Find out more about the leading space tech focused accelerator for European startups:
http://ow.ly/4brj30lxwbG



LEAF’s August 2018 roundup is out!
We hope August has treated you well—it certainly did so for life extension, as this has been another month full of great news for the field. Don’t be upset with the departure of summer and the arrival of autumn, because little by little, we’re getting close to pushing away the autumn of years.
More investments against aging
The fight against aging is being taken more and more seriously by a growing number of investors, who realize the world-changing potential of effective rejuvenative treatments as well as the great opportunity for profit. Juvenescence Limited, which recently closed a 10-million deal with Ichor Therapeutics‘ Antoxerene, has now announced the purchase of 14.4 million shares of BioTime’s AgeX Therapeutics—a company focused on extending healthy human lifespan—for a total of over $43 million. AgeX’s work focuses on telomerase upregulation and cell therapies, and Juvenescence has invested in AgeX before. The news has been reported and commented on on Fight Aging! as well.
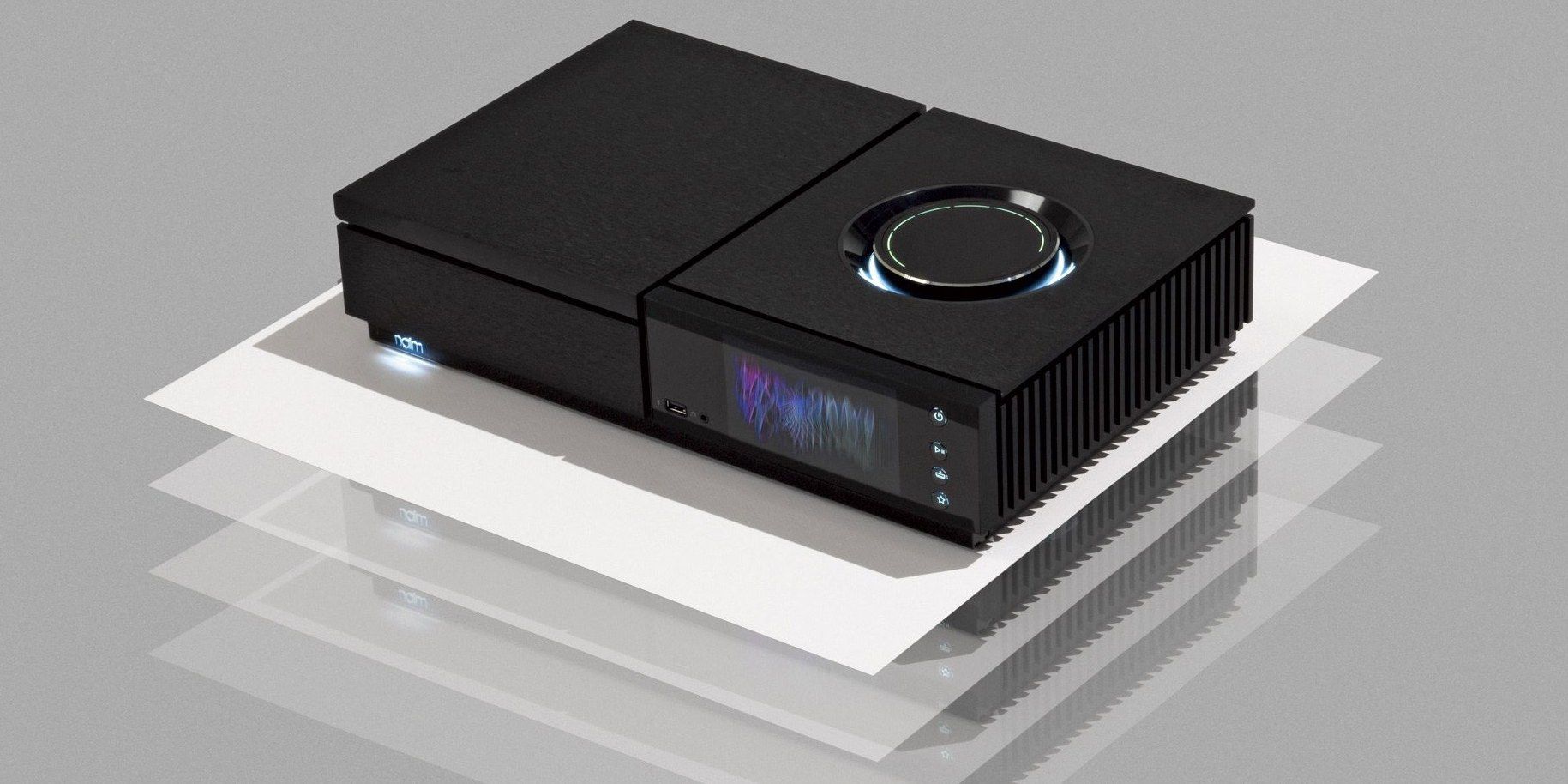


