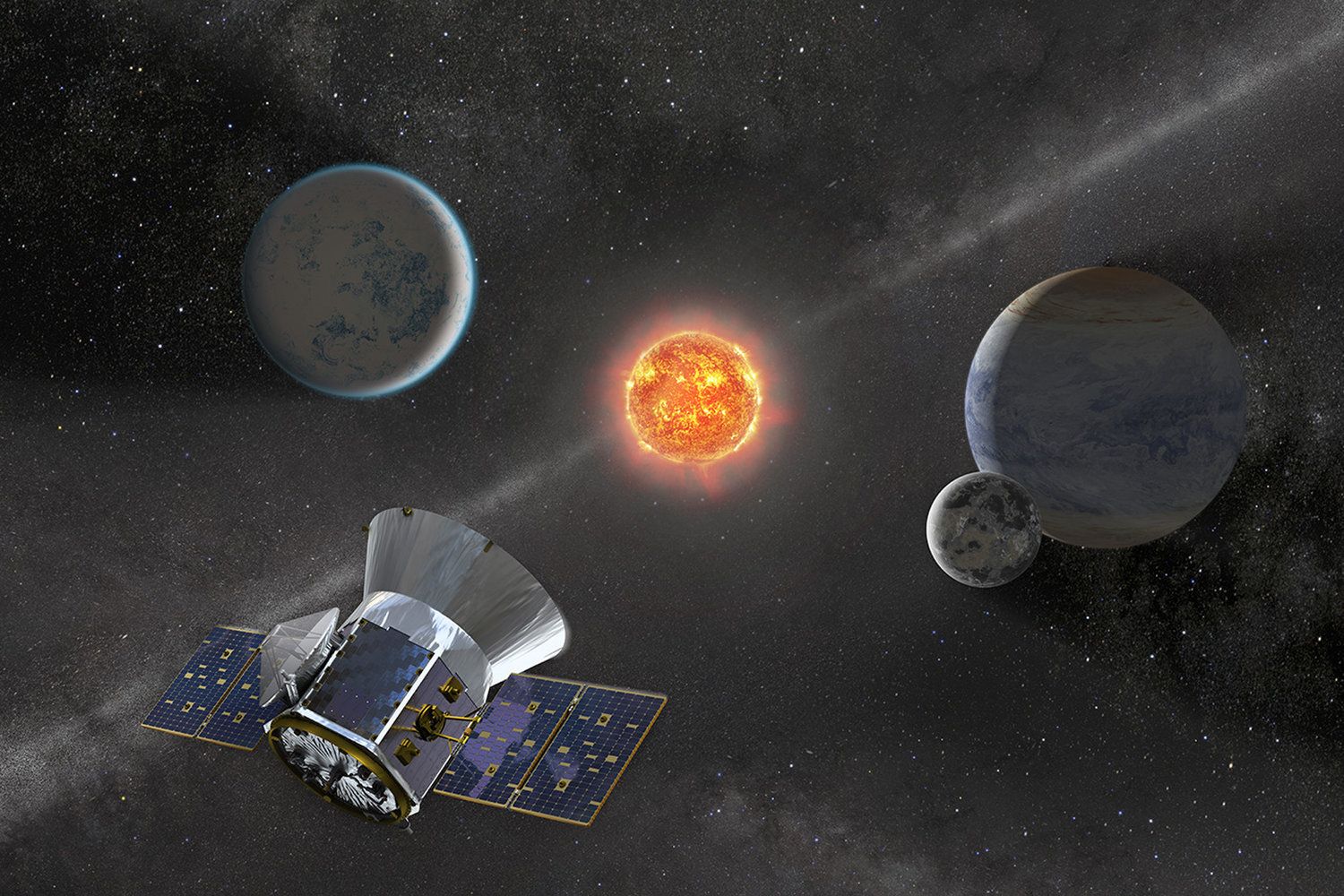
On Monday, April 16, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NASA’s new exoplanet hunter will train its sights on nearer, brighter stars than its predecessors did. If TESS lives up to scientists’ predictions, it could energize our search for life in the cosmos.
When the Kepler space telescope launched in 2009, scientists didn’t know what fraction of stars hosted planets. The Kepler mission was a statistical exploration looking to see how frequently planets occur around stars, Harvard astronomer David Latham told Space.com. “One of the big surprises from Kepler was to find this whole population of planets with sizes between that of Neptune and Earth — and there aren’t any in our solar system, zero — and they’re everywhere out there,” said Latham, who’s worked on the Kepler project for nearly 20 years.
“Kepler is what made us become aware that planets are as common as telephone poles,” SETI Institute astronomer Seth Shostak told Space.com.” But the stars that Kepler was staring at for four years … they were all somewhere between 500 and 1,500 light-years away.” TESS will survey the local neighborhood for planets like Earth. [NASA’s TESS Exoplanet-Hunter in Pictures].