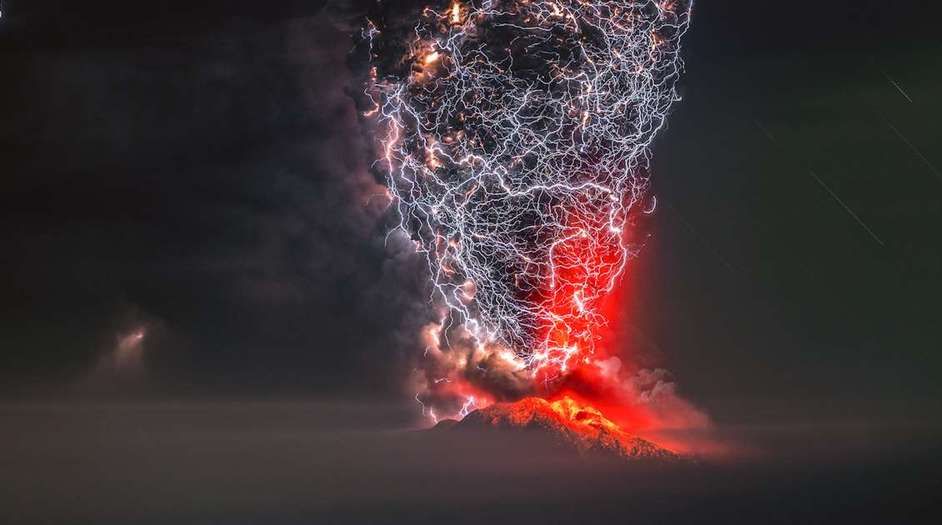
Sensors are usually thought of in terms of physical devices that receive and respond to electromagnetic signals – from everyday sensors in our smartphones and connected home appliances to more advanced sensors in buildings, cars, airplanes and spacecraft. No physical sensor or aggregation of electronic sensors, however, can continuously and globally detect disturbances that take place on or above the earth’s surface. But the physical atmosphere itself may offer such a sensing capability, if it can be understood and tapped into.
To that end, DARPA recently announced its Atmosphere as a Sensor (AtmoSense) program, whose goal is to understand the fundamentals of energy propagation from the ground to the ionosphere to determine if the atmosphere can be used as a sensor. A Proposers Day is scheduled for February 14, 2020, in Arlington, Virginia.
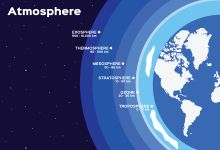
It’s well known that energy propagates from the Earth’s surface to the ionosphere, but the specifics of how that happens is not currently known enough to use the atmosphere as a sensor. Scientific literature has clearly documented that events like thunderstorms, tornadoes, volcanos, and tsunamis make big “three-dimensional wakes” that propagate to the upper reaches of the ionosphere and leave a mark there. Since that energy traverses several other layers of atmosphere – the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere – on its way up to the ionosphere, the idea is to try and identify the disturbances the “wake” is making along its way to see if researchers can capture information to indicate what type of event caused it.