#CRISPR can be used to alter the genes of not only one organism, but an entire species, through a method of inheritance known as a gene drive. But what happens if something goes awry?


#CRISPR can be used to alter the genes of not only one organism, but an entire species, through a method of inheritance known as a gene drive. But what happens if something goes awry?

More insights on human conscientious in relation to its state after we die.
Personally, (this is only my own opinion) I believe much of the human conscientious will remain a mystery even in the living as it relates to the re-creation of the human brain and its thinking and decision making patterns on current technology. Namely because any doctor will tell you that a person’s own decisions (namely emotional decision making/ thinking) can be impacted by a whole multitude of factors beyond logical information such as the brain’s chemical balance, physical illness or even injury, etc. which inherently feeds into conscientious state. In order to try to replicate this model means predominantly development of a machine that is predominantly built with synthetic biology; and even then we will need to evolve this model to finally understand human conscientious more than we do today.
Sir Roger Penrose, a mathematical physicist at Oxford University, has asked “what right do we have to claim, as some might, that human beings are the only inhabitants of our planet blessed with an actual ability to be “aware”? It is hard to see how one could begin to develop a quantum-theoretical description of brain action when one might well have to regard the brain as “observing itself” all the time! Beneath all this technicality is the feeling that it is indeed “obvious” that the conscious mind cannot work like a computer, even though much of what is involved in mental activity might do so.
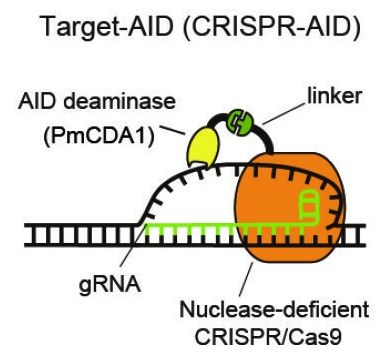
Major advancement in Gene Editing.
A team involving Kobe University researchers has succeeded in developing ‘Target-AID’, a genome editing technique that does not cleave the DNA. The technique offers, through high-level editing operation, a method to address the existing issues of genome editing. It is expected that the technique will be applied to gene therapy in the future in addition to providing a powerful tool for breeding useful organisms and conducting disease and drug-discovery research. The findings were published online in Science on August 5.
The team consists of Project Associate Professor NISHIDA Keiji and Professor KONDO Akihiko (Graduate School of Science, Technology and Innovation, Kobe University) as well as Associate Professor YACHIE Nozomu (Synthetic Biology Division, Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Tokyo) and Professor HARA Kiyotaka (Department of Environmental Sciences, Graduate School of Nutritional and Environmental Sciences, University of Shizuoka).
Genome editing — which can directly manipulate the genome information of various organisms without leaving an artificial strand — has seen rapid progress in recent years and it is gradually becoming a revolutionary tool in fields ranging from life sciences to advanced medical research.
New updated article on the evolution of the processors of tomorrow.
Personally, I find this article runs short in only focusing on carbon, organics aka plastics, and QC as future replacement. With the ongoing emergence of synthetic biology and what this could mean for processors; I would suggest the author explore further the future of synthetic bio.
From stacked CPUs to organic and quantum processing.
