The research paves the way for brain implants that would translate the thoughts of people who have lost power of speech.
Ian Sample, science correspondent.

The research paves the way for brain implants that would translate the thoughts of people who have lost power of speech.
Ian Sample, science correspondent.

Some of the strongest materials to build with are titanium alloys but they are not only expensive but heavy as well. Researchers at the University of Maryland (UMD) have used a new densification process to make super wood that has the same strength and toughness as steel.
Wood is probably the most used construction material already and the UMD team is working to make it even more useful. Liangbing Hu is leading the team responsible for developing the super wood. The researchers first boil samples of wood in a watery mixture of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfite, which partially removes lignin and hemicellulose from the material. This wood is then hot-pressed causing the cell walls to collapse and form highly-aligned cellulose nanofibers. This gives rise to densified wood, which is stronger than natural wood.

But that doesn’t mean the company isn’t working on cool new features. During the earnings call, Tesla CEO Elon Musk said that within three to six months, he expects Tesla cars to be able to drive autonomously from U.S. coast to coast.
SEE ALSO: Tesla’s bringing Powerwall batteries to 50,000 homes in Australia
Musk originally promised this in Oct. 2016, which is when the company also showed a video of a Tesla car driving itself to work without human intervention. But that was just after the company ended its partnership with Mobileye, the developer of the original self-driving system for Tesla cars, and switched to a system built in-house. It took quite a while for Tesla’s technology to catch up with what Mobileye had built.


A new study by researchers at Ohio University found that vitamin D3 – a vitamin that is naturally produced when skin is exposed to sunlight – could prevent and restore damage caused by several cardiovascular diseases, including diabetes, hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Credit: polaris50d/Shutterstock.com
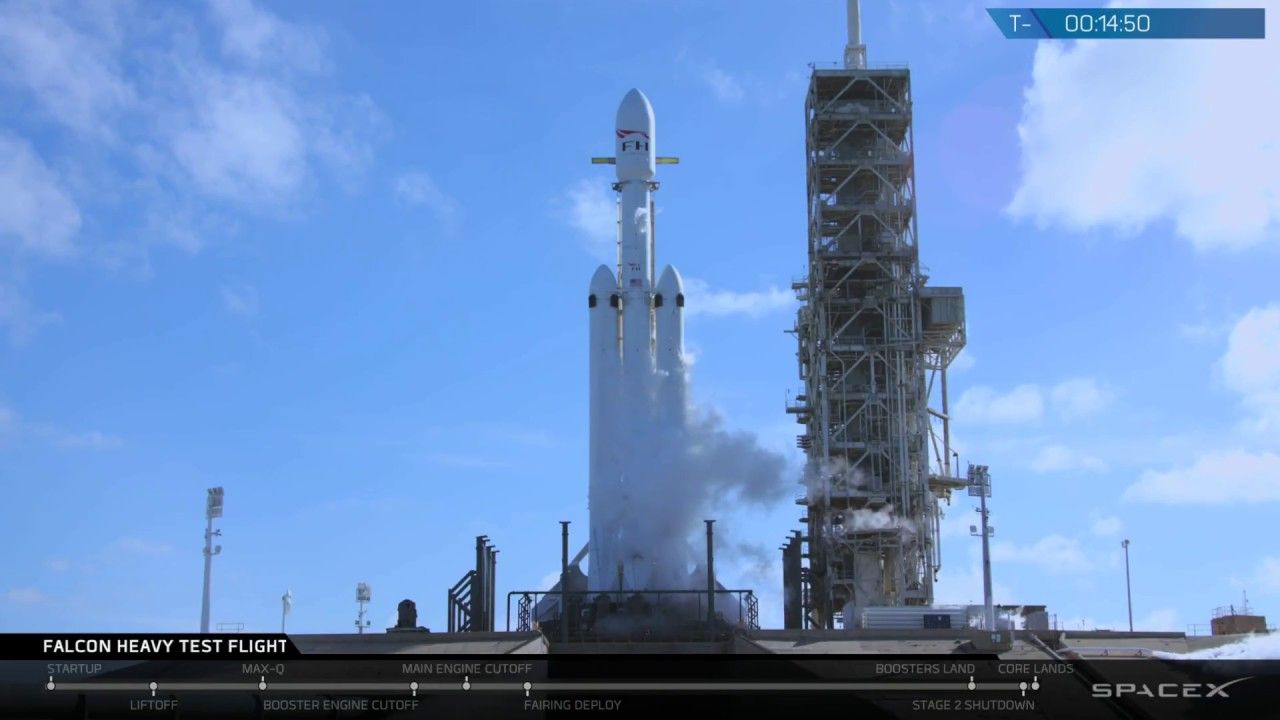

The Falcon Heavy is finally on its way to mars and this rocket has had its fair share of delays. Elon Musk gave us a first glimpse of the rocket a couple of months ago and then a little later announced the unique cargo that it would be carrying. At the start of this year, he announced that the rocket will be launched within the first month but there were more unexpected delays and things finally got back on track as it completed the static test last week.
The Falcon Heavy Rocket launched its test flight successfully from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Millions of fans from all around the globe watched the launch go off without a hitch. The Falcon Heavy has 27 engines which give a thrust equal to 18 Boeing (BA) 747 jetliners making it the biggest rocket ever made. “It’s the biggest rocket in the world by far,” SpaceX CEO Musk told CNN’s Rachel Crane on Monday.
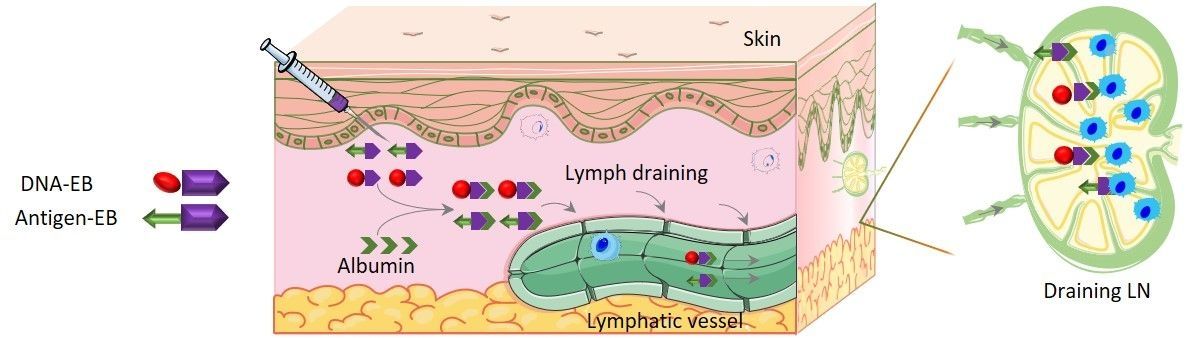
Cancer fighting nanovaccines have shown significant promise, but clinical application has been hampered by complications in large-scale manufacturing, quality control, and safety. Biomedical engineers at the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) developed a new technology that enables nanovaccines to bind to the albumin protein naturally present in the body. The albumin protein then delivers these nanocomplexes to the lymph nodes, resulting in potent immune activation against multiple tumor types in mouse cancer models. The use of natural albumin as a universal vaccine shuttle is a significant step towards the application of cancer nanovaccine immunotherapy in humans.
Nanovaccines that work to mount an immune response against a tumor basically consist of two components: the part that delivers the vaccine to the correct site, the lymph nodes, where immune system activation happens; and the part that activates the immune cells to expand and specifically target the tumor.

