It might be days before production resumes after an “organized cybersecurity attack” affected some servers supporting JBS USA’s North American and Australian IT systems, officials said.
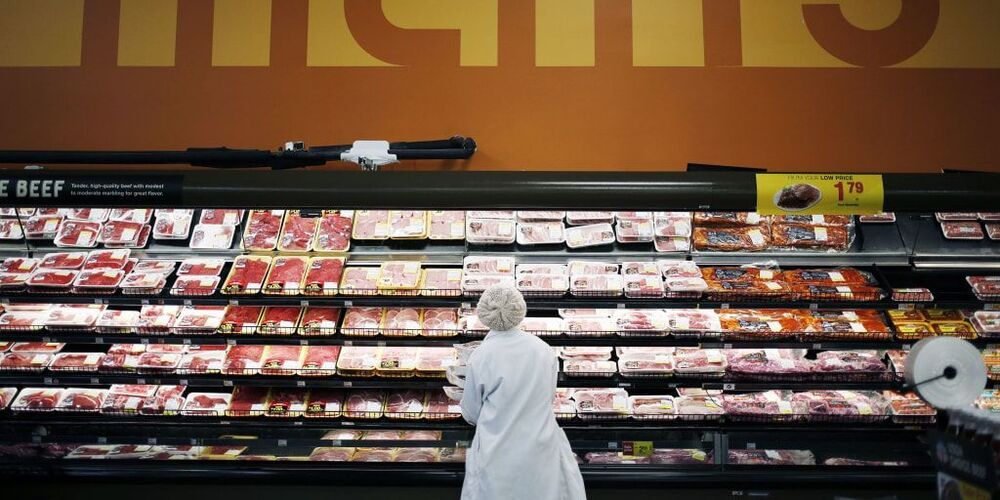
CANBERRA, Australia — Thousands of meat workers had no work for a second day on Tuesday after a cyberattack crippled the world’s largest meat processing company. A government minister said it might be days before production resumes.
JBS is also Australia’s largest meat and food processing company, with 47 facilities across the country including abattoirs, feedlots and meat processing sites. JBS employs around 11000 people.
JBS USA said in a statement from Greeley, Colorado, on Monday that it was the target on Sunday of an “organized cybersecurity attack” affecting some of its servers supporting its North American and Australian IT systems.