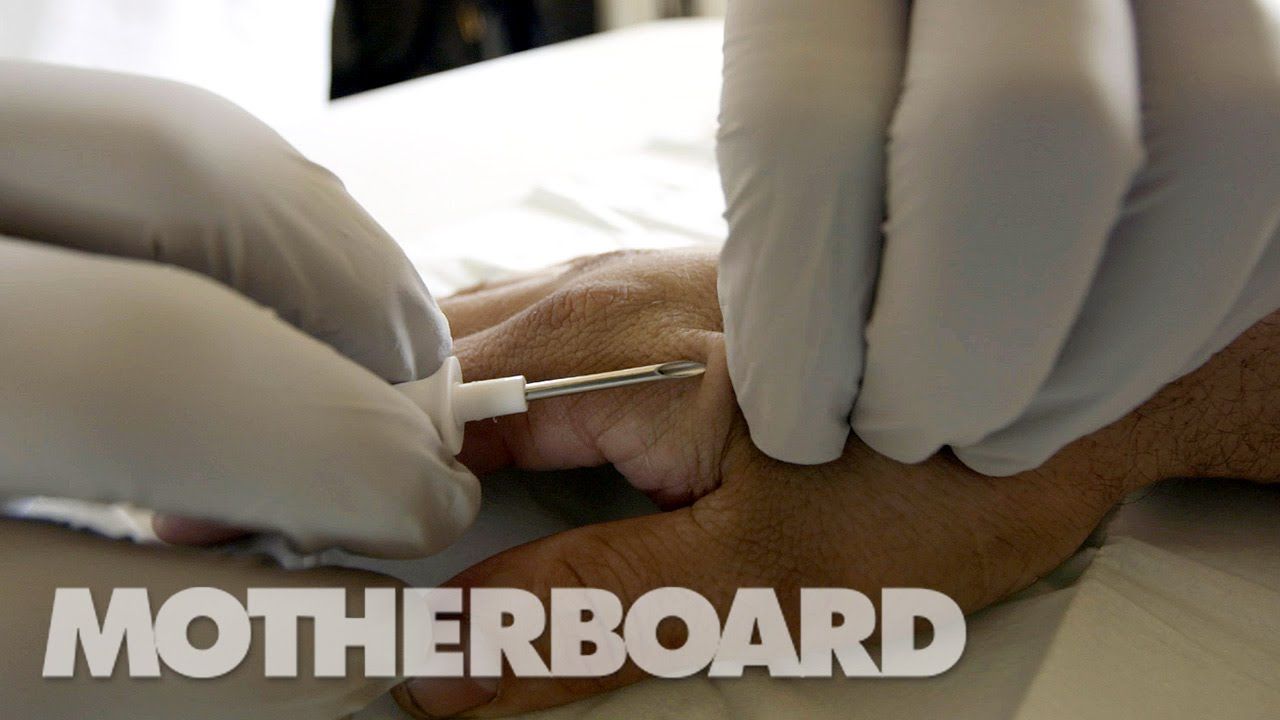
A pioneer in the biohacking scene since the mid-2000s, Amal Graafstra’s been experimenting with RFID implants for more than a decade. Now Graafstra is developing implants that go beyond RFIDs.
In episode 2 of Humans+, Motherboard travels to his company Dangerous Things’ garage headquarters to get an early look at UKI, a prototype implant focused on encryption that’s expected to be released in 2017. Amal hopes that this technology will bring us one step closer to merging our physical and digital identities, but how will society react to having these technologies implanted beneath our skin?
WATCH NEXT:
This Mind-Controlled Bionic Arm Can Touch and Feel: http://bit.ly/2bShxqj
Follow MOTHERBOARD
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/motherboardtv
Twitter: http://twitter.com/motherboard
Tumblr: http://motherboardtv.tumblr.com/

Fraud detection technology is in high demand and growing thanks to areas such as India. However, there is a huge growing demand for synthetic diamonds in their use in technology, medical, synthetic biology as well.
It takes billions of years to produce a natural diamond, but a laboratory can grow one in days and to the untrained eye they look the same. In an attempt to protect its reputation, De Beers has developed technology that can spot the difference. Ivor Bennett reports.
When dealing with diamonds, one can never be too sure. That’s why at De Beers, it’s not just humans checking the gems anymore, but machines too. SOUNDBITE (English) JONATHAN KENDALL, PRESIDENT, INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE OF DIAMOND GRADING AND RESEARCH, SAYING: “A synthetic is a man-made product. It’s not a gem, it’s not a beautiful product. It’s not about love and affection and emotion. And it’s not unique and it’s not mysterious. And that’s everything that a diamond is.” It takes about 3 billion years to make a natural diamond. but just three weeks for a synthetic one. To the naked eye though, they look the same. So how do you tell the difference? SOUNDBITE (English) IVOR BENNETT, REUTERS REPORTER, SAYING: “It’s all to do with how the stone looks under UV light. A natural diamond for example will appear dark blue in colour with a regular structure. But if i click on the synthetic one, you can see it’s much lighter with these block-like structures, which is down to its irregular growth.


