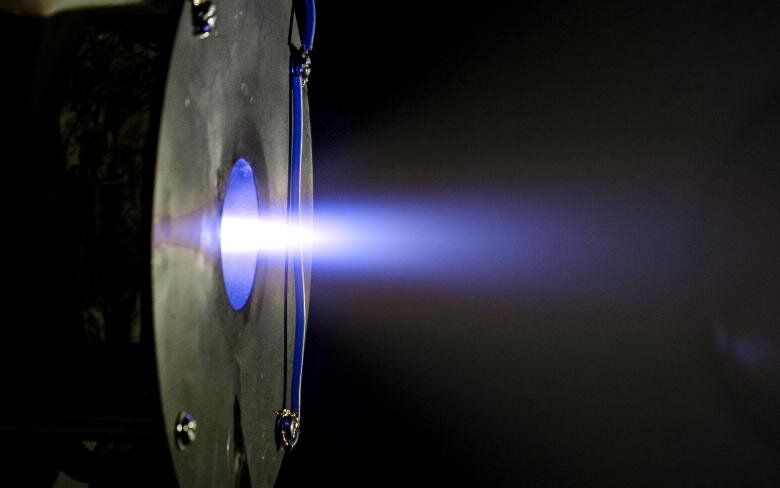
A test firing of Europe’s Helicon Plasma Thruster, developed with ESA by SENER and the Universidad Carlos III’s Plasma & Space Propulsion Team (EP2-UC3M) in Spain. This compact, electrodeless and low voltage design is ideal for the propulsion of small satellites, including maintaining the formation of large orbital constellations.
While traditional chemical propulsion have fundamental upper limits, electric propulsion pumps extra energy into the thrust reaction to reach much higher propellant velocities by accelerating propellant using electrical energy. There are many methods of electric propulsion, many of which require electrodes to apply a current, increasing thruster cost and complexity.
By contrast the Helicon Plasma Thruster uses high power radio frequency waves to excite the propellant into a plasma.