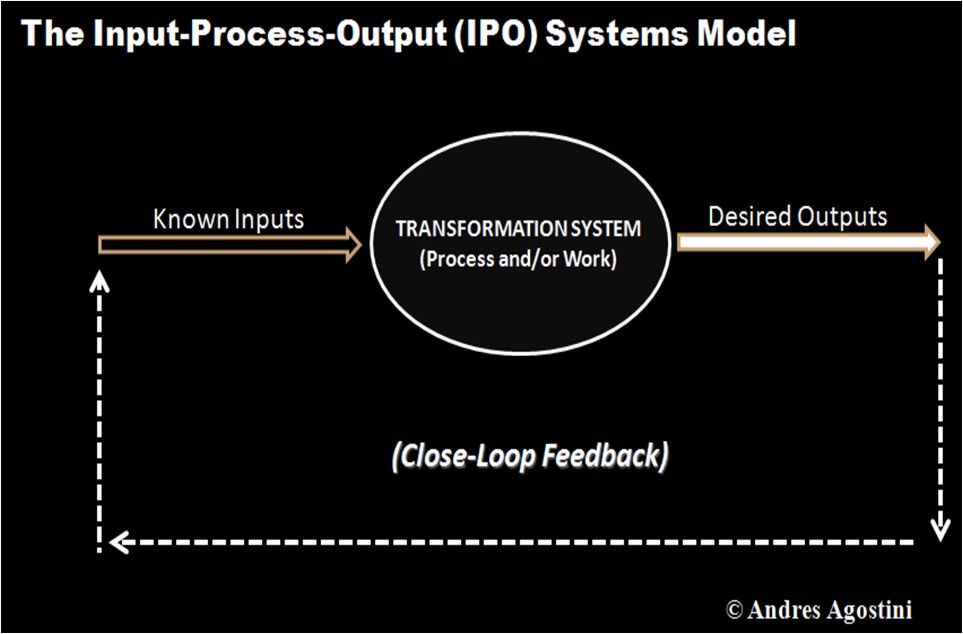
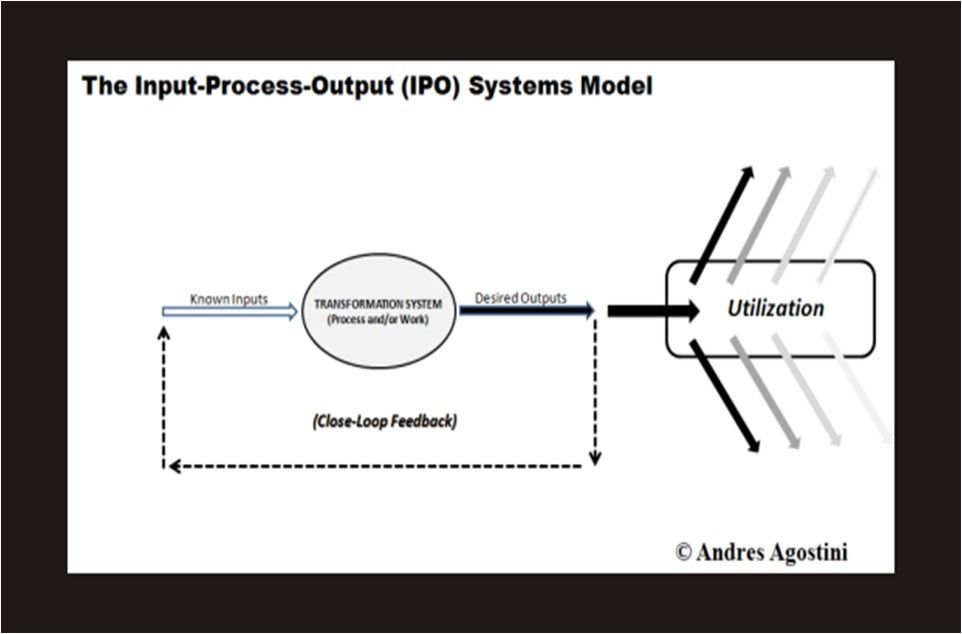
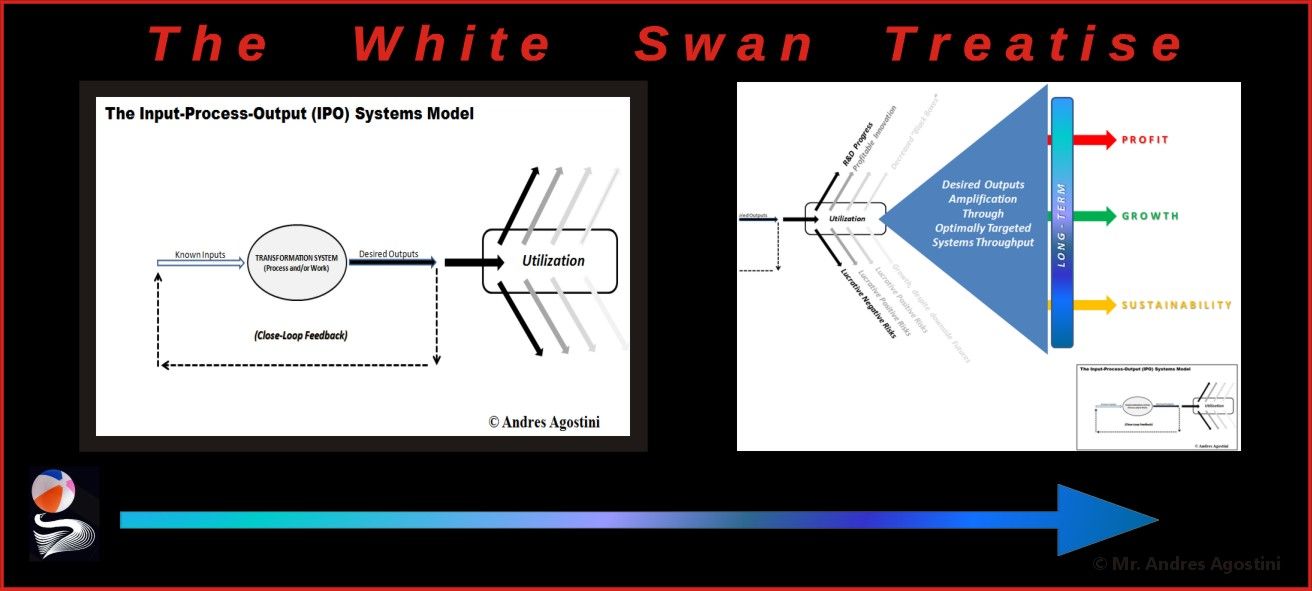
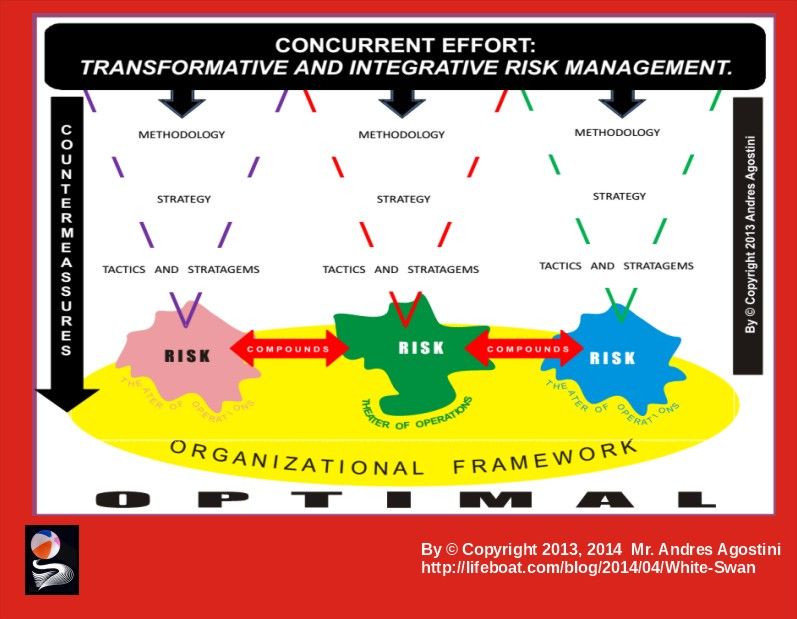
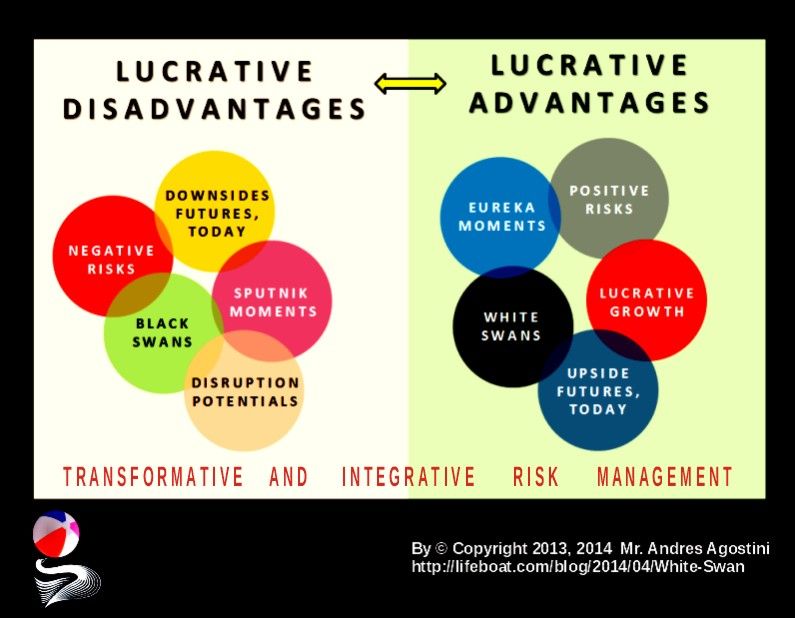
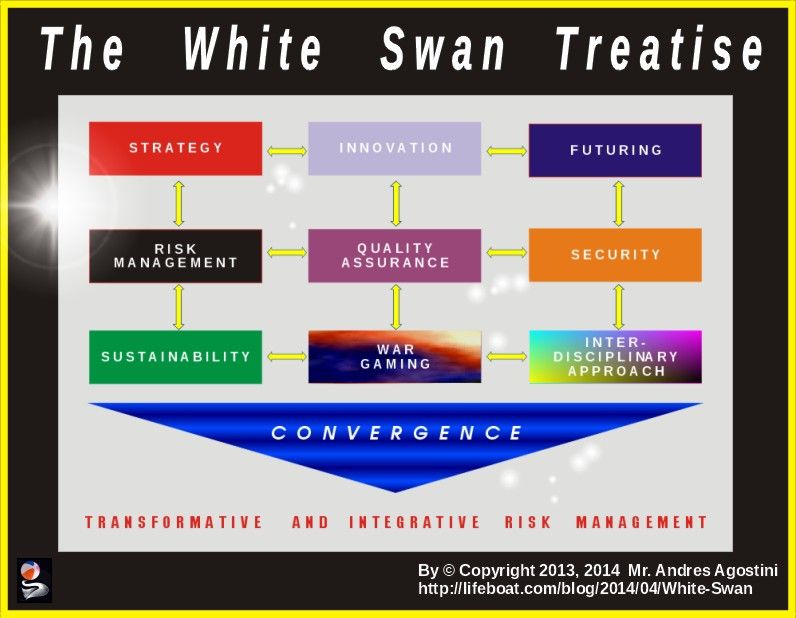
