There is increasing evidence that the microbiome contributes to esophageal disease. Diet, especially fiber and fat intake, is a known potent modifier of the colonic microbiome, but its impact on the esophageal microbiome is not well described. We hypothesized that dietary fiber and fat intake would be associated with a distinct esophageal microbiome.
We collected esophageal samples from 47 ambulatory patients scheduled to undergo endoscopy who completed a validated food frequency questionnaire quantifying dietary fiber and fat intake. Using 16S high-throughput sequencing, we determined composition of the esophageal microbiome and predicted functional capacity of microbiota based on fiber and fat intake.
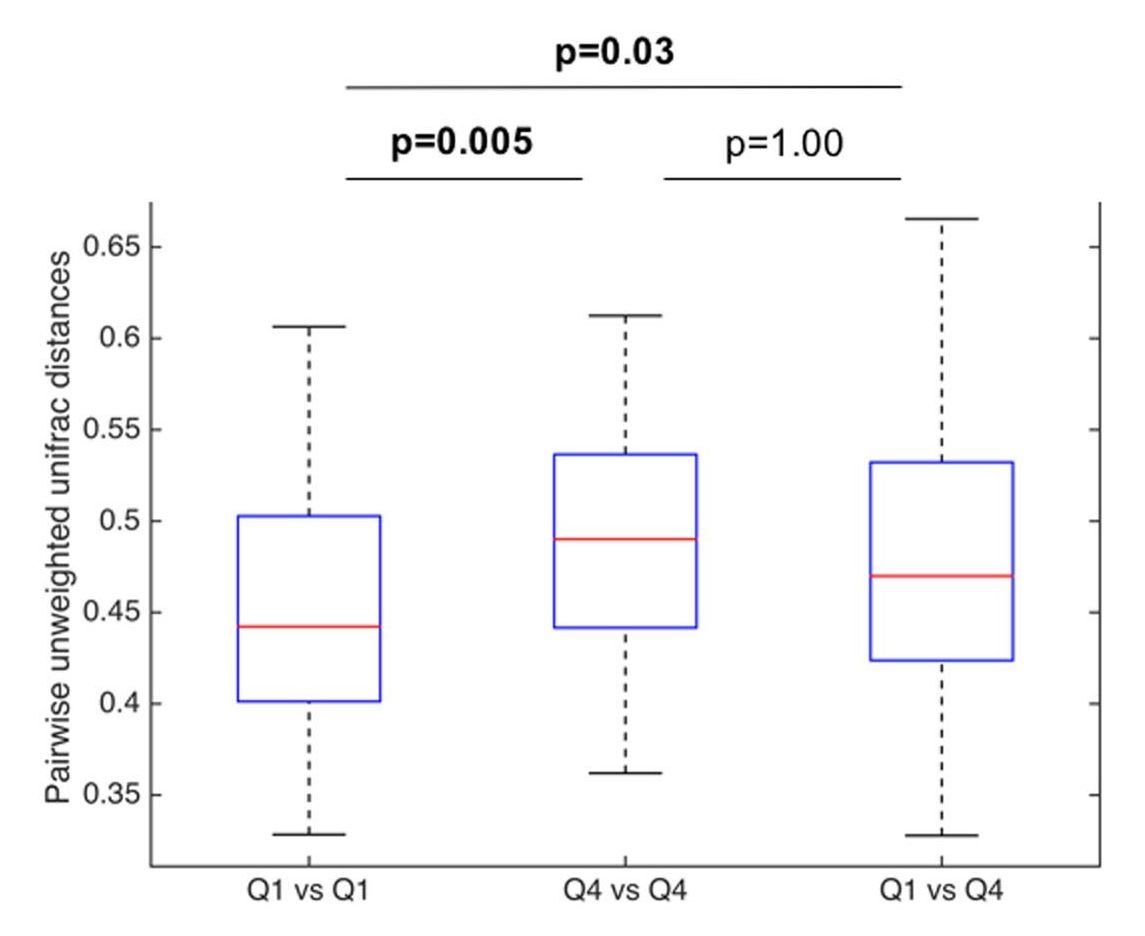
Among all samples, the most abundant phyla were Firmicutes (54.0%), Proteobacteria (19.0%), Bacteroidetes (17.0%), Actinobacteria (5.2%), and Fusobacteria (4.3%). Increasing fiber intake was significantly associated with increasing relative abundance of Firmicutes (p = 0.04) and decreasing relative abundance of Gram-negative bacteria overall (p = 0.03). Low fiber intake was associated with increased relative abundance of several Gram-negative bacteria, including Prevotella, Neisseria, and Eikenella. Several predicted metabolic pathways differed between highest and lowest quartile of fiber intake. Fat intake was associated with altered relative abundance of few taxa, with no alterations at the phylum level and no changes in microbiome functional composition.
Read more