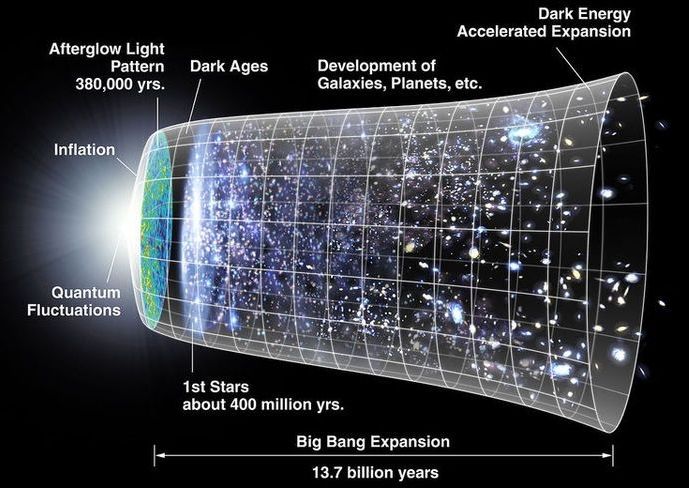
Roughly 13.8 billion years ago, the Universe as we know it expanded from an infinitely hot and dense singularity in space and time, first in a furious torrent of rapid cosmic inflation for a fraction of a second, and then in the more calm manner we see today – gradual, yet accelerating expansion fueled by dark energy.
This fleetingly describes the Big Bang model of cosmology, the most successful theoretical explanation for our grand Universe. Backed by boatloads of observational evidence, we can be very sure of its veracity. Caltech astrophysicist Sean Caroll even described the Big Bang as “100 percent true.”
But that percentage of surety dwindles to nothing when discussing the singularity that supposedly started it all. Where did it come from? What came before it? What caused it to “bang” in such a big way? As Carroll admitted, this singularity and its accompanying “bang” are essentially stand-ins for what we don’t – and currently can’t – actually know.