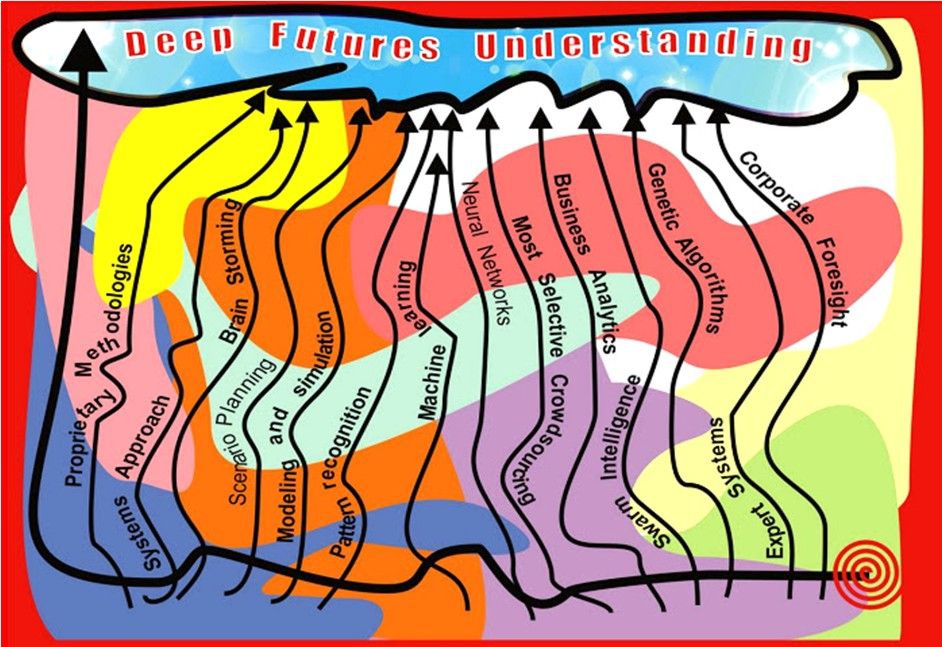
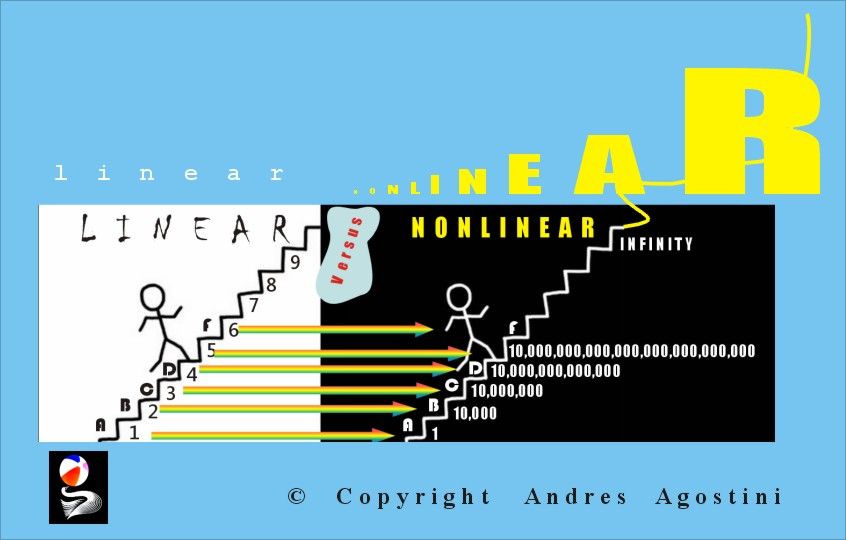
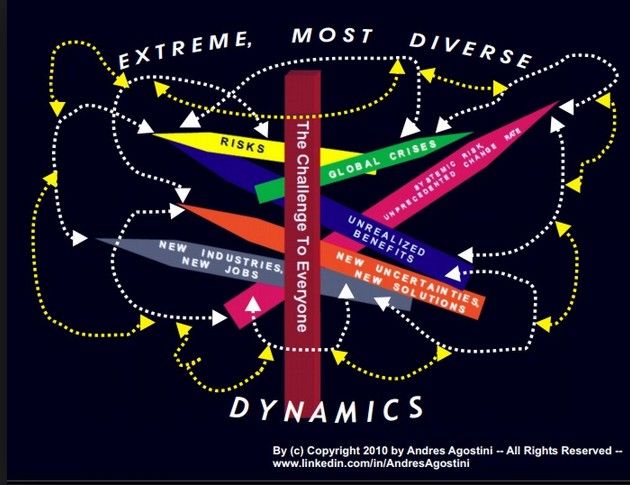
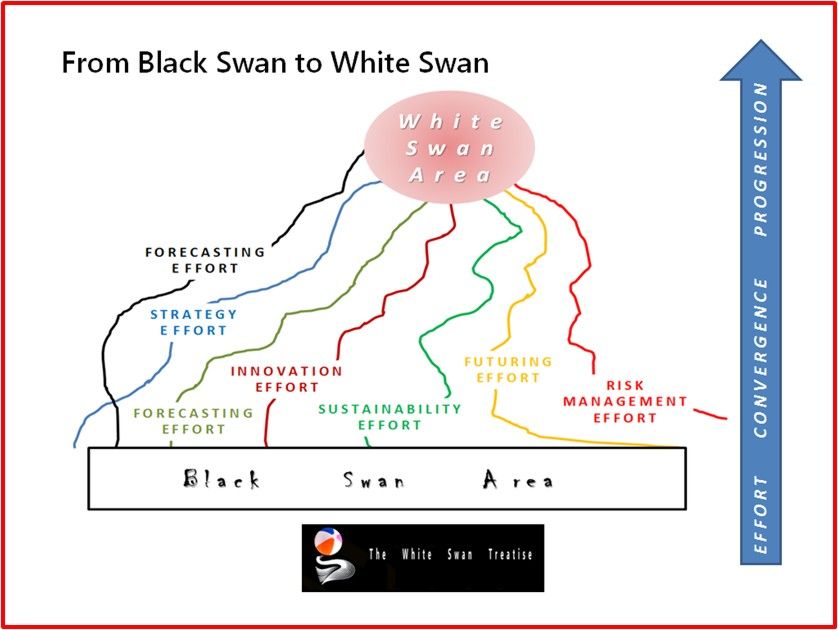
The Lifeboat Foundation Worldwide Ambassador Mr. Andres Agostini’s own White Swan Dictionary, Countermeassuring Every Unthinkable Black Swan, at https://lifeboat.com/blog/2014/04/white-swan
WHITE SWAN — UNABRIDGED DICTIONARY
Altogetherness.— Altogetherness is the quality of conforming to the ability to investigate with all or everything included.
