A medical miracle happened about 170 years ago when scientists discovered general anesthesia that enables millions of patients to undergo invasive, life-saving surgeries without pain. However, in spite of decades of research, scientists cannot understand why general anesthesia works.
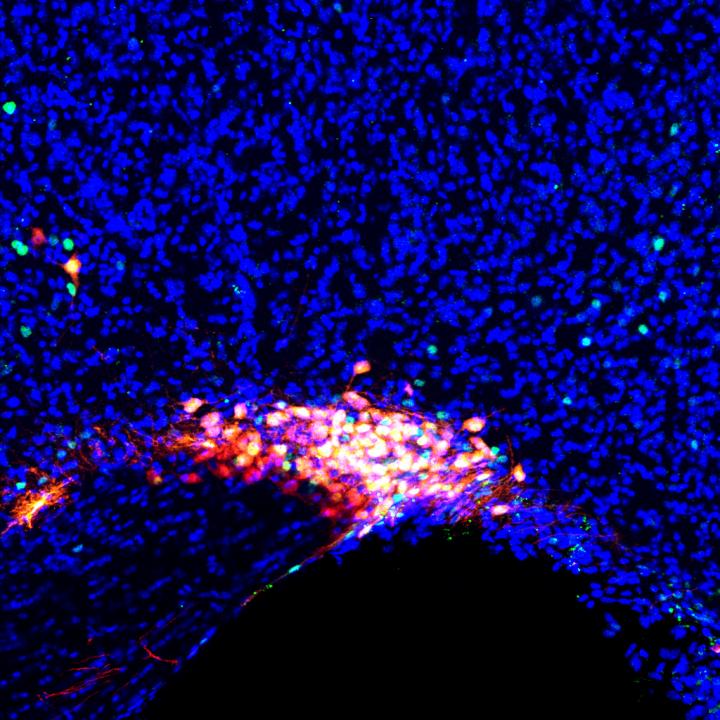
In a new study published online in Neuron, scientists believe they have discovered the part of the answer. A team of researchers from a Duke University found that several different general anesthesia drugs knock out the patient by hijacking the neural circuitry that the person falls asleep.
They traced this neural circuitry to a tiny cluster of cells at the base of the brain responsible for churning out hormones to regulate bodily functions, moods, and sleep. The discovery is one of the first to indicate a role for the hormones in maintaining the state of general anesthesia and provides valuable insights for generating newer drugs that could put people to sleep with fewer side effects.