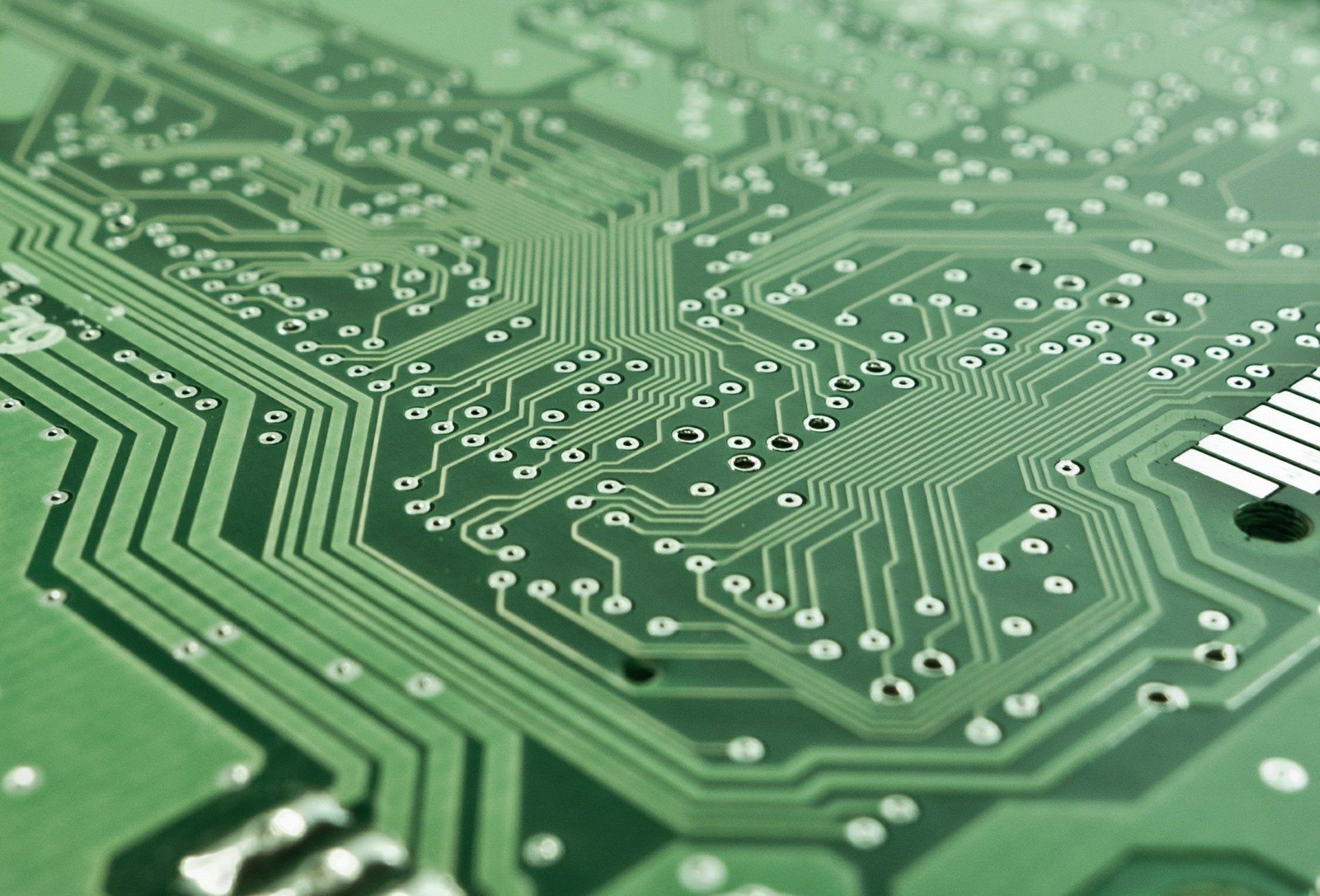
A new form of electronics manufacturing which embeds silicon nanowires into flexible surfaces could lead to radical new forms of bendable electronics, scientists say.
In a new paper published today in the journal Microsystems and Nanoengineering, engineers from the University of Glasgow describe how they have for the first time been able to affordably ‘print’ high-mobility semiconductor nanowires onto flexible surfaces to develop high-performance ultra-thin electronic layers.
Those surfaces, which can be bent, flexed and twisted, could lay the foundations for a wide range of applications including video screens, improved health monitoring devices, implantable devices and synthetic skin for prosthetics.
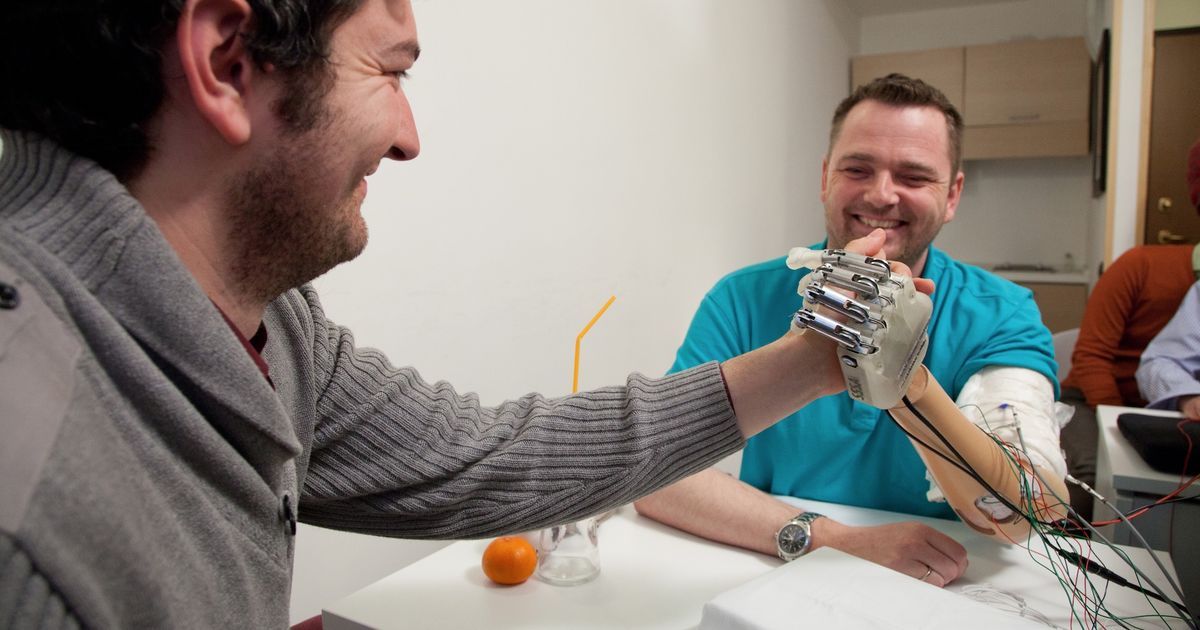

