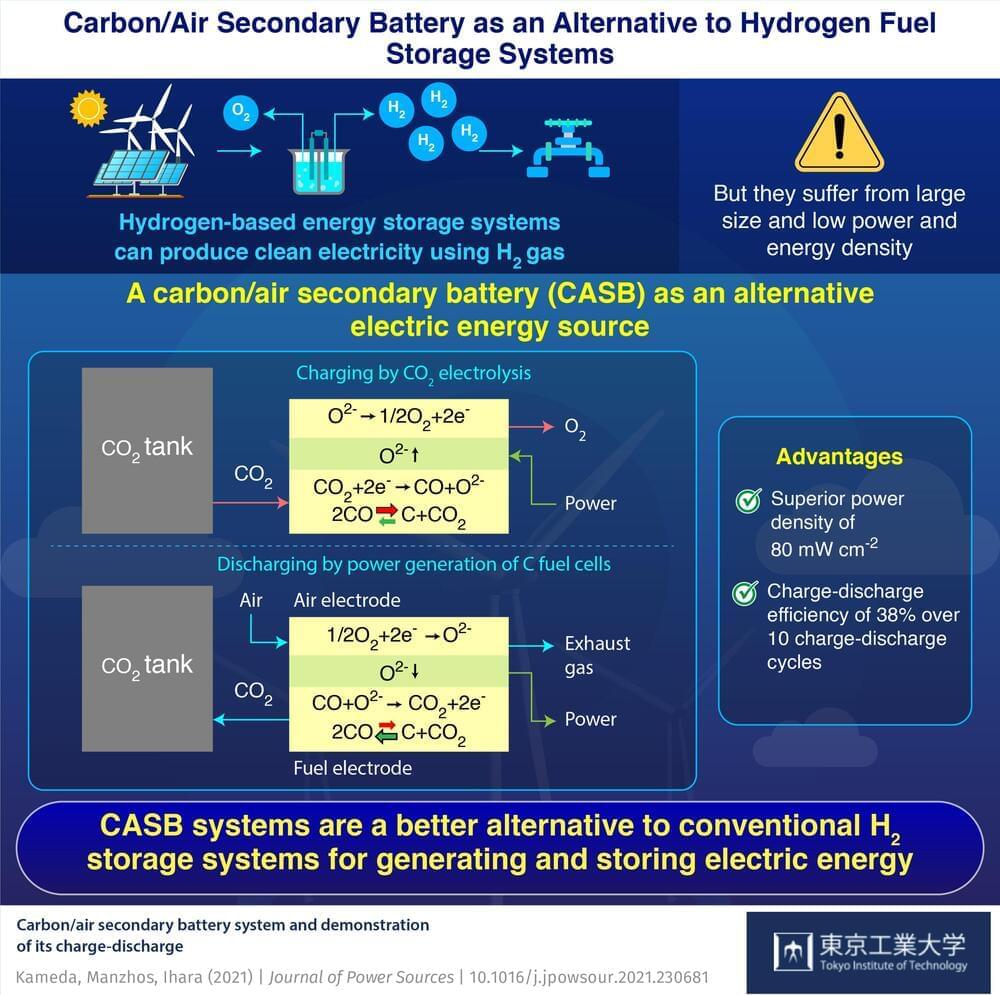
One of the barriers to generating electricity from wind and solar energy is their intermittent nature. A promising alternative to accommodate the fluctuations in power output during unfavorable environmental conditions are hydrogen storage systems, which use hydrogen produced from water splitting to generate clean electricity. However, these systems suffer from poor efficiency and often need to be large in size to compensate for it. This, in turn, makes for complex thermal management and a lowered energy and power density.
In a study published in Journal of Power Sources, researchers from Tokyo Tech have now proposed an alternative electric energy storage system that utilizes carbon © as an energy source instead of hydrogen. The new system, called a “carbon/air secondary battery (CASB),” consists of a solid-oxide fuel and electrolysis cell (SOFC/ECs) where carbon generated via electrolysis of carbon dioxide (CO2), is oxidized with air to produce energy. The SOFC/ECs can be supplied with compressed liquefied CO2 to make up the energy storage system.
“Similar to a battery, the CASB is charged using the energy generated by the renewable sources to reduce CO2 to C. During the subsequent discharge phase, the C is oxidized to generate energy,” explains Prof. Manabu Ihara from Tokyo Tech.