A Posteriori.— “ … A Posteriori indicates the demonstration that entails the ascendance of the effect to the cause, or the properties of the essence of something [….] After examining the matter that is dealt with [….] Derived by or designating the process of reasoning from facts or particulars to general principles or from effects to causes; inductive; empirical [….] Knowable from experience [….] relating to or involving inductive reasoning from particular facts or effects to a general principle [….] derived from or requiring evidence for its validation or support; empirical; open to revision [….] from particular instances to a general principle or law; based on observation or experiment [….] not existing in the mind prior to or apart from experience [….] the process of reasoning from effect to cause, based upon observation …”
A Priori.— “ … A Priori comprises that proceeds from a known or assumed cause to a necessarily related effect; deductive [….] Derived by or designating the process of reasoning without reference to particular facts or experience [….] Knowable without appeal to particular experience [….] Made before or without examination; not supported by factual study [….] relating to or involving deductive reasoning from a general principle to the expected facts or effects [….] to be true independently of or in advance of experience of the subject matter; requiring no evidence for its validation or support [….] existing in the mind independent of experience [….] conceived beforehand …”
Blitzkrieg.— “ … Blitzkrieg is a German MEME for war-waging White Swan Corporate Strategy conducted against competitors and with great speed and force; specifically: a violent techno-surprise offensive by massed brick-and-mortar forces and through digitized ground and World-Wide Web forces in close beyond-perfection coordination …”
Change .— “… Change is to transfer from (one conveyance) to another and/or to undergo transformation or transition and/or to go from one phase to another and/or the act, process, or result of altering or modifying and/or the replacing of one thing for another; substitution and/or a transformation or transition from one state, condition, or phase to another and/or to make or become different and/or a variation, deviation, or modification and/or anything that is or may be substituted for something else and/or to transform and/or to transfer from one (conveyance) to another and/or to pass gradually into and/or to pass from one phase to another and/or the act of changing or the result of being changed and/or a transformation or modification and/or the substitution of one thing for another and/or the process of becoming different and/or impermanence and/or biological metamorphosis …”
Closenessfulness.— (Closenessfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to see immediate and near-term foreseeable futures and likely prospects).
Complexity Science .— “ … Complexity Science is the systematic study of the nature and behavior of the material and physical universe, based on observation, experiment, and measurement, and the formulation of laws to describe these facts in general terms with the utter purpose of instituting the perusal of the phenomena which emerge from a collection of interacting objects [….] Complexity expresses a condition of numerous elements in a system and numerous forms of relationships among the elements [….] The use of the term complex is often confused with the term complicated. In today’s systems, this is the difference between myriad connecting ‘stovepipes’ and effective ‘integrated’ solutions. This means that complex is the opposite of independent, while complicated is the opposite of simple [….] While this has led some fields to come up with specific definitions of complexity, there is a more recent movement to regroup observations from different fields to study complexity in itself, whether it appears in anthills, human brains, or stock markets. One such interdisciplinary group of fields is relational order theories …”
Counter-closenessfulness.— (Counter-closenessfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to see alternate immediate and near-term foreseeable futures and likely prospects).
Counter-DoctorStangelovesness.— (Counter-DoctorStangelovesness is the quality of conforming to the ability to investigate, through alternate military strategy and practical systems theory as they are instituted in corporate theater of operations, as claims of management phenomena with potential corporate for-lucre application, such as ‘remote viewing’ through scenario-planning methodology ‘unthinkables’, the purported ability to physically ‘see’ unknown events, sites, or information from a great temporal distance, including those of the environment, industries and specially those of direct and indirect competitors to said corporations. Taken by Applied Thinkers and Savvy Corporation by and beyond the prescription of the RAND Corporation and the Hudson Institute).
Counter-farsightfulness.— (Counter-farsightfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to see alternate foreseeable futures and likely prospects).
Counter-foresightfulness.— (Counter-foresightfulness is the quality of conforming to the alternate perception of the significance and nature of events before they have occurred).
Counter-hindsightfulness.— (Counter-hindsightfulness is the quality of conforming to an alternate perception of the significance and nature of events after they have occurred).
Counter-insightfulness.— (Counter-insightfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to engage the alternate acute observation and deduction, penetration, discernment, perception and understanding of a specific cause and effect in a specific context).
Counter-intuitvenessfulness.— (Counter-intuitvenessfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to perceiving alternate intuitive knowledge).
Counter-Stargatenessfulness.— (Counter-Stargatenessfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to investigate alternate claims of psychic phenomena with potential corporate for-lucre application, such as ‘remote viewing’, the purported ability to psychically ‘see’ events, sites, or information from a great distance, including those of the environment, industries and specially those of direct and indirect competitors. Taken by Applied Thinkers and Visionary Corporation by the U.S. Federal Government’ and the U.S. Defense Intelligence Agency’s Stargate Project).
DoctorStangelovesness.— (DoctorStangelovesness is the quality of conforming to the ability to investigate, through military strategy and practical systems theory as they are instituted in corporate theater of operations, as claims of management phenomena with potential corporate for-lucre application, such as ‘remote viewing’ through scenario-planning methodology ‘unthinkables’, the purported ability to physically ‘see’ unknown events, sites, or information from a great temporal distance, including those of the environment, industries and specially those of direct and indirect competitors to said corporations. Taken by Applied Thinkers and Savvy Corporation by and beyond the prescription of the RAND Corporation and the Hudson Institute).
Dynamic Driving Forces .— “…Dynamic Driving Forces are forces outside the firm (external factors) that trigger the change of strategy in an organization. Industry conditions change because important forces (the most dominant ones that have the biggest influence on what kinds of changes will take place in the industry’s structure and competitive environment) are driving industry participants (competitors, customers, or suppliers) to alter their actions, and thus the driving forces in an industry are the major underlying causes of changing industry and competitive conditions. Driving forces analysis has two steps: identifying what the driving forces are and assessing the impact they will have on the industry .… The Most Common Dynamic Driving Forces include: 1. The Internet and new e-commerce opportunities and threats it breeds in the industry; 2. Increasing globalization of the industry; 3. Changes in the long-run industry growth rate; 4. Changes in who buys the products and how they use it. 5. Product innovation; 6. Technological change; 7. Market innovation; 8. Entry or exit of major firms; 9. Diffusion of technical know-how across more companies and more countries; 10. Changes in cost and efficiency. 11. Growing buyer for preferences for differentiated products instead of a commodity product (or for a more standardized product instead of strongly differentiated products); 12. Regulatory influences and government policy changes; 13. Changing societal concerns, attitudes, and lifestyles; 14. Reductions in uncertainty and business risk … Other dynamic driving forces include geologic, climatological, political, geopolitical, demographic, social, ethical, economic, technological, financial, legal and environmental forces, among others …”
Dynamics.— “…Dynamics is a branch of mechanics that deals with forces and their relation primarily to the motion but sometimes also to the equilibrium of bodies …. an underlying cause of change or growth …. a pattern or process of change, growth, or activity *population dynamics* …”
Far-fetched.— “ … Far-fetched is improbable in nature; unlikely. But given the emergent as-of-now nature of the Omniverse, far-fetched is omniverseral nature’s most probable and so probable to tectonically reform our cosmovisions, in front and beyond our smartest observations, and other constellations believed indisputable by our folly human assumptions …”
Farsightfulness.— (Farsightfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to see the foreseeable futures and likely prospects).
