Here’s what you need to know about the United Arab Emirates’ first interplanetary spacecraft, the Hope mission to Mars.
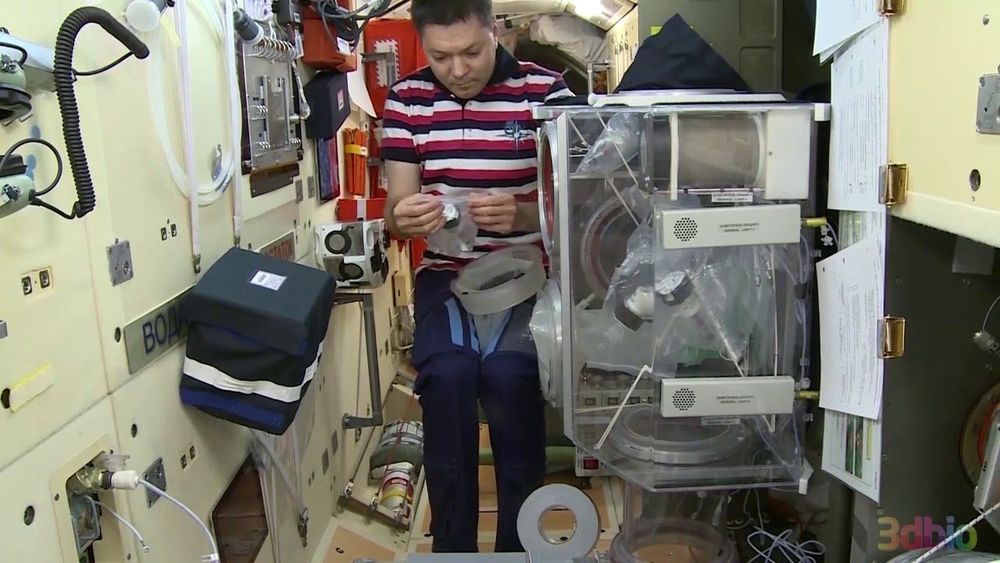



One small step for cells, one giant leap for science.
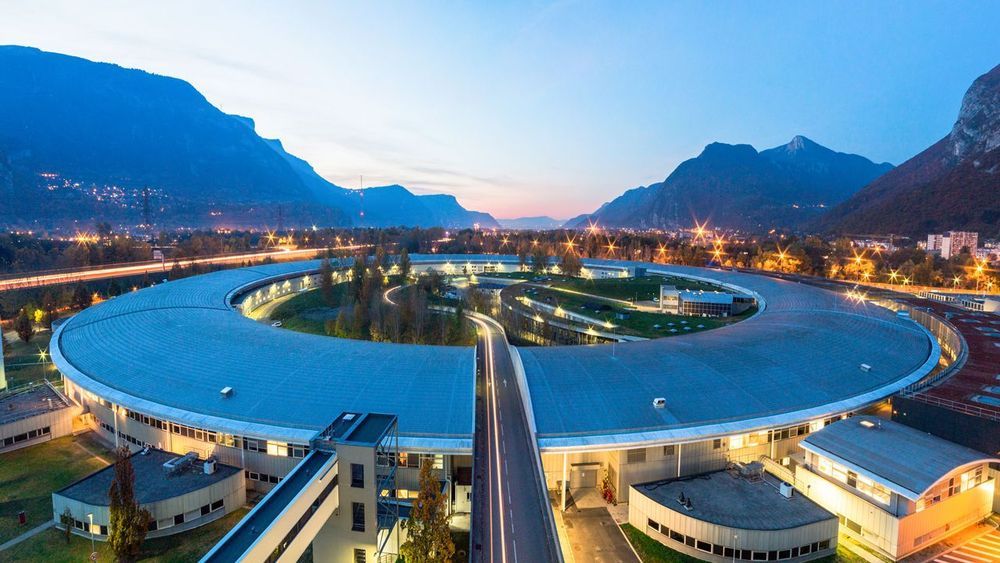

