Anxiety disorders are severe mental disorders in which patients suffer from intense fears and anxiety or from sudden, inexplicable panic attacks. In extreme cases, the affected individuals barely leave their homes, which can have serious consequences for their relationships with family and friends as well as for their professional lives. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Experimental Medicine in Göttingen have now identified a synaptic protein which, when inactivated, has an anxiolytic effect in mice.
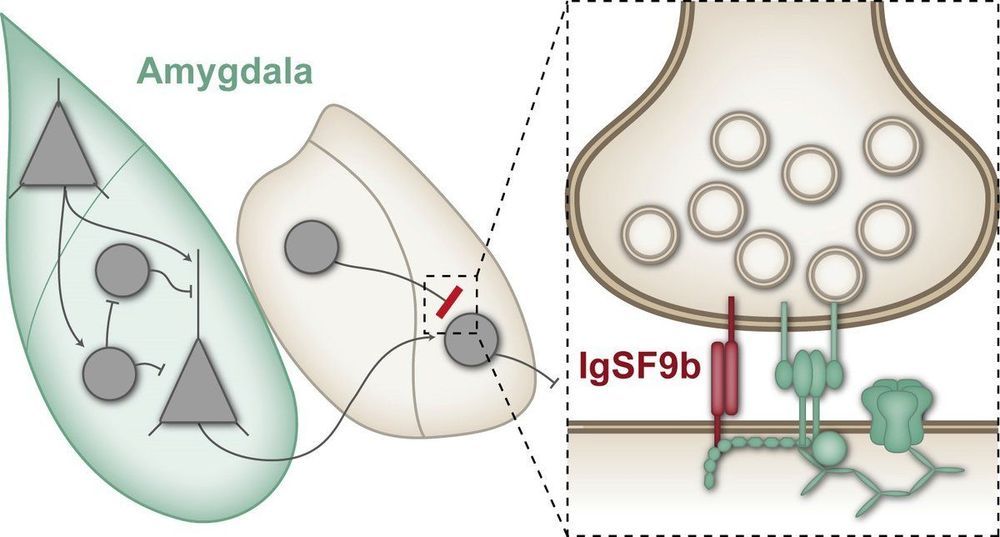
Around 10 percent of the population suffer from anxiety disorders, and current treatment options only offer effective help for a proportion of those affected. One of the changes observed in the brains of patients with anxiety disorders is an increased neuronal activity in the amygdala, a brain region that plays a key role in processing emotions such as anxiety or fear. An overactivation of the amygdala is thought to be involved in causing exaggerated anxiety. Many anxiolytic medications such as benzodiazepines presumably normalize this overactivation by strengthening the function of inhibitory synapses.
Synapses are connections between nerve cells in the brain, at which information is transmitted from one nerve cell to another. At inhibitory synapses, this transmission results in a reduction in the activity of the neighbouring nerve cells. In the amygdala, for instance, this inhibits the transmission of stimuli that trigger fear and anxiety. Benzodiazepines strengthen this inhibitory effect—but unfortunately they affect not only those inhibitory synapses that transmit anxiogenic stimuli but also many other inhibitory synapses in the brain. This can lead to significant side effects such as pronounced sedation and impaired concentration. Accordingly, scientists are searching for new, more specific targets for anxiolytic medications.