Multi-resistant pathogens are a serious and increasing problem in today’s medicine. Where antibiotics are ineffective, these bacteria can cause life-threatening infections. Researchers at Empa and ETH Zurich are currently developing nanoparticles that can be used to detect and kill multi-resistant pathogens that hide inside our body cells. The team published the study in the current issue of the journal Nanoscale (“Inorganic nanohybrids combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria hiding within human macrophages”).
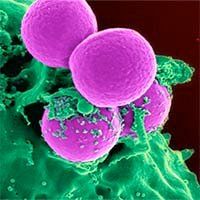
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are being swallowed by a human white blood cell. Colorized, scanning electron microscopic (SEM) image. (Image: CDC/NIAID)
In the arms race “mankind against bacteria”, bacteria are currently ahead of us. Our former miracle weapons, antibiotics, are failing more and more frequently when germs use tricky maneuvers to protect themselves from the effects of these drugs. Some species even retreat into the inside of human cells, where they remain “invisible” to the immune system. These particularly dreaded pathogens include multi-resistant staphylococci (MRSA), which can cause life-threatening diseases such as sepsis or pneumonia.