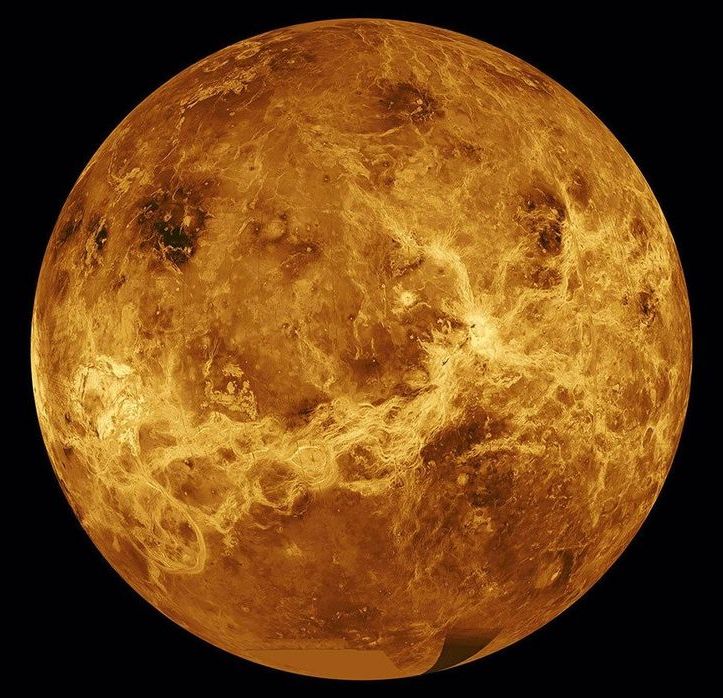
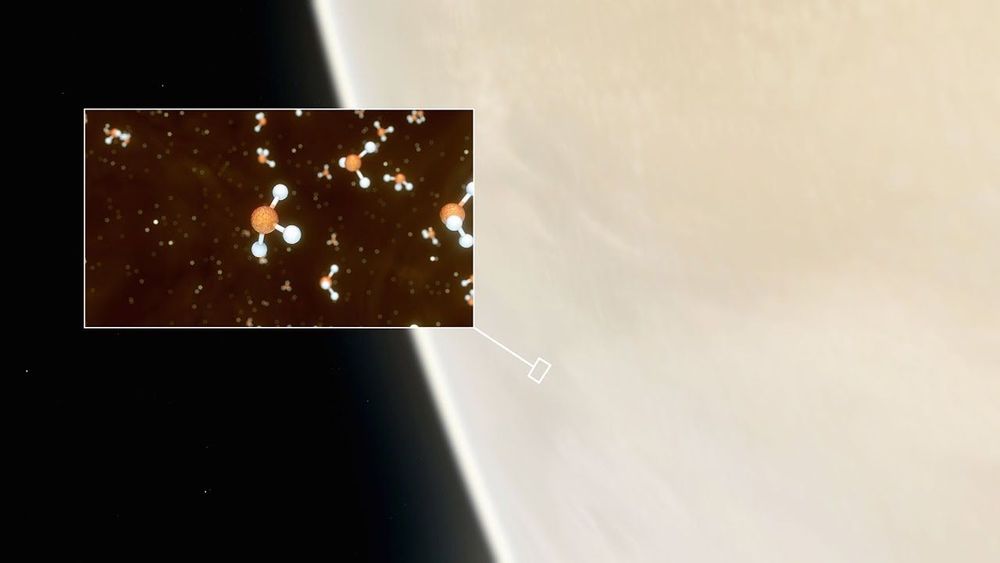
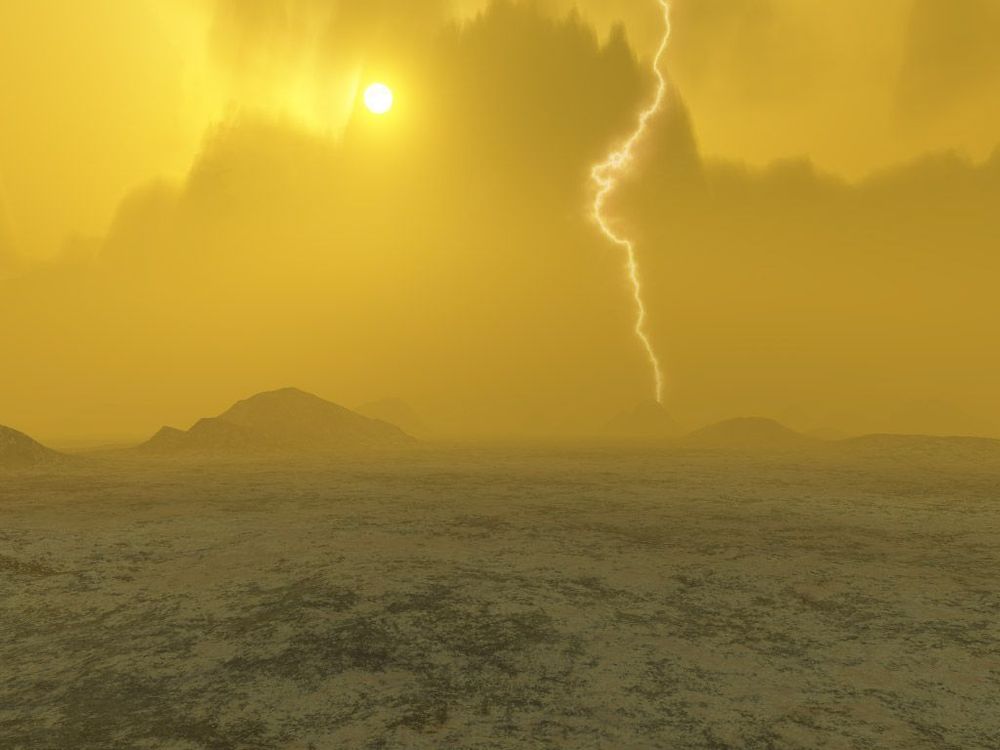
Independent Premium Comments can be posted by members of our membership scheme, Independent Premium. It allows our most engaged readers to debate the big issues, share their own experiences, discuss real-world solutions, and more. Our journalists will try to respond by joining the threads when they can to create a true meeting of independent Premium. The most insightful comments on all subjects will be published daily in dedicated articles. You can also choose to be emailed when someone replies to your comment.
The existing Open Comments threads will continue to exist for those who do not subscribe to Independent Premium. Due to the sheer scale of this comment community, we are not able to give each post the same level of attention, but we have preserved this area in the interests of open debate. Please continue to respect all commenters and create constructive debates.