A brilliant new light shines in Grenoble, France, where officials at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility(ESRF) last week announced the reopening of their completely rebuilt x-ray source. The ring-shaped machine, 844 meters around, generates x-ray beams 100 times brighter than its predecessor and 10 trillion times brighter than medical x-rays. The intense radiation could open up new vistas in x-ray science, such as imaging whole organs in three dimensions while resolving individual cells.
Shining 100 times brighter than its predecessor, the new European Synchrotron Radiation Facility is the first of more than a dozen of its kind in the works.
The snake bites its tail
Google AI can independently discover AI methods.
Then optimizes them
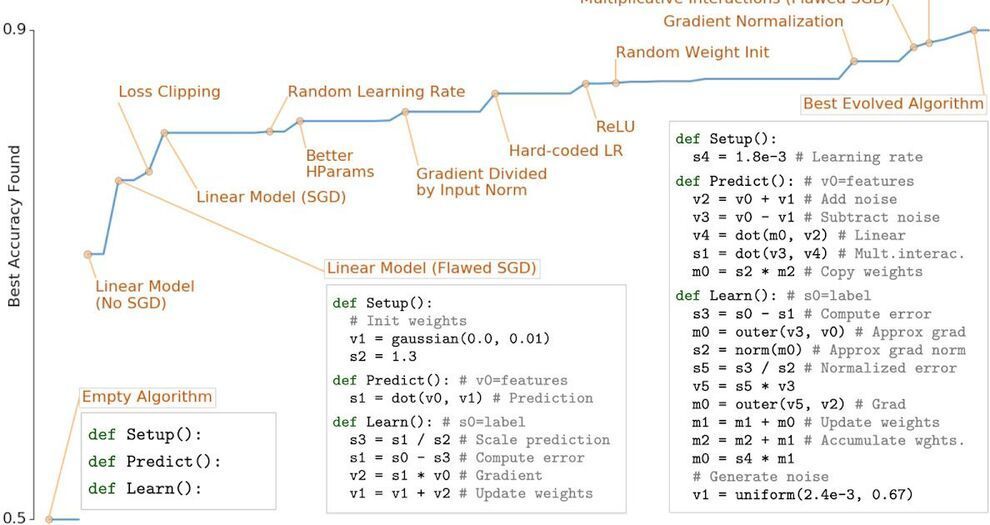
It Evolves algorithms from scratch—using only basic mathematical operations—rediscovering fundamental ML techniques & showing the potential to discover novel algorithms.
AutoML-Zero: new research that that can rediscover fundamental ML techniques by searching a space of different ways of combining basic mathematical operations. Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.
Machine learning (ML) has seen tremendous successes recently, which were made possible by ML algorithms like deep neural networks that were discovered through years of expert research. The difficulty involved in this research fueled AutoML, a field that aims to automate the design of ML algorithms. So far, AutoML has focused on constructing solutions by combining sophisticated hand-designed components. A typical example is that of neural architecture search, a subfield in which one builds neural networks automatically out of complex layers (e.g., convolutions, batch-norm, and dropout), and the topic of much research.
An alternative approach to using these hand-designed components in AutoML is to search for entire algorithms from scratch. This is challenging because it requires the exploration of vast and sparse search spaces, yet it has great potential benefits — it is not biased toward what we already know and potentially allows for the discovery of new and better ML architectures. By analogy, if one were building a house from scratch, there is more potential for flexibility or improvement than if one was constructing a house using only prefabricated rooms. However, the discovery of such housing designs may be more difficult because there are many more possible ways to combine the bricks and mortar than there are of combining pre-made designs of entire rooms. As such, early research into algorithm learning from scratch focused on one aspect of the algorithm, to reduce the search space and compute required, such as the learning rule, and has not been revisited much since the early 90s. Until now.
Extending our research into evolutionary AutoML, our recent paper, to be published at ICML 2020, demonstrates that it is possible to successfully evolve ML algorithms from scratch. The approach we propose, called AutoML-Zero, starts from empty programs and, using only basic mathematical operations as building blocks, applies evolutionary methods to automatically find the code for complete ML algorithms. Given small image classification problems, our method rediscovered fundamental ML techniques, such as 2-layer neural networks with backpropagation, linear regression and the like, which have been invented by researchers throughout the years. This result demonstrates the plausibility of automatically discovering more novel ML algorithms to address harder problems in the future.

(Reuters) — Nearly a third of more than 40 large companies seeking U.S. bankruptcy protection during the coronavirus pandemic awarded bonuses to executives within a month of filing their cases, according to a Reuters analysis of securities filings and court records.
Under a 2005 bankruptcy law, companies are banned, with few exceptions, from paying executives retention bonuses while in bankruptcy. But the firms seized on a loophole by granting payouts before filing.
Six of the 14 companies that approved bonuses within a month of their filings cited business challenges executives faced during the pandemic in justifying the compensation.

So, you’ve set aside a chunk of change to build a new gaming PC and are just waiting for AMD and Nvidia to launch their next-gen GPUs, is that it? A solid plan, except for one thing—your next build is already obsolete. That’s because whatever you spec’d out is undoubtedly sitting on an AMD or Intel foundation, and didn’t you hear, x86 computing is basically dead. Finished. Kaput. We’re on the cusp of the end of an era, and all because Apple is dumping Intel for ARM.
Okay, maybe not, but that’s essentially the case made by Jean-Louis Gassée, a former Apple executive who led the development of Mac computers in the late 1980s. In no uncertain terms, he says Apple’s decision to phase out Intel CPUs in favor of its own silicon based on ARM will force “PC OEMs to reconsider their allegiance to x86 silicon…and that will have serious consequences for the old Wintel partnership.”

Do you agree with these predictions?
The first few months of 2020 have radically reshaped the way we work and how the world gets things done. While the wide use of robotaxis or self-driving freight trucks isn’t yet in place, the Covid-19 pandemic has hurried the introduction of artificial intelligence across all industries. Whether through outbreak tracing or contactless customer pay interactions, the impact has been immediate, but it also provides a window into what’s to come. The second annual Forbes’ AI 50, which highlights the most promising U.S.-based artificial intelligence companies, features a group of founders who are already pondering what their space will look like in the future, though all agree that Covid-19 has permanently accelerated or altered the spread of AI.
“We have seen two years of digital transformation in the course of the last two months,” Abnormal Security CEO Evan Reiser told Forbes in May. As more parts of a company are forced to move online, Reiser expects to see AI being put to use to help businesses analyze the newly available data or to increase efficiency.
With artificial intelligence becoming ubiquitous in our daily lives, DeepMap CEO James Wu believes people will abandon the common misconception that AI is a threat to humanity. “We will see a shift in public sentiment from ‘AI is dangerous’ to ‘AI makes the world safer,’” he says. “AI will become associated with safety while human contact will become associated with danger.”
