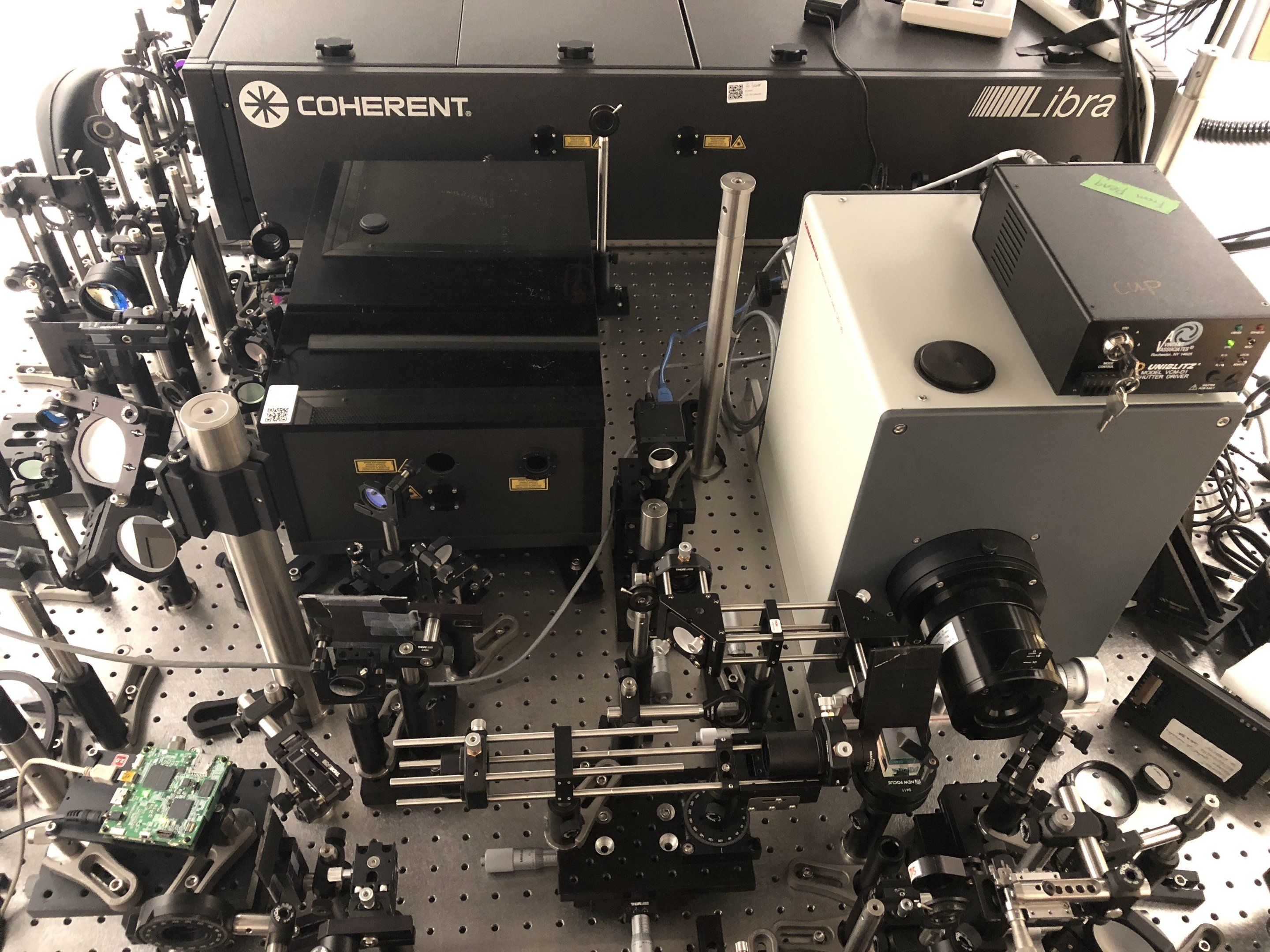
What happens when a new technology is so precise that it operates on a scale beyond our characterization capabilities? For example, the lasers used at INRS produce ultrashort pulses in the femtosecond range (10-15 s), which is far too short to visualize. Although some measurements are possible, nothing beats a clear image, says INRS professor and ultrafast imaging specialist Jinyang Liang. He and his colleagues, led by Caltech’s Lihong Wang, have developed what they call T-CUP: the world’s fastest camera, capable of capturing 10 trillion (1013) frames per second (Fig. 1). This new camera literally makes it possible to freeze time to see phenomena—and even light—in extremely slow motion.
In recent years, the junction between innovations in non-linear optics and imaging has opened the door for new and highly efficient methods for microscopic analysis of dynamic phenomena in biology and physics. But harnessing the potential of these methods requires a way to record images in real time at a very short temporal resolution—in a single exposure.
Using current imaging techniques, measurements taken with ultrashort laser pulses must be repeated many times, which is appropriate for some types of inert samples, but impossible for other more fragile ones. For example, laser-engraved glass can tolerate only a single laser pulse, leaving less than a picosecond to capture the results. In such a case, the imaging technique must be able to capture the entire process in real time.
Read more