A DARPA-funded research team has created a novel neural-recording device that can be implanted into the brain through blood vessels, reducing the need for invasive surgery and the risks associated with breaching the blood-brain barrier. The technology was developed under DARPA’s Reliable Neural-Interface Technology (RE-NET) program, and offers new potential for safely expanding the use of brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) to treat physical disabilities and neurological disorders.
In an article published in Nature Biotechnology, researchers in the Vascular Bionics Laboratory at the University of Melbourne led by neurologist Thomas Oxley, M.D., describe proof-of-concept results from a study conducted in sheep that demonstrate high-fidelity measurements taken from the motor cortex—the region of the brain responsible for controlling voluntary movement—using a novel device the size of a small paperclip.
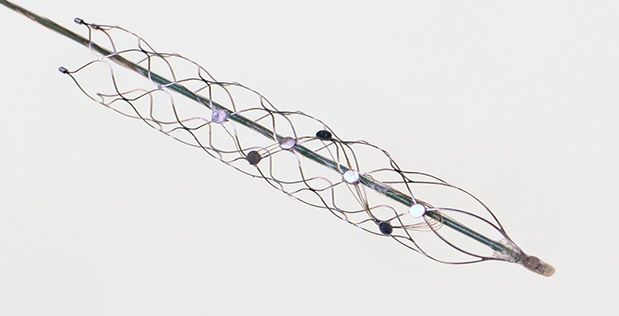
This new device, which Oxley’s team dubbed the “stentrode,” was adapted from off-the-shelf stent technology—a familiar therapeutic tool for clearing and repairing blood vessels—to include an array of electrodes. The researchers also addressed the dual challenge of making the device flexible enough to safely pass through curving blood vessels, yet stiff enough that the array can emerge from the delivery tube at its destination.