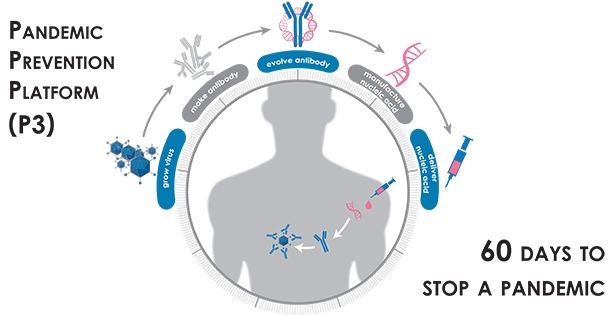
Over the past several years, DARPA-funded researchers have pioneered RNA vaccine technology, a medical countermeasure against infectious diseases that uses coded genetic constructs to stimulate production of viral proteins in the body, which in turn can trigger a protective antibody response. As a follow-on effort, DARPA funded research into genetic constructs that can directly stimulate production of antibodies in the body., DARPA is now launching the Pandemic Prevention Platform (P3) program, aimed at developing that foundational work into an entire system capable of halting the spread of any viral disease outbreak before it can escalate to pandemic status. Such a capability would offer a stark contrast to the state of the art for developing and deploying traditional vaccines—a process that does not deliver treatments to patients until months, years, or even decades after a viral threat emerges.
“DARPA’s goal is to create a technology platform that can place a protective treatment into health providers’ hands within 60 days of a pathogen being identified, and have that treatment induce protection in patients within three days of administration. We need to be able to move at this speed considering how quickly outbreaks can get out of control,” said Matt Hepburn, the P3 Program Manager. “The technology needs to work on any viral disease, whether it’s one humans have faced before or not.”
Recent outbreaks of viral infectious diseases such as Zika, H1N1 influenza, and Ebola have cast into sharp relief the inability of the global health system to rapidly contain the spread of a disease using existing tools and procedures. State-of-the-art medical countermeasures typically take many months or even years to develop, produce, distribute, and administer. These solutions often arrive too late—if at all—and in quantities too small to respond to emerging threats. In contrast, the envisioned P3 platform would cut response time to weeks and stay within the window of relevance for containing an outbreak.