Stories are equipment for living. But our equipment is obsolete. We must upgrade or go obsolete too. “ReWriting the Human Story” is my proposal to do that.
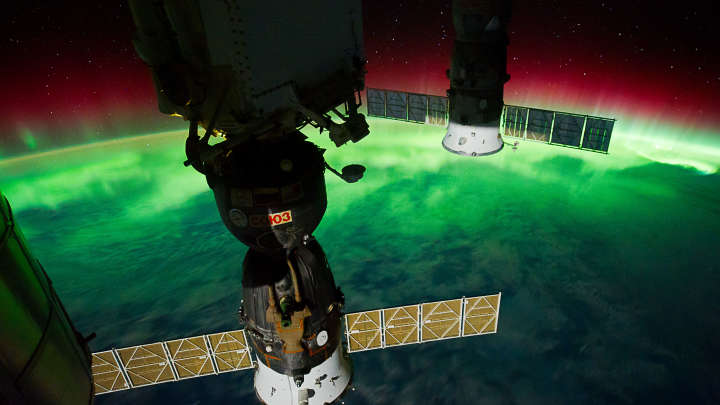



There’s a renewed interest right now in Earth’s magnetic poles – specifically, whether or not they’re about to flip, and what may happen. The consequences of this seemingly rapid geomagnetic backflip may sound a little ominous, but don’t worry: we’re not sure when the next reversal will happen, and even when it does, the risks aren’t likely to be as scary as you may think.
Let’s start with the basics.
As Earth’s liquid, iron-rich outer core gradually cools, it sloshes around through colossal convection currents, which are also somewhat warped by Earth’s own rotation. Thanks to a quirk of physics known as the dynamo theory, this generates a powerful magnetic field, with a north and south end.
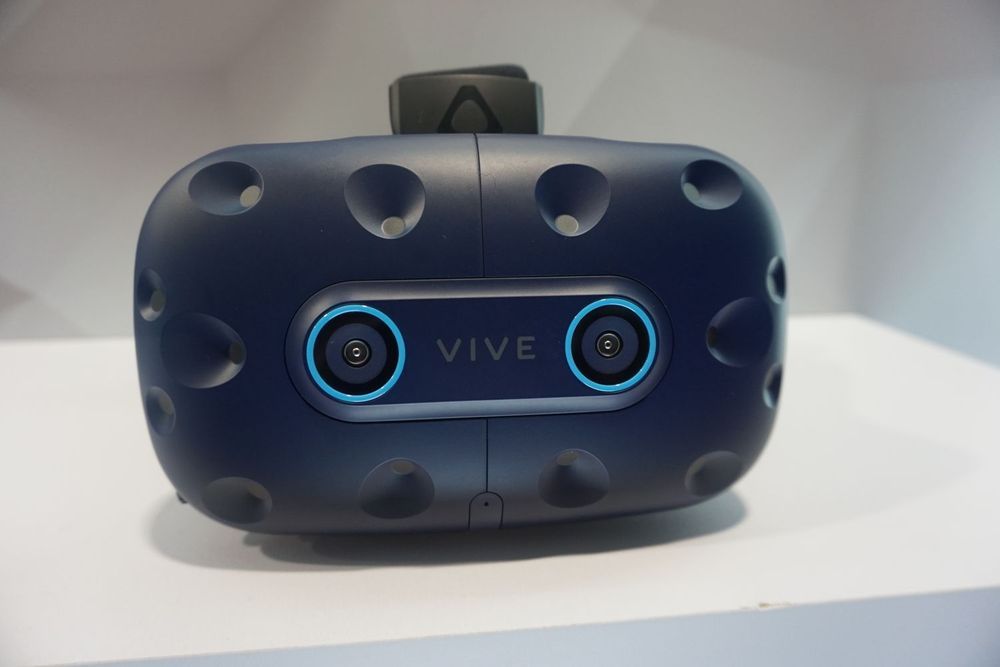


Hands are old news. VR navigation, control and selection is best done with the eyes—at least that’s what HTC Vive is banking on with the upcoming HTC Vive Pro Eye, a VR headset with integrated Tobii eye tracking initially targeting businesses. I tried out a beta version of the feature myself on MLB Home Run Derby VR. It’s still in development and, thus, was a little wonky, but I can’t deny its cool factor.
HTC announced the new headset Tuesday at the CES tech show in Las Vegas. The idea is that by having eye tracking built into the headset, better use cases, such as enhanced training programs, can be introduced. The VR player also says users can expect faster VR interactions and better efficiency in terms of tapping your PC’s CPU and GPU.
Of course, before my peepers could be tracked I needed to calibrate the headset for my special eyes. It was quite simple, after adjusting the interpupillary distance appropriately, the headset had me stare at a blue dot that bounced around my field of view (FOV). The whole thing took less than a minute.


