Climate change: fossil fuel burning will become a thing of the past for new homes.


My colleague Conor Sen recently made a bold prediction: Government will be the driver of the U.S. economy in coming decades. The era of Silicon Valley will end, supplanted by the imperatives of fighting climate change and competing with China.
This would be a momentous change. The biggest tech companies — Amazon.com, Apple Inc., Facebook Inc., Google (Alphabet Inc.) and (a bit surprisingly) Microsoft Corp. — have increasingly dominated both the headlines and the U.S. stock market:

One of the key misconceptions about solar geoengineering—putting aerosols into the atmosphere to reflect sunlight and reduce global warming—is that it could be used as a fix-all to reverse global warming trends and bring temperature back to pre-industrial levels.
It can’t. Applying huge doses of solar geoengineering to offset all warming from rising atmospheric C02 levels could worsen the climate problem—particularly rainfall patterns—in certain regions. But could smaller doses work in tandem with emission cuts to lower the risks of a changing climate?
New research from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), in collaboration with MIT and Princeton University, finds that if solar geoengineering is used to cut global temperature increases in half, there could be worldwide benefits without exacerbating change in any large geographic area.
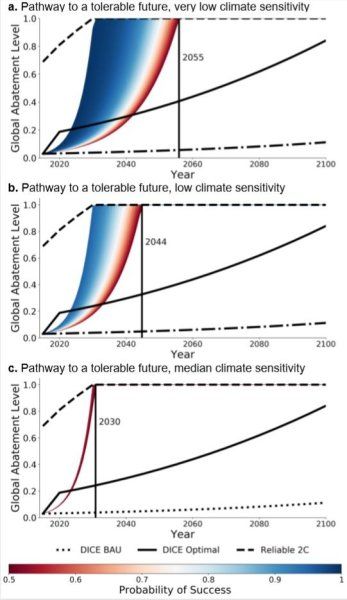
A new comprehensive study of climate change has painted over 5 million pictures of humanity’s potential future, and few foretell an Earth that has not severely warmed. But with immediate action and some luck, there are pathways to a tolerable climate future, according to a research team led by Tufts University.

Abstract
The aim of the passive igloo project is to explore the possibilities of creating an ecological and self-sufficient habitat by using sound constructive measures and renewable energy resources to guarantee thermal comfort in the most severe cold climates.
The passive igloo is a self-sufficient housing module built into a polar exploration sailboat to accommodate a crew of 2 to 6 people in conditions of severe cold to live and work. In order to test the passive igloo, the boat was voluntarily trapped in the ice in North West Greenland during the winter of 2015–2016 and monitored during the 10 months of ‘stationary navigation’.
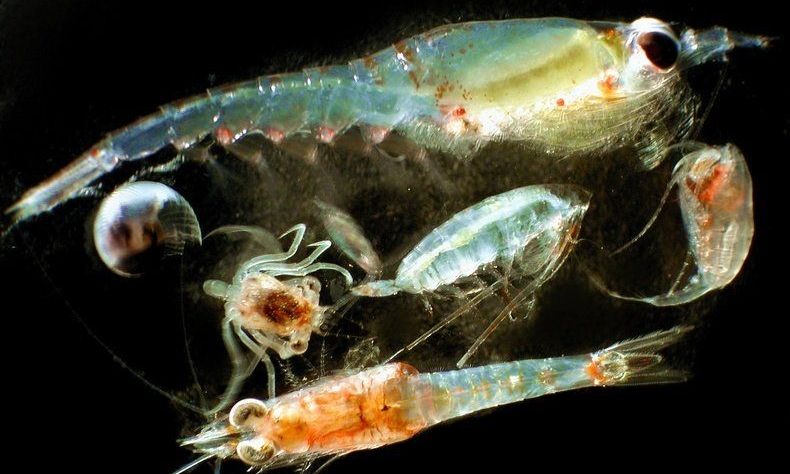



Widespread and sometimes drastic marine oxygen declines are stressing sensitive species—a trend that will continue with climate change.
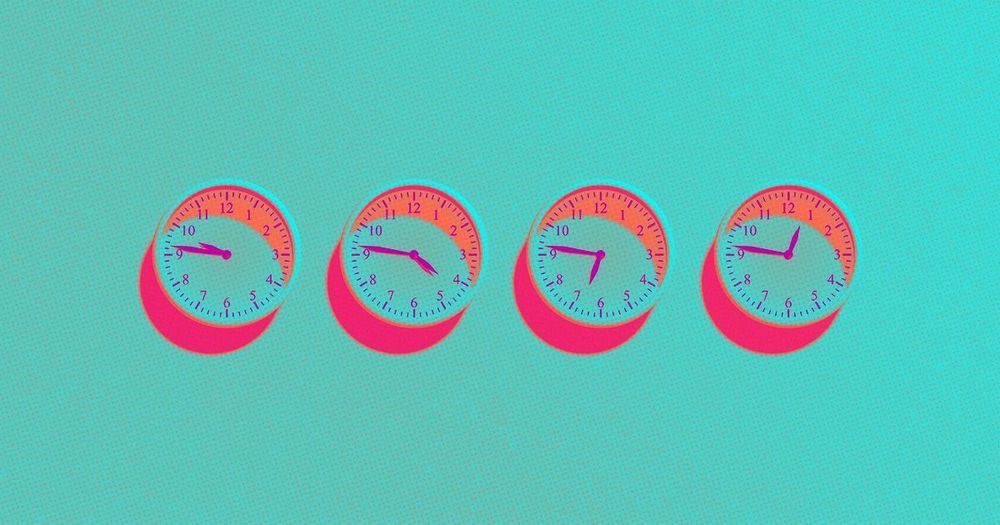
According to the Bulletin, we’ve done nothing in the past year to make the situation any less precarious — humanity still faces not one, but two “existential threats” in the form of nuclear weapons and climate change.
While the clock remains set at 11:58, the potential of either threat to destroy humanity has increased over the past 12 months, according to the Bulletin’s 2019 statement. We must do something to alter our path.
“Though unchanged from 2018, this setting should be taken not as a sign of stability but as a stark warning to leaders and citizens around the world,” the scientists wrote. “The current international security situation — what we call the ‘new abnormal’ — has extended over two years now… Th e longer world leaders and citizens carelessly inhabit this new and abnormal reality, the more likely the world is to experience catastrophe of historic proportions.”

China has opened its first Mars simulation base to the public to encourage young people to get involved in space exploration.
The Mars simulation base, which opened on Friday, is located in Mangya city, in Northwest China’s Qinghai Province.
The red rock area in the Qaidam Basin in Qinghai has been called the most “Martian” place on Earth, with its natural features, landscape and climate all similar to those on the red planet, said Gao Junling, the project founder.