Free-space optical communication, the communication between two devices at a distance using light to carry information, is a highly promising system for achieving high-speed communication. This system of communication is known to be immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI), a disturbance generated by external sources that affects electrical circuits and can disrupt radio signals.
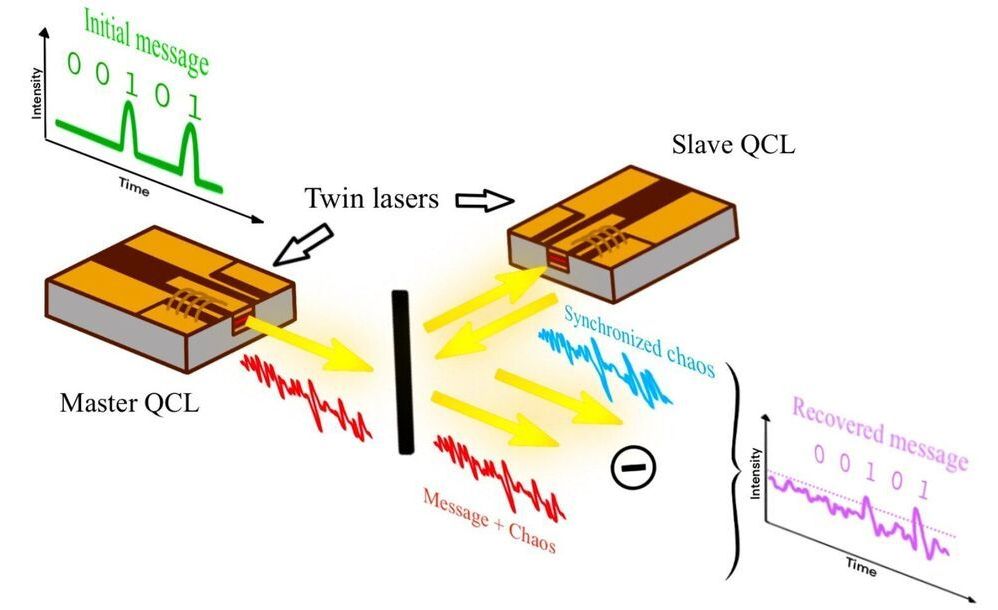
While some studies have highlighted the possible advantages of free-space optical communication, this system of communication has so far come with certain limitations. Most notably, it is known to offer limited security against eavesdroppers. Researchers at Télécom Paris (member of Institut Polytechnique de Paris), mirSense, Technische Universität Darmstadt and University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) have recently introduced a unique system for more secure free-space optical communication based on a technology known as quantum cascade laser, a specific type of semiconductor laser that typically emits mid–infrared light.
“The core idea behind our research is that private free-space communication with quantum key distribution (i.e., based on quantum physics properties) is promising, but it is probably years away, or even further,” Olivier Spitz, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “Currently, the main limitations of this technology are the requirements for cryogenic systems, very slow data rates and costly equipment.”