Technologists envisage an electronically interconnected future that will depend on cheap, lightweight, flexible devices. Efforts to optimize the semiconductor materials needed for these electronic devices are therefore necessary. Researchers from the University of Tsukuba have reported a record-breaking germanium (Ge) thin film on a plastic substrate that offers flexibility without compromising performance. Their findings are published in ACS Applied Electronic Materials.
Ge is a popular semiconductor for use in transistors because it has high charge carrier mobility (charge carrier refers to the electrons and electron holes that move through the material). Ge can also be processed at the relatively low temperature of ~500 degrees Celsius and has a low Young’s modulus, which means it is a softer alternative to commonly used materials such as silicon.
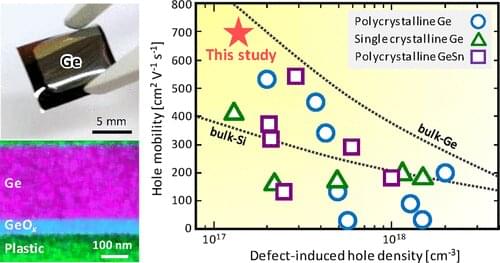
Ge thin films can be grown using the solid-phase crystallization technique. These thin films are polycrystalline, meaning they are made up of many Ge crystals. In general, larger crystals lead to greater carrier mobilities because bigger crystals form fewer grain boundaries that obstruct the current. Recent increases in grain size have therefore led to effective Ge thin-film transistors on rigid substrates such as glass.