In a significant step toward large-scale hydrogen production, researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed a low-cost catalyst that can speed up the splitting of water to produce hydrogen gas.
Splitting water using electricity is a widely-explored method to generate hydrogen gas, a long sought-after clean power source for fuel cells, batteries and zero-emission vehicles. One of two major reactions involved in this process—called the Oxygen Evolution Reaction—is notoriously slow, restricting the overall efficiency. Researchers have focused on developing better catalysts — materials that can speed up the reaction while remaining neutral. The most efficient catalysts today are made from precious metals such as ruthenium and platinum, which are both expensive and rare.
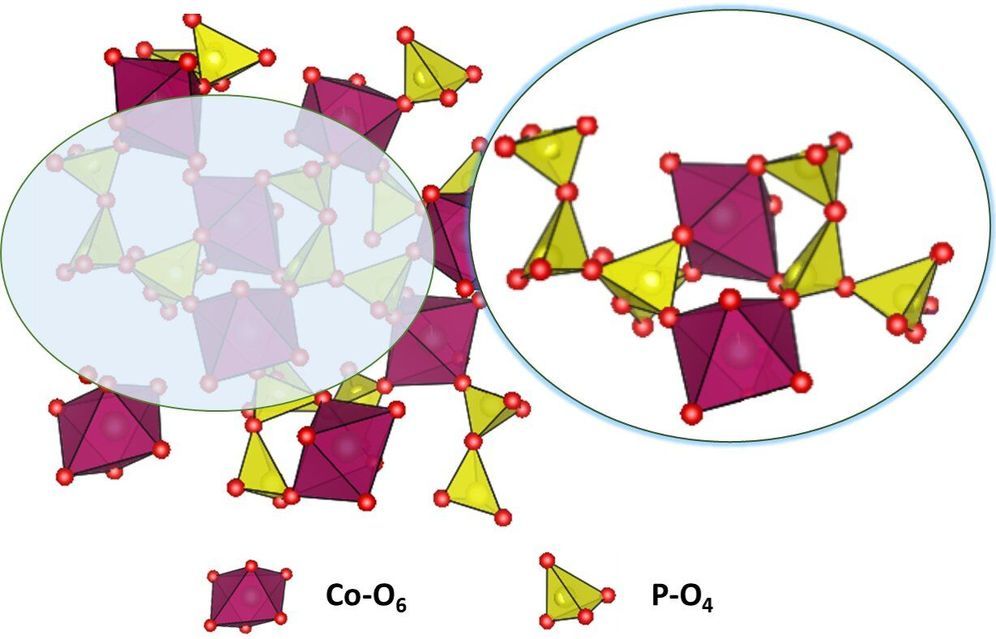
An IISc team has now developed a low-cost catalyst by combining cobalt oxide with phosphate salts of sodium. The material cost is over two hundred times less expensive than the current state-of-the-art ruthenium dioxide catalyst, and the reaction rate is also faster, says Ritambhara Gond, PhD student at the Materials Research Centre (MRC), IISc, who is the first author of the paper published in Angewandte Chemie.