CISO & CSO at many companies are certainly going to have their work cut out for them in the long-term future as more and more new tech such as 3D Printing, Synthetic Bio, etc. are adopted into companies; really brings a new level of security concerns not only in government; but also the private sector.
He pointed out that while there were international organisations to prevent the spread of nuclear and chemical weapons, there was no such agency to deal with biological weapons.
Speaking at the Council debate on weapons of mass destruction (WMD), he sought to expand its definition beyond nuclear, chemical and biological to embrace the threats arising from 21st century science, technology and globalisation.
Information and communication technologies, artificial intelligence, 3D printing and synthetic biology have the potential massive destruction, he said. “The nexus between these emerging technologies and WMD needs close examination and action.”
Nice.
Algae (a term used to group many photosynthetic organisms into a rather heterologous mash-up) do not have a kind place in the public imagination. Take for example the following passage from Stephen King’s Pet Semetary:
“Dead fields under a November sky, scattered rose petals brown and turning up at the edges, empty pools scummed with algae, rot, decomposition, dust…”
Leaving aside their use in a horror novel as a way to set an image of decay, algae attract significant scientific attention, and are even considered cool (well, at least by some). But when I tell people I work on algal Synbio, one question that eventually comes up (or is silently implied) is why do I bother, when there are more prominent and better-developed systems? In this blog I will try to partly address this point of view, as well as provide a small perspective on the subject.
My sociology of knowledge students read Yuval Harari’s bestselling first book, Sapiens, to think about the right frame of reference for understanding the overall trajectory of the human condition. Homo Deus follows the example of Sapiens, using contemporary events to launch into what nowadays is called ‘big history’ but has been also called ‘deep history’ and ‘long history’. Whatever you call it, the orientation sees the human condition as subject to multiple overlapping rhythms of change which generate the sorts of ‘events’ that are the stuff of history lessons. But Harari’s history is nothing like the version you half remember from school.
In school historical events were explained in terms more or less recognizable to the agents involved. In contrast, Harari reaches for accounts that scientifically update the idea of ‘perennial philosophy’. Aldous Huxley popularized this phrase in his quest to seek common patterns of thought in the great world religions which could be leveraged as a global ethic in the aftermath of the Second World War. Harari similarly leverages bits of genetics, ecology, neuroscience and cognitive science to advance a broadly evolutionary narrative. But unlike Darwin’s version, Harari’s points towards the incipient apotheosis of our species; hence, the book’s title.
This invariably means that events are treated as symptoms if not omens of the shape of things to come. Harari’s central thesis is that whereas in the past we cowered in the face of impersonal natural forces beyond our control, nowadays our biggest enemy is the one that faces us in the mirror, which may or may not be able within our control. Thus, the sort of deity into which we are evolving is one whose superhuman powers may well result in self-destruction. Harari’s attitude towards this prospect is one of slightly awestruck bemusement.
Here Harari equivocates where his predecessors dared to distinguish. Writing with the bracing clarity afforded by the Existentialist horizons of the Cold War, cybernetics founder Norbert Wiener declared that humanity’s survival depends on knowing whether what we don’t know is actually trying to hurt us. If so, then any apparent advance in knowledge will always be illusory. As for Harari, he does not seem to see humanity in some never-ending diabolical chess match against an implacable foe, as in The Seventh Seal. Instead he takes refuge in the so-called law of unintended consequences. So while the shape of our ignorance does indeed shift as our knowledge advances, it does so in ways that keep Harari at a comfortable distance from passing judgement on our long term prognosis.
