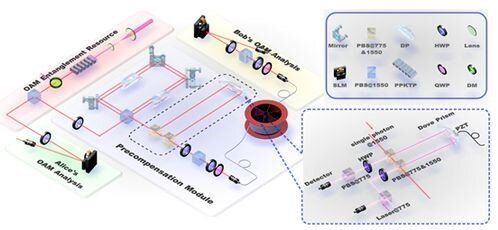
A team led by Prof. Guo Guangcan from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and collaborators first realized distribution of high-dimensional orbital angular momentum entanglement over a 1 km few-mode fiber. The result is published in Optica.
Increasing the channel capacity and tolerance to noise in quantum communications is a strong practical motivation for encoding quantum information in multilevel systems, qudits as opposed to qubits. From a foundational perspective, entanglement in higher dimensions exhibits more complex structures and stronger non-classical correlations. High-dimensional entanglement has demonstrated its potential for increasing channel capacity and resistance to noise in quantum information processing. Despite these benefits, the distribution of high-dimensional entanglement is relatively new and remains challenging.
The orbital angular momentum of photon is a high dimensional system which has been paid much attention to in recent years. However, orbital angular momentum entanglement is susceptible to atmospheric turbulence or mode crosstalk and mode dispersion in optical fibers. It can only transmit a few meters, and is limited to two-dimensional entanglement distribution.