Flawness.— (Flawness is the quality of conforming to maximum error and failure).
Foresightfulness.— (Foresightfulness is the quality of conforming to perception of the significance and nature of events before they have occurred).
Fortuitousness.— (Unexpected and casually happening[s], as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Futilitifulness Thinking.— (Futilitifulness is the quality of conforming to maximum futility).
Future (the ‚) .— “ … The Future is 1) What is yet to come, 2) What can happen or not, 3) The future is a tranquil country, 4) The indefinite time yet to come, 5) Something that will happen in time to come, 6) A prospective or expected condition, 7) Undetermined events that will occur in that time, 8) time that is to be or come hereafter, 9) Something that will exist or happen in time to come, 9) The period of time following the present moment and continuing on indefinitely, 10) The situation or condition of someone or something in the future, 11) One of a plurality of possible future conditions or situations, 12) The time or a period of time following the moment of speaking or writing; time regarded as still to come, 13) The future is what will happen in the time period after the present. Its arrival is considered inevitable due to the existence of time and the laws of physics. Due to the apparent nature of reality and the inevitability of the future, everything that currently exists and will exist can be categorized as either permanent, meaning that it will exist for the whole of the future, or temporary, meaning that it won’t and thus will come to an end. The future and the concept of eternity have been major subjects of philosophy, religion, and science, and defining them non-controversially has consistently eluded the greatest of minds. In the Occidental view, which uses a linear conception of time, the future is the portion of the projected time line that is anticipated to occur. In special relativity, the future is considered absolute future, or the future light cone. 14) The only way you can see the future is if you’re ahead of your own time, 15) Learning how to be ahead of your time, today!, 16) The future is that the future is something that happens to us, not something we create, 17) Our future is determined by the actions of all of us alive today. our choices determine our destiny, 18) The future is a phenomenon that will be completely real someday even though it does not exist today, 19) Future is too important to be lost under the burden of juvenile folly and ignorant superstition, 20) Our intuition about the future is linear, which is hard-wired in our brains, 21) The future is being colonized all the time by people who have the resources, who do spend time thinking about it, planning for it and trying to shape it in their direction, 22) The future is already here; it’s just not evenly distributed, 23) the future is called ‘perhaps,’ which is the only possible thing to call the future. and the important thing is not to allow that to scare you, 24) The future is unsure. that’s the way it should be, 25) The past cannot be changed. The future is yet in your power, 26) The future is the past of to-morrow, 27) The best way to predict the future is to invent it, 28) To be masters of the future is to change the past, 29) The future is extremely important to high morale, to dynamism, to consensus, and in general to help the wheels of society turn smoothly, 30) The past is gone, the future is not to come, and the present becomes the past even while we attempt to define it, 31) The future is not for the fainthearted, 32) The future is not an echo of the past, 33) The future is not a privilege but a perpetual conquest, 34) The future is not what will happen; the future is what is happening, 35) The future is more challenging than playing catch up, 36) The future is not an extrapolation of the past, 37) The future is not something we enter. The future is something we create, 38) The future is an unknown country which requires tough visas for anyone to enter. not all of us will get the chance to visit it, 39) The future is not what is coming at us, but what we are headed for, 40) The future is where I expect to spend the rest of my life, 41) The danger of the future is that men may become robots, 42) The future is the creation of millions of independent economic actors, 43) The future is independent of the past, 44) The future is alive. Like the present, the future is not a single, uniform state but an ongoing process that reflects the plenitude of human life, 45) The future is natural, out of anyone’s control, 46) The future is continually stalking on the present, 47) The future is technocracy in perpetuity, 48) The future is eternally clashing the present, 49) The future is absolute hard science dominance, 50) The future is going to get invented, with you or without you, 51) The future is S-H-A-Z-A-M (“…The wisdom of Solomon, the stamina of Atlas, the power of Zeus, the courage of Achilles, and the speed of Mercury.…” and 52) The future is not something that happens to us, but something we create.
Fuzzy Logic.— (A form of algebra employing a range of values from “true” to “false” that is used in decision-making with imprecise data, as in artificial intelligence systems, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Haphazardness.— (the quality of lacking any predictable order or plan, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Hindsightfulness.— (Hindsightfulness is the quality of conforming to perception of the significance and nature of events after they have occurred).
Inflection point .— “…Inflection point is a moment of dramatic change, especially in the development of a company, industry, or market … And/or a time of significant change in a situation; a turning point … A moment of dramatic change, especially in the development of a company, industry, or market … A point on a chart that marks the beginning of a significant move, either up or down … An event that results in a significant change in the progress of a company, industry, sector, economy or geopolitical situation. An inflection point can be considered a turning point after which a dramatic change, with either positive or negative results, is expected to result. Companies, industries, sectors and economies are dynamic and constantly evolving. Inflection points are more significant than the small day-to-day progress that is made and the effects of the change are often well-known and widespread … Andy Grove, Intel’s co-founder, described a strategic inflection point as ‘…an event that changes the way we think and act …’ … What Intel’s Grove calls ‘…strategic inflection point …, Andres terms « … Sputnik Moment inflection point … » … Inflection points can be a result of action taken by a company, or through actions taken by another entity, that has a direct impact on the company. Regulatory changes, for instance, could lead to an inflection point for a corporation that was previously held back by regulatory compliance issues. Inflection points in technology include the advent of the Internet and smart phones. Politically, an inflection point can be illustrated by the fall of the Berlin Wall or the fall of Communism in Poland and other Eastern Bloc countries …”
Insightfulness.— (Insightfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to engage the acute observation and deduction, penetration, discernment, perception and understanding of a specific cause and effect in a specific context).
