Hokkaido University researchers have found a soft and wet material that can memorize, retrieve, and forget information, much like the human brain. They report their findings in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
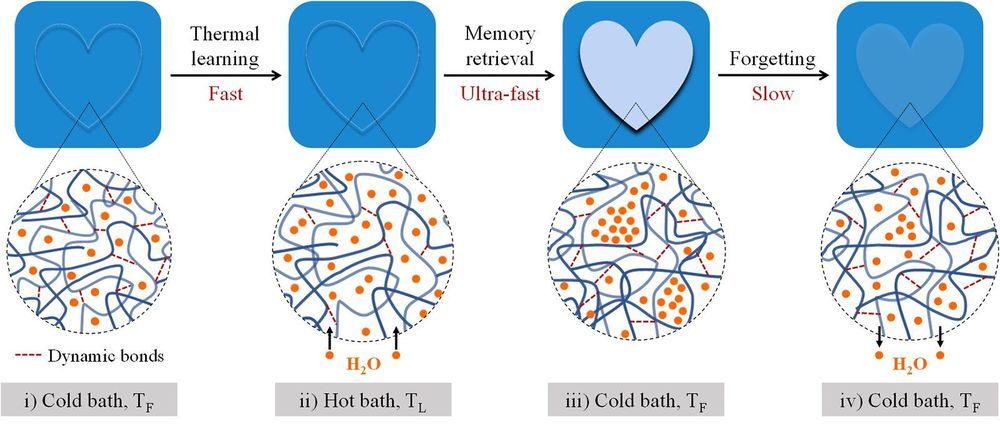
The human brain learns things, but tends to forget them when the information is no longer important. Recreating this dynamic memory process in manmade materials has been a challenge. Hokkaido University researchers now report a hydrogel that mimics the dynamic memory function of the brain: encoding information that fades with time depending on the memory intensity.
Hydrogels are flexible materials composed of a large percentage of water—in this case about 45%—along with other chemicals that provide a scaffold-like structure to contain the water. Professor Jian Ping Gong, Assistant Professor Kunpeng Cui and their students and colleagues in Hokkaido University’s Institute for Chemical Reaction Design and Discovery (WPI-ICReDD) are seeking to develop hydrogels that can serve biological functions.