When it comes to recovering from insult, the adult human brain has very little ability to compensate for nerve-cell loss. Biomedical researchers and clinicians are therefore exploring the possibility of using transplanted nerve cells to replace neurons that have been irreparably damaged as a result of trauma or disease. However, it is not clear whether transplanted neurons can be integrated sufficiently, to result in restored function of the lesioned network. Now researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology in Martinsried, the Ludwig Maximilians University Munich, and the Helmholtz Zentrum München have demonstrated that, in mice, transplanted embryonic nerve cells can indeed be incorporated into an existing network and correctly carry out the tasks of damaged cells originally found in that region.
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease, but also stroke or certain injuries lead to a loss of brain cells. The mammalian brain can replace these cells only in very limited areas, making the loss in most cases a permanent one. The transplantation of young nerve cells into an affected network of patients, for example with Parkinson’s disease, allow for the possibility of a medical improvement of clinical symptoms. However, if the nerve cells transplanted in such studies help to overcome existing network gaps or whether they actually replace the lost cells, remained unknown.
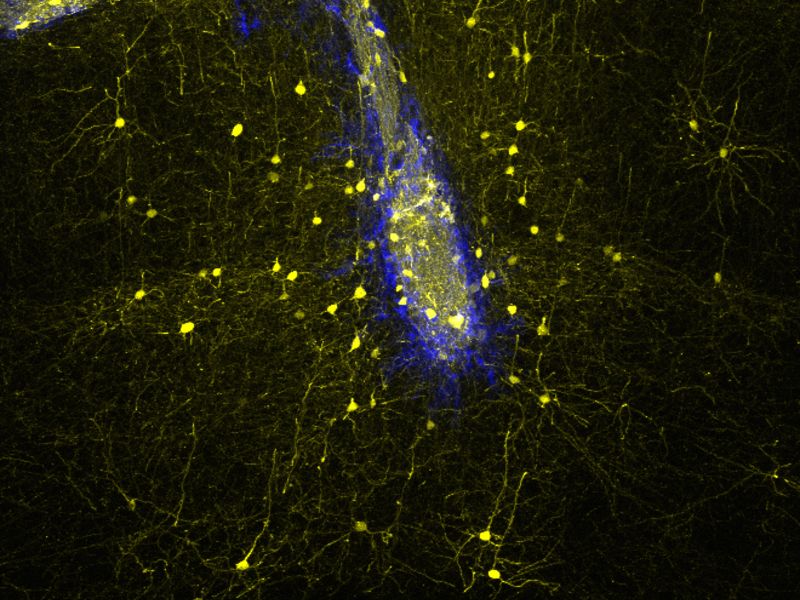
In the joint study, researchers of the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology, the Ludwig Maximilians University Munich, and the Helmholtz Zentrum München have specifically asked whether transplanted embryonic nerve cells can functionally integrate into the visual cortex of adult mice. The study was supported by the center grant (SFB) 870 of the German Research Foundation (DFG). “This brain region is ideal for such experiments,” says Magdalena Götz, joint leader of the study together with Mark Hübener, who continues to explain: “By now, we know so much about the functions of the nerve cells in the visual cortex and the connections between them that we can readily assess whether the new nerve cells actually perform the tasks normally carried out by the network.”