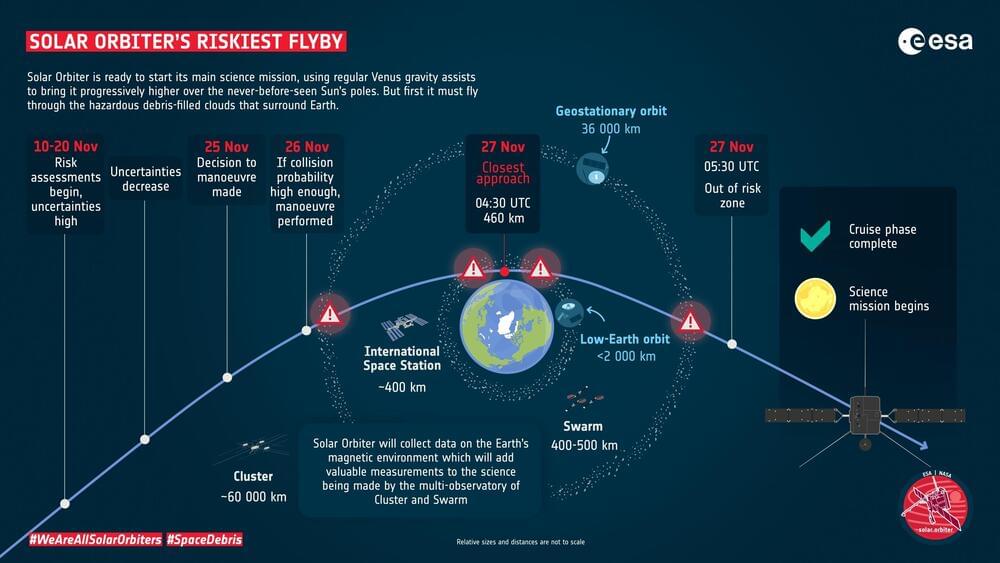
The chance that ESA’s Solar Orbiter spacecraft will encounter space debris during its upcoming Earth flyby is very, very low. However, the risk is not zero and is greater than any other flyby ESA has performed. That there is this risk at all highlights the mess we’ve made of space—and why we need to take action to clean up after ourselves.
On 27 November, after a year and eight months flying through the inner Solar System, Solar Orbiter will swing by home to ‘drop off’ some extra energy. This will line the spacecraft up for its next six flybys of Venus. These final gravity assists will hone and tilt Solar Orbiter’s orbit, enabling the heat-protected probe to capture the first-ever direct images of our star’s poles, and much more.