This semi-detachment makes Homo Deus a suave but perhaps not deep read of the human condition. Consider his choice of religious precedents to illustrate that we may be approaching divinity, a thesis with which I am broadly sympathetic. Instead of the Abrahamic God, Harari tends towards the ancient Greek and Hindu deities, who enjoy both superhuman powers and all too human foibles. The implication is that to enhance the one is by no means to diminish the other. If anything, it may simply make the overall result worse than had both our intellects and our passions been weaker. Such an observation, a familiar pretext for comedy, wears well with those who are inclined to read a book like this only once.
One figure who is conspicuous by his absence from Harari’s theology is Faust, the legendary rogue Christian scholar who epitomized the version of Homo Deus at play a hundred years ago in Oswald Spengler’s The Decline of the West. What distinguishes Faustian failings from those of the Greek and Hindu deities is that Faust’s result from his being neither as clever nor as loving as he thought. The theology at work is transcendental, perhaps even Platonic.
In such a world, Harari’s ironic thesis that future humans might possess virtually perfect intellects yet also retain quite undisciplined appetites is a non-starter. If anything, Faust’s undisciplined appetites point to a fundamental intellectual deficiency that prevents him from exercising a ‘rational will’, which is the mark of a truly supreme being. Faust’s sense of his own superiority simply leads him down a path of ever more frustrated and destructive desire. Only the one true God can put him out of his misery in the end.
In contrast, if there is ‘one true God’ in Harari’s theology, it goes by the name of ‘Efficiency’ and its religion is called ‘Dataism’. Efficiency is familiar as the dimension along which technological progress is made. It amounts to discovering how to do more with less. To recall Marshall McLuhan, the ‘less’ is the ‘medium’ and the ‘more’ is the ‘message’. However, the metaphysics of efficiency matters. Are we talking about spending less money, less time and/or less energy?
It is telling that the sort of efficiency which most animates Harari’s account is the conversion of brain power to computer power. To be sure, computers can outperform humans on an increasing range of specialised tasks. Moreover, computers are getting better at integrating the operations of other technologies, each of which also typically replaces one or more human functions. The result is the so-called Internet of Things. But does this mean that the brain is on the verge of becoming redundant?
Those who say yes, most notably the ‘Singularitarians’ whose spiritual home is Silicon Valley, want to translate the brain’s software into a silicon base that will enable it to survive and expand indefinitely in a cosmic Internet of Things. Let’s suppose that such a translation becomes feasible. The energy requirements of such scaled up silicon platforms might still be prohibitive. For all its liabilities and mysteries, the brain remains the most energy efficient medium for encoding and executing intelligence. Indeed, forward facing ecologists might consider investing in a high-tech agronomy dedicated to cultivating neurons to function as organic computers – ‘Stem Cell 2.0’, if you will.
However, Harari does not see this possible future because he remains captive to Silicon Valley’s version of determinism, which prescribes a migration from carbon to silicon for anything worth preserving indefinitely. It is against this backdrop that he flirts with the idea that a computer-based ‘superintelligence’ might eventually find humans surplus to requirements in a rationally organized world. Like other Singularitarians, Harari approaches the matter in the style of a 1950s B-movie fan who sees the normative universe divided between ‘us’ (the humans) and ‘them’ (the non-humans).
The bravest face to put on this intuition is that computers will transition to superintelligence so soon – ‘exponentially’ as the faithful say — that ‘us vs. them’ becomes an operative organizing principle. More likely and messier for Harari is that this process will be dragged out. And during that time Homo sapiens will divide between those who identify with their emerging machine overlords, who are entitled to human-like rights, and those who cling to the new acceptable face of racism, a ‘carbonist’ ideology which would privilege organic life above any silicon-based translations or hybridizations. Maybe Harari will live long enough to write a sequel to Homo Deus to explain how this battle might pan out.
NOTE ON PUBLICATION: Homo Deus is published in September 2016 by Harvil Secker, an imprint of Penguin Random House. Fuller would like to thank The Literary Review for originally commissioning this review. It will appear in a subsequent edition of the magazine and is published here with permission.