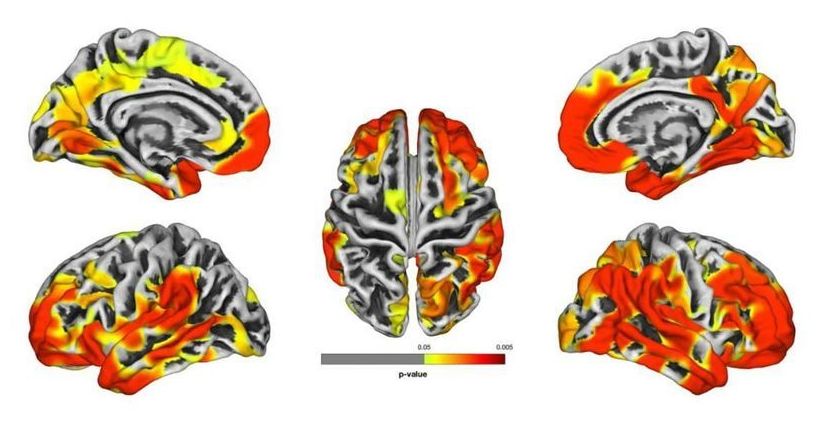
Summary: First responders at the World Trade Center have reduced cortical gray matter thickness, which was consistent with neurodegenerative conditions and evidence their brain age is, on average, ten years older than those of similar ages in the general population.
Source: Stony Brook University
Two studies led by Stony Brook University researchers to be presented virtually at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference on July 28, 2020, indicate that World Trade Center (WTC) first responders are at risk for developing dementia. The studies included individuals with signs of cognitive impairment (CI) who show neuroradiological abnormalities and changes in their blood similar to that seen in Alzheimer’s disease patients and those with related dementias.