Circa 2015
Researchers have used an infrared laser to cool water by about 2°C (36°F) — a major breakthrough in the field. As they are cooled by the laser, the nanocrystals developed by the University of Washington team emit a reddish-green ‘glow’ (shown) that can be seen by the naked eye.
‘Typically, when you go to the movies and see Star Wars laser blasters, they heat things up’, senior author and assistant professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Washington Peter Pauzauskie explained.
‘It was really an open question as to whether this could be done because normally water warms when illuminated.’

Magnetic north is not where it used to be.
Since 2015, the place to which a compass points has been sprinting toward Siberia at a pace of more than 30 miles (48 kilometres) a year. And this week, after a delay caused by the month-long partial government shutdown in the United States, humans have finally caught up.
Scientists on Monday released an emergency update to the World Magnetic Model, which cellphone GPS systems and military navigators use to orient themselves.
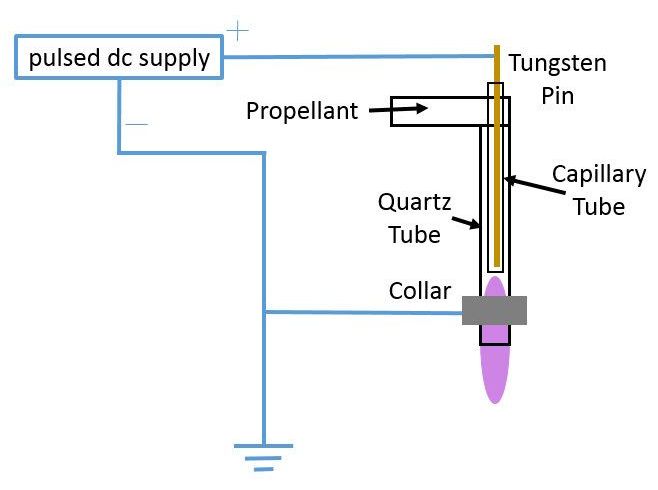
Many of today’s methods of purifying water rely on filters and chemicals that need regular replenishing or maintenance. Millions of people, however, live in areas with limited access to such materials, leading the research community to explore new options of purifying water in using plasmas. Many plasma-based approaches are expensive, but a new class of plasma devices may change that.
Researchers at the University of Alabama in Huntsville have been studying a new type of plasma generator for water purification. The new generator pulses voltage signals to ionize gas at atmospheric pressure and produce many useful byproducts, including hydroxyl radicals, which cause a cascade of reactions that lead to purer water samples.
“We’re finding ways to speed up the purification process,” said Ryan Gott, a doctoral candidate in aerospace engineering at UAH who will present the research next week at the American Physical Society 71st Annual Gaseous Electronics Conference and the 60th Annual meeting of the APS Division of Plasma Physics, which will take place Nov. 5–9 at the Oregon Convention Center in Portland.
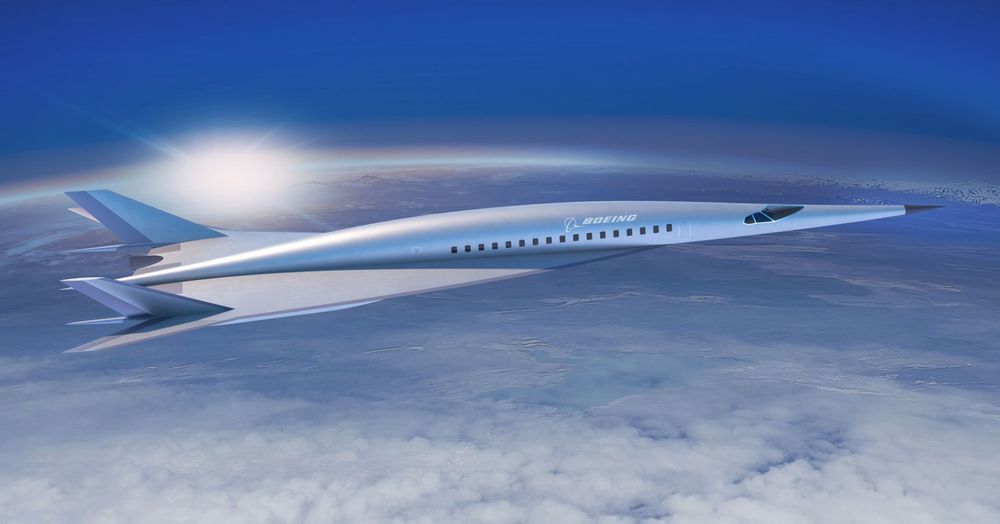

Boeing unveiled a rendering of its first-ever design for a hypersonic passenger plane at an aerospace conference in Atlanta. While the idea and potential of the plane will generate plenty of buzz, this is a concept that is likely decades from being built.
The hypersonic passenger plane could, in theory, fly as fast as Mach 5, or just under 3,900 miles per hour. That would allow the plane to carry passengers between Los Angeles and Tokyo in roughly three hours. A flight from New York to London could be as quick as two hours. Right now, those flights take about 11 hours and 7 hours, respectively.
Boeing CEO Dennis Muilenburg is pushing the aerospace giant to explore the potential of ultra-fast passenger planes.