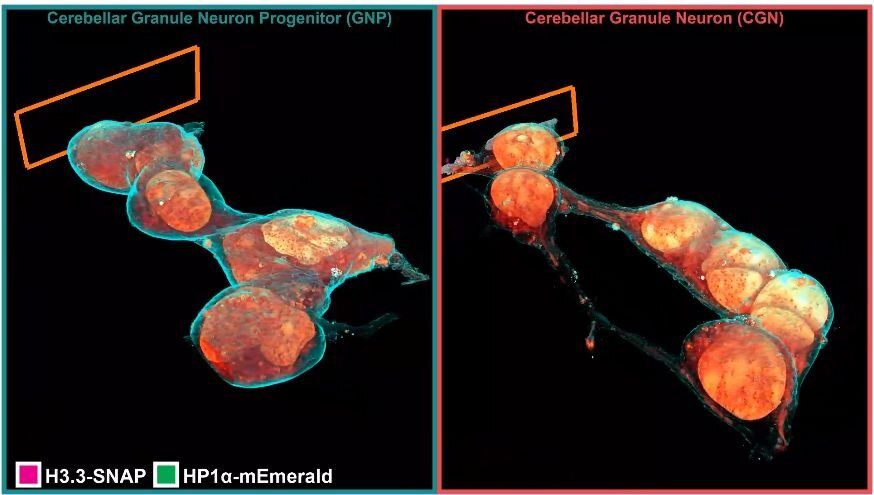
Inside a cell, tentacled vesicles shuttle cargo for sorting. DNA rearranges in the nucleus as stem cells differentiate into neurons. Neighboring neurons cling to one another through a web-like interface. And a new microscopy technique shows it all, in exquisite detail.
The technique, called cryo-SR/EM, melds images captured from electron microscopes and super-resolution light microscopes, resulting in brilliant, clear detailed views of the inside of cells—in 3D.
For years, scientists have probed the microscopic world inside cells, developing new tools to view these basic units of life. But each tool comes with a tradeoff. Light microscopy makes it simple to identify specific cellular structures by tagging them with easy-to-see fluorescent molecules. With the development of super-resolution (SR) fluorescence microscopy, these structures can be viewed with even greater clarity. But fluorescence can reveal only a few of the more than 10,000 proteins in a cell at a given time, making it difficult to understand how these few relate to everything else. Electron microscopy (EM), on the other hand, reveals all cellular structures in high-resolution pictures—but delineating one feature from all others by EM alone can be difficult because the space inside of cells is so crowded.