I know that I reported on this a few weeks ago; however, this article shares some additional insights on how this new method will enable more efficient smaller devices including promoting stabilization in Quantum Computing (QC)…
A multi-institutional team of researchers has discovered novel magnetic behavior on the surface of a specialized material that holds promise for smaller, more efficient devices and other advanced technology.
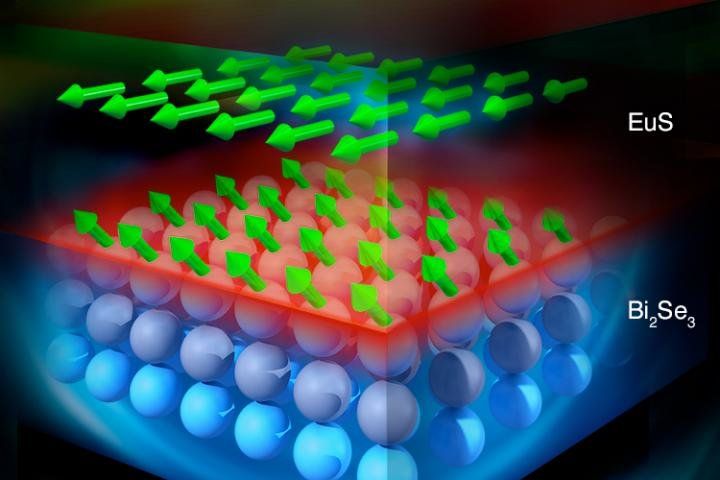
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology and their collaborators used neutron scattering to reveal magnetic moments in hybrid topological insulator (TI) materials at room temperature, hundreds of degrees Fahrenheit warmer than the extreme sub-zero cold where the properties are expected to occur.
The discovery promises new opportunities for next-generation electronic and spintronic devices such as improved transistors and quantum computing technologies. Their research is discussed in a paper published in the journal Nature.