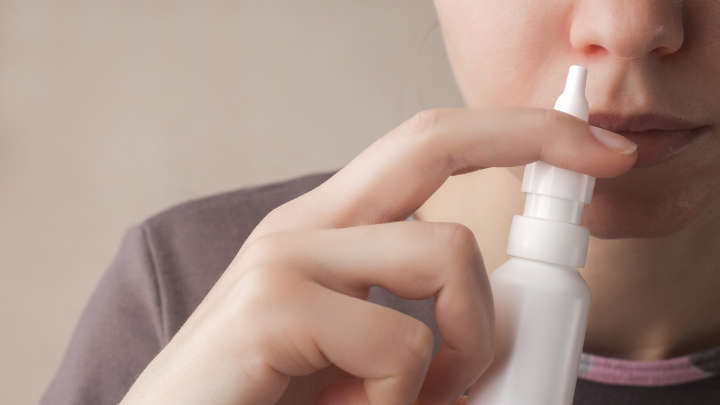
A nasal spray that could alleviate symptoms of depression in just a few hours has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) – though the decision has attracted its share of criticism and controversy. The new drug, called esketamine, is a molecular variation of ketamine, which is already being used as an anesthetic, an antidepressant, and a party drug.
Esketamine will be sold as a spray called Spravato and is intended for patients with treatment-resistant depression, meaning they have failed to respond to at least two other types of antidepressant. Because of ketamine’s mind-altering effects and high potential for abuse, patients will be required to take Esketamine in a doctor’s office or clinic and remain under medical supervision for two hours after administration.
Most people with a diagnosis of depression are prescribed selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as Prozac. These ensure that neurons have access to an increased amount of the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is a key emotional regulator. However, it is thought that around one-third of people with major depressive disorder (MDD) do not respond to conventional medications for the condition, which is why researchers are hunting for alternative treatments.
Read more