Intuitvenessfulness.— (Intuitvenessfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to perceiving intuitive knowledge).
Litmus Test.— “… Litmus Test is a critical indication of future success or failure …”
Minimax.— “… Minimax is a decision rule used in decision theory, game theory, statistics and philosophy for minimizing the possible loss for a worst case (maximum loss) scenario. Alternatively, it can be thought of as maximizing the minimum gain (maximin or MaxMin). Originally formulated for two-player zero-sum game theory, covering both the cases where players take alternate moves and those where they make simultaneous moves, it has also been extended to more complex games and to general decision making in the presence of uncertainty …. In the theory of simultaneous games, a minimax strategy is a mixed strategy which is part of the solution to a zero-sum game. In zero-sum games, the minimax solution is the same as the Nash equilibrium …”
Mishaps.— (an unknown and unpredictable phenomenon that causes an event to result one way rather than another, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Mistakenness .— (Mistakenness is the quality of conforming to maximum mistake and an unintentional act, omission).
Narrow-mindedness.— (Narrow-mindedness is the quality of conforming to unresponsive to new ideas).
Normalness.— (Normalness is the quality of conforming to maximum normal quality or normal condition).
Omniscience .— “… Applied non-theological omniscience consists of having total knowledge; knowing everything, having infinite knowledge, the current state of knowledge, the ability to know anything that one chooses to know and can be known and actually knowing everything that can be known. Synonyms to omniscience include panshopy, polyhistory and all-knowingness.…”
Open-mindedness.— (Open-mindedness is the quality of conforming to receptiveness to new ideas).
Prospective.— “ … Prospective comprises something that is likely or expected to happen [….] that looks forward to the future [….] that it is anticipated or likely to happen [….] of or in the future [….] potential, likely, or expected [….] yet to be or coming [….] of or concerned with or related to the future Set of analyzes and studies developed with the utter end of exploring or foretelling the future, regarding a determined subject matter …”.
Pseudo-fortuitousness.— (quasi-unexpected and quasi-casually happening[s], as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Pseudo-Fuzzy Logic.— (A form of algebra employing a range of values from quasi-“true” to quasi-“false” that is used in decision-making with quasi-imprecise data, as in artificial intelligence systems, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Pseudo-Haphazardness.— (the quality of quasi-lacking any predictable order or plan, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Pseudo-Mishaps.— (a quasi-unknown and quasi-unpredictable phenomenon that causes an event to result one way rather than another, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Pseudoserendipity.— Pseudoserendipity means PURPOSEFULLY CREATING the constant preconditions and conditions to seize “fortuitous happenstance” and/or “pleasant surprise” and/or “always making discoveries, by accidents and sagacity, of things which they were not in quest of”. And also entails unexpected positive and beneficial accident(s) [….] the art of finding something unintended [….] the common experience of observing unexpected, anomalous and strategic data and events, which are transformed into the instance and context to develop a new theory or to complement an existing theory [….] And the faculty of making fortunate Technological Breakthroughs and Scientific Discoveries And Innovation Developments by accident, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles and tangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits and planes [….] Somewhat Expected Accidental Beneficial Discoveries in Science, Technology, Strategy, Business and Management …”
Pseudo-Randomness.— (Pseudo-Randomness means quasi-lacking of pattern or quasi-predictability in events. Pseudo-Randomness suggests a quasi-non-order or quasi-non-coherence in a sequence of symbols or steps, such that there is no intelligible pattern or combination, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Pseudo-recusriveness.— (quasi-pertaining to or using a rule or procedure that can be applied repeatedly, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Qualitative Analysis.— “…Qualitative Analysis refers to the skills, technologies, applications and practices for continuous iterative exploration and investigation of past business performance to gain insight and drive business, risk and futures planning. Qualitative Analysis focuses on developing new insights and understanding of sustainable business performance based on narrative data …”
Qualt.— “…A qualt is brand of systems engineering who applies mathematical and ESPECIALLY non-mathematical models of uncertainty to financial and ESPECIALLY non-financial data and complex industrial operations. And a person who also studies the errors, the flaws and the limits of these qualitative models, understanding that there is a point of (i) inflection and (ii) Event horizon, in anything pursued by the for-lucre corporations …. A qualt has a combined background of advanced management, extreme project management (Agile) and systems engineering. A qualt spreads the usage of most-advanced business analytics and transformative and integrative risk management …. Whether he or she acknowledges it or not, the qualt is extremely AWARE of the many critical short-comings of many quantitative strategies and works hard at it advance to eliminate every form of downside through qualitative strategies …. For instance, qualts know that “…systemic risks …” are direct brainchildren of (a) Ignorance, (b) Manipulation, © Greed and (d) Corruption [….] Systems engineering, hugely embraced by Qualts, is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how to design and manage complex engineering projects over their life cycles. Issues such as reliability, logistics, coordination of different teams (requirements management), evaluation measurements, and other disciplines become more difficult when dealing with large or complex projects. Systems engineering deals with work-processes, optimization methods, and risk management tools in such projects. It overlaps technical and human-centered disciplines such as control engineering, industrial engineering, organizational studies, and project management. Systems Engineering ensures that all likely aspects of a project or system are considered, and integrated into a whole. White Swans are the brainchildren of Qualts …”
Quantitative Analysis.— “ … Quantitative Analysis refers to the skills, technologies, applications and practices for continuous iterative exploration and investigation of past business performance to gain insight and drive business, risk and futures planning. Quantitative Analysis focuses on developing new insights and understanding of sustainable business performance based on numerical data, narrative data, alphanumerical data and statistical methods …”
Quant.— “ … A quant is brand of industrial scientist and engineers who applies mathematical model of uncertainty to financial and/or socioeconomic data and complex financial instruments. And a person who also studies the flaws and the limits of these models, understanding that there is a point of breakdown …. A quant has a combined background of applied mathematics, engineering and statistics. A quant spreads the usage of artificial intelligence in today’s markets …. Whether he or she acknowledges it or not, the quant is extremely AWARE of the many critical short-comings of many quantitative strategies (as he is never interested in qualitative analytics), such as their tendency to lead to crowded trades and their underestimation of the likelihood of chaotic, volatile moves in the markets …. Along with Central Bank chairpersons and world’s finance ministers, quants are the first ones to “…elicit…” that the global economy is being “ …affected…” by “ …systemic risks…”, that systemic risk turbo-charged by several corrupted politicians, manipulative economists and beautiful quants that never understand what the tangible corporate theater of operations is [….] Industrial engineering, partly used by so-called Quants, is a branch of engineering dealing with the optimization of complex processes or systems. It is concerned with the development, improvement, implementation and evaluation of integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information, equipment, energy, materials, analysis and synthesis, as well as the mathematical, physical and social sciences together with the principles and methods of engineering design to specify, predict, and evaluate the results to be obtained from such systems or processes. Its underlying concepts overlap considerably with certain business-oriented disciplines such as operations management. Black Swans are the brainchildren of quants …”
Randomness.— (Randomness means lack of pattern or predictability in events. Randomness suggests a non-order or non-coherence in a sequence of symbols or steps, such that there is no intelligible pattern or combination, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Recursiveness.— (pertaining to or using a rule or procedure that can be applied repeatedly, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits.
