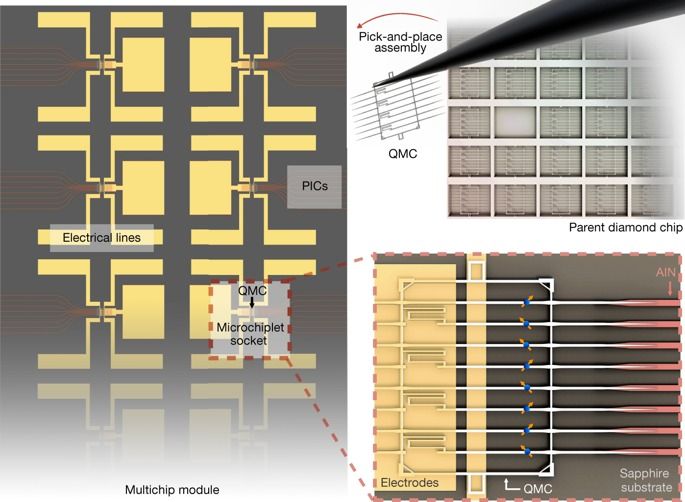
A central challenge in developing quantum computers and long-range quantum networks is the distribution of entanglement across many individually controllable qubits1. Colour centres in diamond have emerged as leading solid-state ‘artificial atom’ qubits2,3 because they enable on-demand remote entanglement4, coherent control of over ten ancillae qubits with minute-long coherence times5 and memory-enhanced quantum communication6. A critical next step is to integrate large numbers of artificial atoms with photonic architectures to enable large-scale quantum information processing systems. So far, these efforts have been stymied by qubit inhomogeneities, low device yield and complex device requirements. Here we introduce a process for the high-yield heterogeneous integration of ‘quantum microchiplets’—diamond waveguide arrays containing highly coherent colour centres—on a photonic integrated circuit (PIC). We use this process to realize a 128-channel, defect-free array of germanium-vacancy and silicon-vacancy colour centres in an aluminium nitride PIC. Photoluminescence spectroscopy reveals long-term, stable and narrow average optical linewidths of 54 megahertz (146 megahertz) for germanium-vacancy (silicon-vacancy) emitters, close to the lifetime-limited linewidth of 32 megahertz (93 megahertz). We show that inhomogeneities of individual colour centre optical transitions can be compensated in situ by integrated tuning over 50 gigahertz without linewidth degradation. The ability to assemble large numbers of nearly indistinguishable and tunable artificial atoms into phase-stable PICs marks a key step towards multiplexed quantum repeaters7,8 and general-purpose quantum processors9,10,11,12.