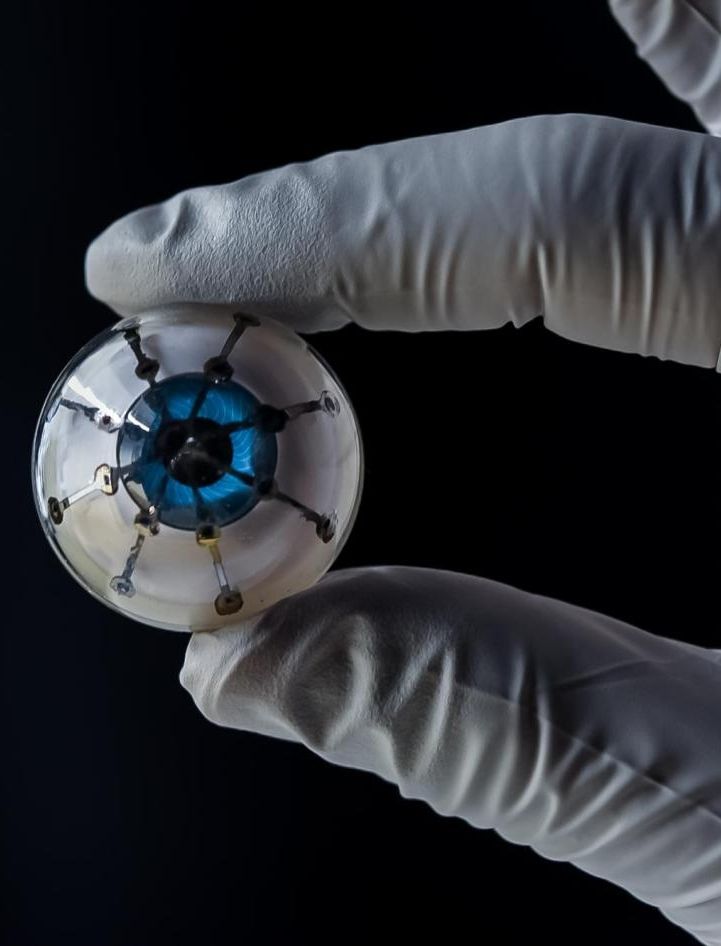
Denis Aabo Sørensen lost his left hand nine years ago, while handling fireworks. Since then, he has used prosthetic hands, but never one like this. Last year, a team of European engineers created for him a prosthetic hand that connects directly to the remaining nerves in his upper arm. That means the hand is able to send sensations of touch back through his arm and into his brain. Plus, when Sørensen wanted to grab something, he could move the hand by simply thinking about it.

Often only a few years separate the tinfoil hats from the millionaires to be. I was writing the piece on the Youbionic arm and thinking of how we will use 3D printing to augment human beings. Clearly augmenting the human body with mechatronics would be a good idea. The flesh is weak but stepper motors are strong! Oh how we will eeck, ooow, brrrr whine in our old stepper augmented age. Machines could very well fill the gaps once our bodies start failing us. But, will old people homes really be filled with Borg grandmas?

Will your grandad get that night vision upgrade he’s always wanted so he can deer hunt whenever he damn pleases? Would it be a good idea if I on a whim replaced my tennis elbow with a tennis racket? We never get the future right and most of our visions of mechatronic augmentations of humans are either a bit Johhny Cab or they’re ruined by that tiara Geordi was wearing across his face in Star Trek. I know he can’t see it, but someone should have told him really.