Retrospective.— “ … Retrospective comprises something that is looking back on, contemplating, or directed to the past [….] looking or directed backward [….] Applying to or influencing the past; retroactive [….] looking or directed backwards, esp in time; characterized by retrospection …. applying to the past; retroactive [….] directed to the past; contemplative of past situations, events, etc. [….] looking or directed backward [….] review, revision, another look, reassessment, fresh look, second look, reconsideration, re-evaluation, re-examination [….] Considering a past event or development [….] Something that is chronologically presented pertaining to business tasks, with the utter object to show the trajectory of said business tasks …”
Risk .— “… The quantitative or qualitative expression of possible loss that considers both the probability that an event will occur and the consequences of that event … and/or the likeliness of injury, harm, damage, disruption or loss multiplied by its potential magnitude …”
Serendipity.— Serendipity means a “fortuitous happenstance” and/or “pleasant surprise” and/or “always making discoveries, by accidents and sagacity, of things which they were not in quest of”. And also entails unexpected positive and beneficial accident(s) [….] And the art of finding something unintended [….] the common experience of observing unexpected, anomalous and strategic data and events, which are transformed into the instance and context to develop a new theory or to complement an existing theory [….] And the faculty of making fortunate Technological Breakthroughs and Scientific Discoveries And Innovation Developments by accident, as a result of corporate manager’s perpetual MOST-RECURSIVE search for lucrative intangibles and tangibles in omniverseral: (a) hidden quadrants and (b) ignored flanks and © forgotten angles, and (d) recondite spheres and (e) hermetic theater of operations and (e) unrealized orbits and planes [….] Unexpected Accidental Beneficial Discoveries in Science, Technology, Strategy, Business and Management …”
Scientific Futuring.— “…Scientific Futuring is in place to develop a scientific method for studying the future. Scientific Futuring comprises: 1) an inductive process consisting of a number of accurate observations which have been consolidated, or generalized, into empirical laws or statements of underlying relationships between key variables and 2) A deductive, intuitive process by which the scientific “investigator” places his observations into a larger system of thought, or theory based on fundamental axioms. Scientific Futuring is instituted with the purpose of seizing knowledge of effects through causes. This method of Scientific Futuring, made up of a process employing the classical scientific steps of induction and deduction, and reinforced by additional steps of contextualization and evolutionization, is a battle-plan for study of tomorrow’s evolving world…”
Stargatenessfulness.— (Stargatenessfulness is the quality of conforming to the ability to investigate claims of psychic phenomena with potential corporate for-lucre application, such as ‘remote viewing’, the purported ability to psychically ‘see’ events, sites, or information from a great distance, including those of the environment, industries and specially those of direct and indirect competitors. Taken by Applied Thinkers and Visionary Corporation by the U.S. Federal Government’ and the U.S. Defense Intelligence Agency’s Stargate Project).
