HUGE deal for wearables and biomed technologies.
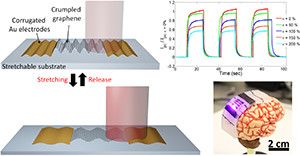
Researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated a new approach to modifying the light absorption and stretchability of atomically thin two-dimensional (2D) materials by surface topographic engineering using only mechanical strain. The highly flexible system has future potential for wearable technology and integrated biomedical optical sensing technology when combined with flexible light-emitting diodes.
“Increasing graphene’s low light absorption in visible range is an important prerequisite for its broad potential applications in photonics and sensing,” explained SungWoo Nam, an assistant professor of mechanical science and engineering at Illinois. “This is the very first stretchable photodetector based exclusively on graphene with strain-tunable photoresponsivity and wavelength selectivity.”
Graphene—an atomically thin layer of hexagonally bonded carbon atoms—has been extensively investigated in advanced photodetectors for its broadband absorption, high carrier mobility, and mechanical flexibility. Due to graphene’s low optical absorptivity, graphene photodetector research so far has focused on hybrid systems to increase photoabsorption. However, such hybrid systems require a complicated integration process, and lead to reduced carrier mobility due to the heterogeneous interfaces.