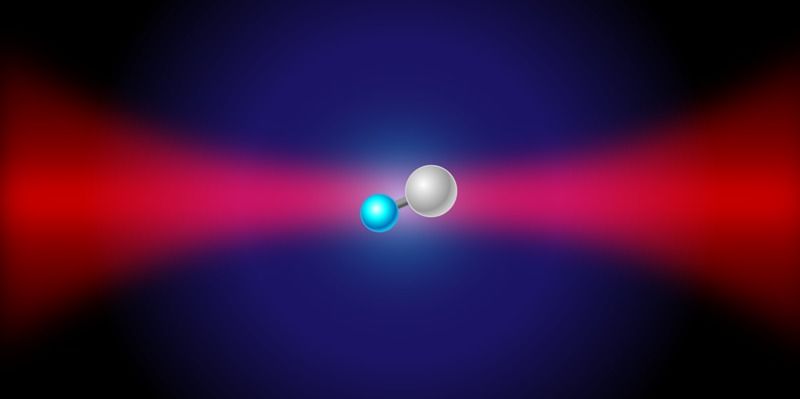
Researchers have created a molecule in a single, precisely characterized quantum state by merging two carefully prepared atoms.
Researchers have demonstrated a quantum molecular assembler—a device that takes individual atoms as inputs and merges them into a molecule in a desired quantum state. The team used lasers to trap and cool one sodium (Na) atom and one cesium (Cs) atom, bring them together, and merge them into an NaCs molecule in a specific quantum state. Such a quantum-controlled molecule is a promising building block for quantum computers and could help researchers study the quantum details of chemical reactions.