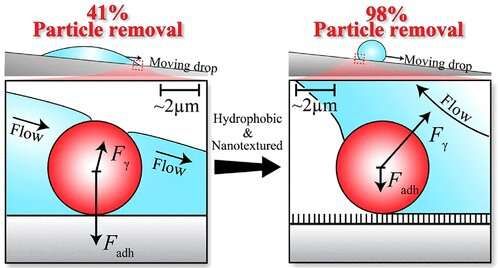
Taking a cue from the self-cleaning properties of the lotus leaf, researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev have shed new light on microscopic forces and mechanisms that can be optimized to remove dust from solar panels to maintain efficiency and light absorption. The new technique removed 98 percent of dust particles.
In a new study published in Langmuir, the researchers confirmed that modifying the surface properties of solar panels may greatly reduce the amount of dust remaining on the surface, and significantly increase the potential of solar energy harvesting applications in the desert.
Dust adhesion on solar panels is a major challenge to energy harvesting through photovoltaic cells and solar thermal collectors. New solutions are necessary to maintain maximum collection efficiency in high dust density areas such as the Negev desert in Israel.