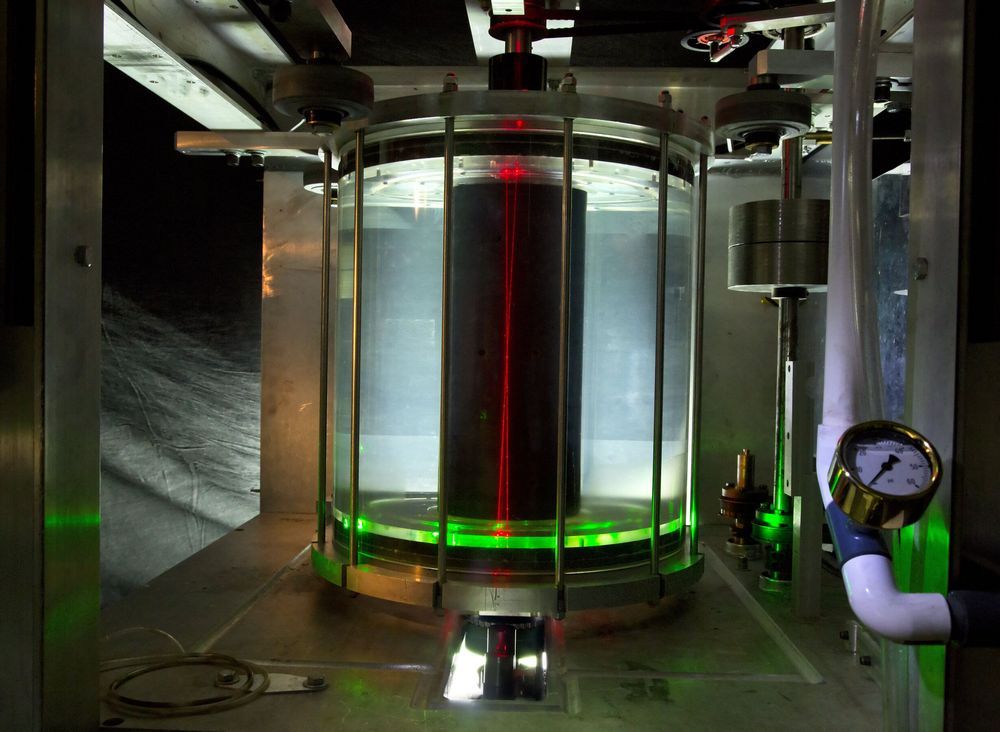
How have stars and planets developed from the clouds of dust and gas that once filled the cosmos? A novel experiment at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has demonstrated the validity of a widespread theory known as “magnetorotational instability,” or MRI, that seeks to explain the formation of heavenly bodies.
The theory holds that MRI allows accretion disks, clouds of dust, gas, and plasma that swirl around growing stars and planets as well as black holes, to collapse into them. According to the theory, this collapse happens because turbulent swirling plasma, technically known as “Keplerian flows,” gradually grows unstable within a disk. The instability causes angular momentum—the process that keeps orbiting planets from being drawn into the sun—to decrease in inner sections of the disk, which then fall into celestial bodies.
Unlike orbiting planets, the matter in dense and crowded accretion disks may experience forces such as friction that cause the disks to lose angular momentum and be drawn into the objects they swirl around. However, such forces cannot fully explain how quickly matter must fall into larger objects for planets and stars to form on a reasonable timescale.