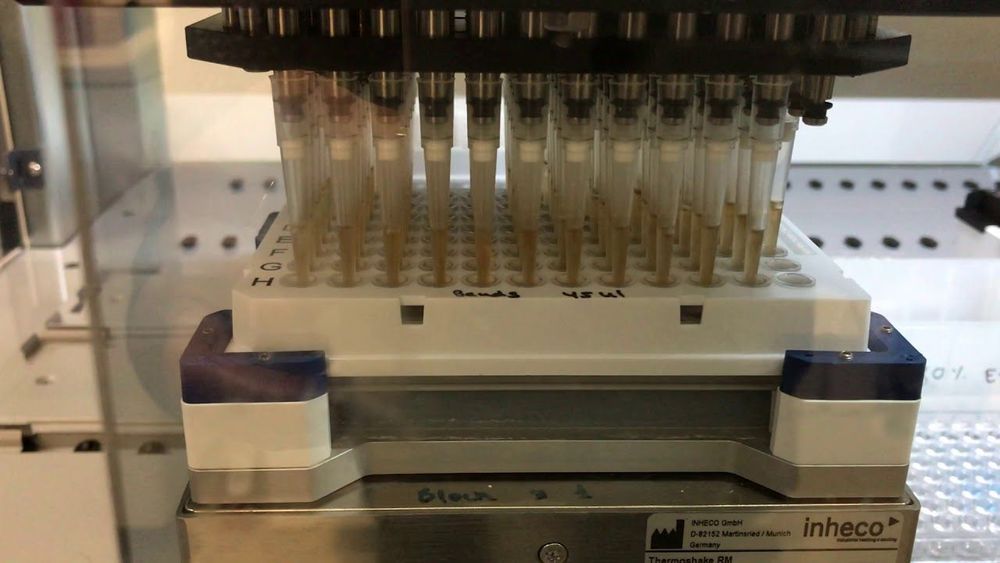
Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem announced on Sunday that they have developed a new method of testing for COVID-19 which is not only 4–10 times faster than the tests most commonly used today, but also significantly cheaper, while supplying the same level of accuracy. Moreover, most of the materials required to perform the new test are already available in Israel, easing significantly both the country’s dire shortage of testing materials and its heavy economic dependence on foreign commercial markets. The method was developed in the labs of Prof. Nir Friedman of the Institute of Life Sciences and the School of Engineering and Computer Sciences and Dr. Naomi Haviv of Hebrew University’s Neuroscience Research Center, and is based on materials which are not affected by global shortages and can be recycled for repeated used on future tests. The method commonly used today for COVID-19 testing involves extracting RNA molecules from a patient’s sample to determine if the molecules produced have viral RNA within them, which confirms the presence of the coronavirus. The new test developed by the researchers performs the same action, but is made from more commonly attainable materials, that produce results at a much higher speed. Dr. Naomi Haviv said that “We have an efficient RNA extraction method, 4–10 times faster than the current method. It is based on magnetic beads and can be performed both robotically and manually.”
Other than the magnetic beads, all of the other materials needed to perform the tests are available for purchase in Israel. The beads themselves are recyclable and can be reused to perform future tests. “The robotic method has already undergone a series of tests at Hadassah Hospital, using hundreds of samples from patients — and is now becoming operational.”
The new test would supply results 4–10 times faster than the current method, and is made almost entirely from materials which are easily available for purchase within the country.