System .— “…System comprises the whole compounded of several parts, members elements, components and subsystems, a group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements forming a complex whole, an organized set of interrelated ideas or principles, a naturally occurring group of objects or phenomena, a condition of harmonious and orderly interaction, and an organized and coordinated method; a procedure. System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole or a set of elements (often called ‘components’) and dynamic relationships which are different from relationships of the set or its elements to other elements or sets. Systems unite and put together elements, components and subsystems toward the entire whole…”
Technology.— “… Technology is instituted in order to solve practical problems (both mild and complex ones) ─ especially in industry, commerce, economy, science, technology, society, and politics (including geopolitics) ─, the methodical practical application of the scientific method, mathematical principles, practical sciences and material used to achieve a commercial or industrial objective and beyond, as well as to achieve practical ends such as the design, manufacture, and operation of efficient and economical structures, machines, processes, and systems …. The profession of and/or the work performed by any engineer …” If you want a briefer definition, please see this: ” … the methodical and systematic application of science in order to solve practical problems …”
Theater of Operation.— “… Theater of Operation is hereby included to mean the four-dimensional coordinate system and beyond it, in which organization’s physical (tangible) and non-physical (intangible) events are located …”
The Eureka Moment.— “ … The Eureka Moment, also known as the ‘…Aha! Moment …’, refers to the common human experience of suddenly understanding a previously incomprehensible problem or concept. The Eureka effect is named after the myth that the Greek polymath Archimedes, having discovered how to measure the volume of an irregular object, leaped out of a public bath, and ran home naked shouting ‘eureka’ (I found it) …”
The Sputnik Moment.— “ … The Sputnik Moment is a point in time in which a country or a society or even a corporation, realizes that it needs to catch up with the apparent technological and scientific gap that exists between it and some other superpower and/or global competitors, increasing its investment efforts into education and innovative R&D&I …”
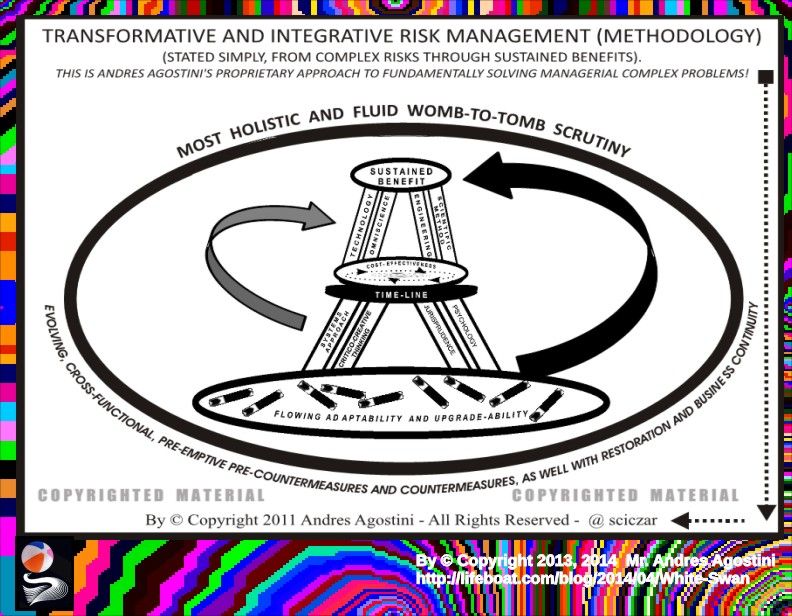
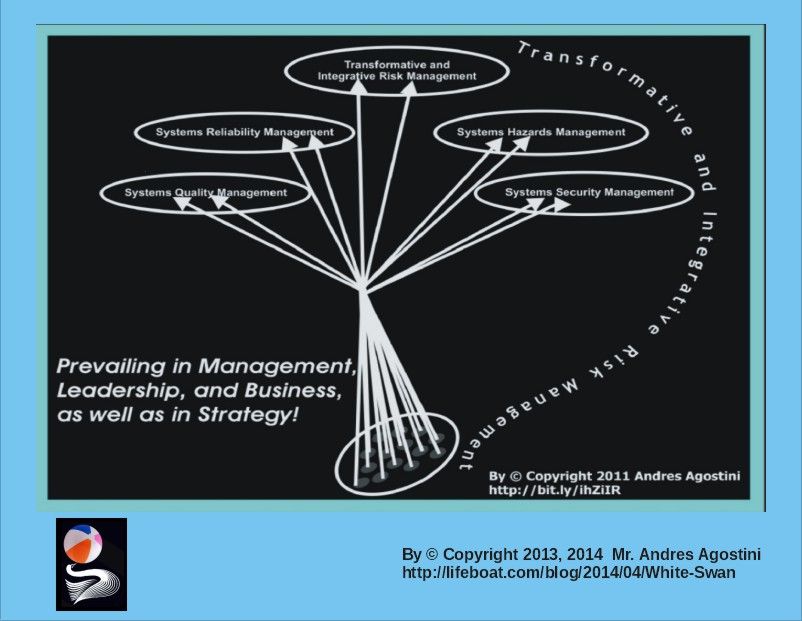
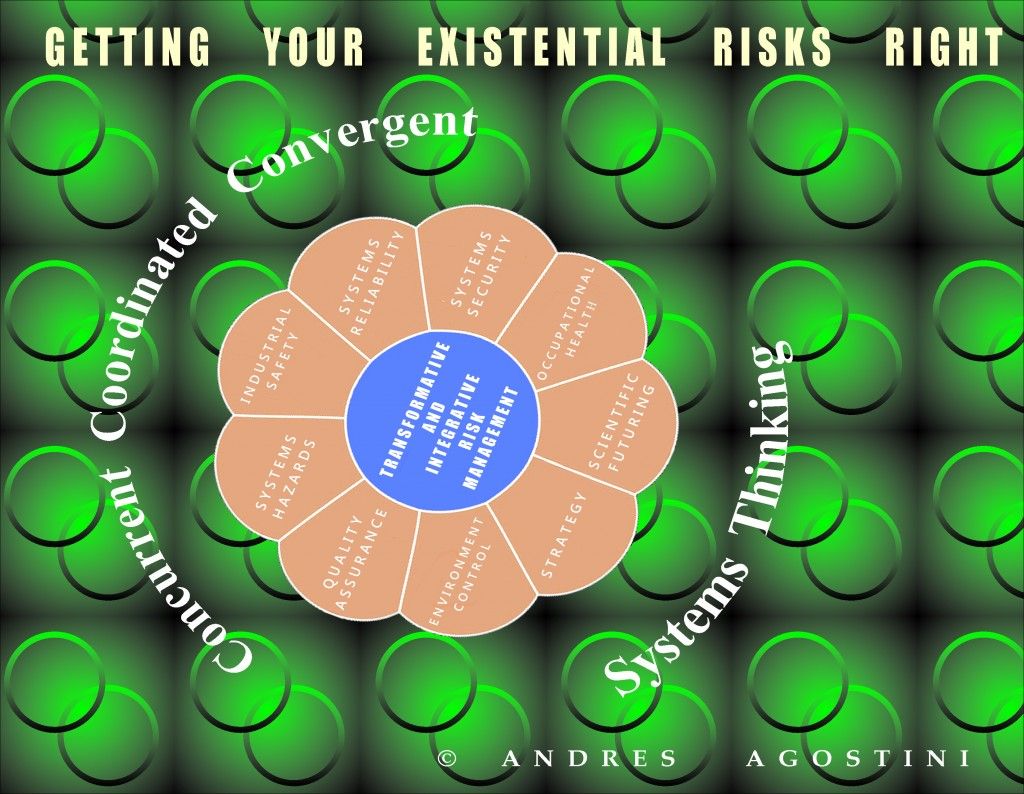
Transformative and Integrative Risk Management.— “…Transformative and Integrative Risk Management comprises of all activities and initiatives required to seize the optimum degree of risk elimination, mitigation, modulation or control within the constraints of operational effectiveness, time, and cost, attained through the specific application of management, scientific, engineering and mathematical principles throughout all phases of system operation.”
Transformative and Integrative Risk Management.— “Transformative and Integrative Risk Management comprises of all activities and initiatives required to seize the optimum degree of risk elimination, mitigation, modulation or control within the constraints of operational effectiveness, time, and cost, attained through the specific application of management, scientific, engineering and mathematical principles throughout all phases of system operation.”
Troublesomeness.— Troublesomeness is the quality of conforming to the ability to cause trouble, annoyance, or difficulty; vexation.
Un-reconnoiterable Cues.— (Un-reconnoiterable cues refers to un-explorable cues).
Wild Card.— “ … A wild card is a future development or event with a relatively low probability of occurrence but a likely high impact on the conduct of business …”