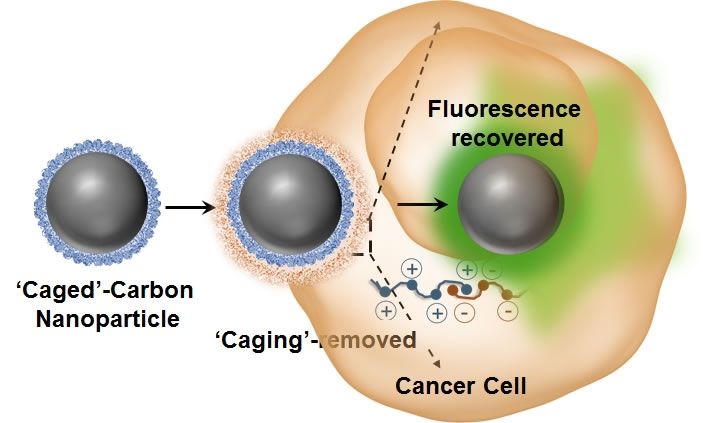
‘Caged’ non-fluorescent carbon dot enters the cancer cell, loses its caging and lights up. Credit: University of Illinois.
Tiny carbon dots have, for the first time, been applied to intracellular imaging and tracking of drug delivery involving various optical and vibrational spectroscopic-based techniques such as fluorescence, Raman, and hyperspectral imaging. Researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated, for the first time, that photo luminescent carbon nanoparticles can exhibit reversible switching of their optical properties in cancer cells.
“One of the major advantages of these agents are their strong intrinsic optical sensitivity without the need for any additional dye/fluorophore and with no photo-bleaching issues associated with it,” explained Dipanjan Pan, an assistant professor of bioengineering and the leader of the study. “Using some elegant nanoscale surface chemistry, we created a molecular ‘masking’ pathway to turn off the fluorescence and then selectively remove the mask leading to regaining the brightness.