Streaming music doesn’t have to mean compromised sound. These hi-fi amps can help you find cloud-connected aural ecstasy.
1. Naim Audio Uniti Star
Best for: Streamcurious audiophiles.
With a built-in CD player that rips tracks to a local drive, the Uniti Star eases the pain of parting with your CDs. Naim’s app summons your newly captured tunes and streams hi-res songs from cloud services. The hardware is pricey, but you get premium guts like a 70-watt-per-channel amp and a huge, velvet-smooth volume knob.

This video is the first in a two-part series discussing 5G. In this video, we’ll be discussing the many many aspects of current generation mobile networks that 5G is set to improve.
As well as the technologies and communication techniques that will be required to enable these upgrades in speed, latency, bandwidth, energy consumption and more!
[0:35–8:15] First we’ll take a look at the core technologies that 5G is composed of, how they work together and the benefits they will each bring.
[8:15–11:50] Following that, we’ll look at the upgrades 5G will bring to current mobile generation speeds, latency, bandwidth and energy consumption.
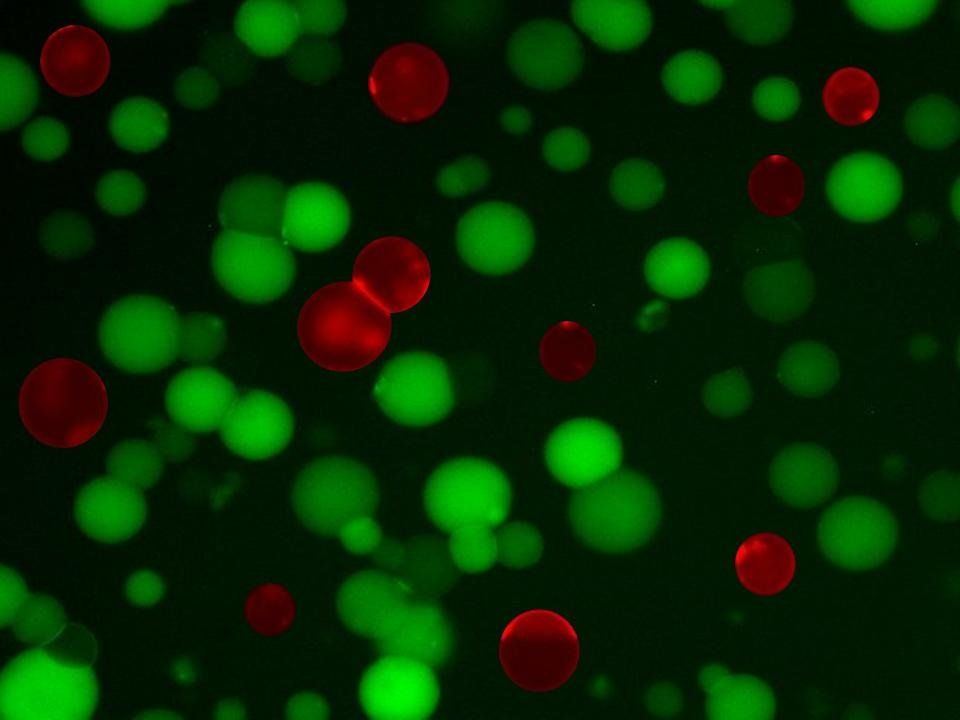
“Lego block” artificial cells that can kill bacteria have been created by researchers at the University of California, Davis Department of Biomedical Engineering. The work is reported Aug. 29 in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
“We engineered artificial cells from the bottom-up – like Lego blocks – to destroy bacteria,” said Assistant Professor Cheemeng Tan, who led the work. The cells are built from liposomes, or bubbles with a cell-like lipid membrane, and purified cellular components including proteins, DNA and metabolites.
“We demonstrated that artificial cells can sense, react and interact with bacteria, as well as function as systems that both detect and kill bacteria with little dependence on their environment,” Tan said.

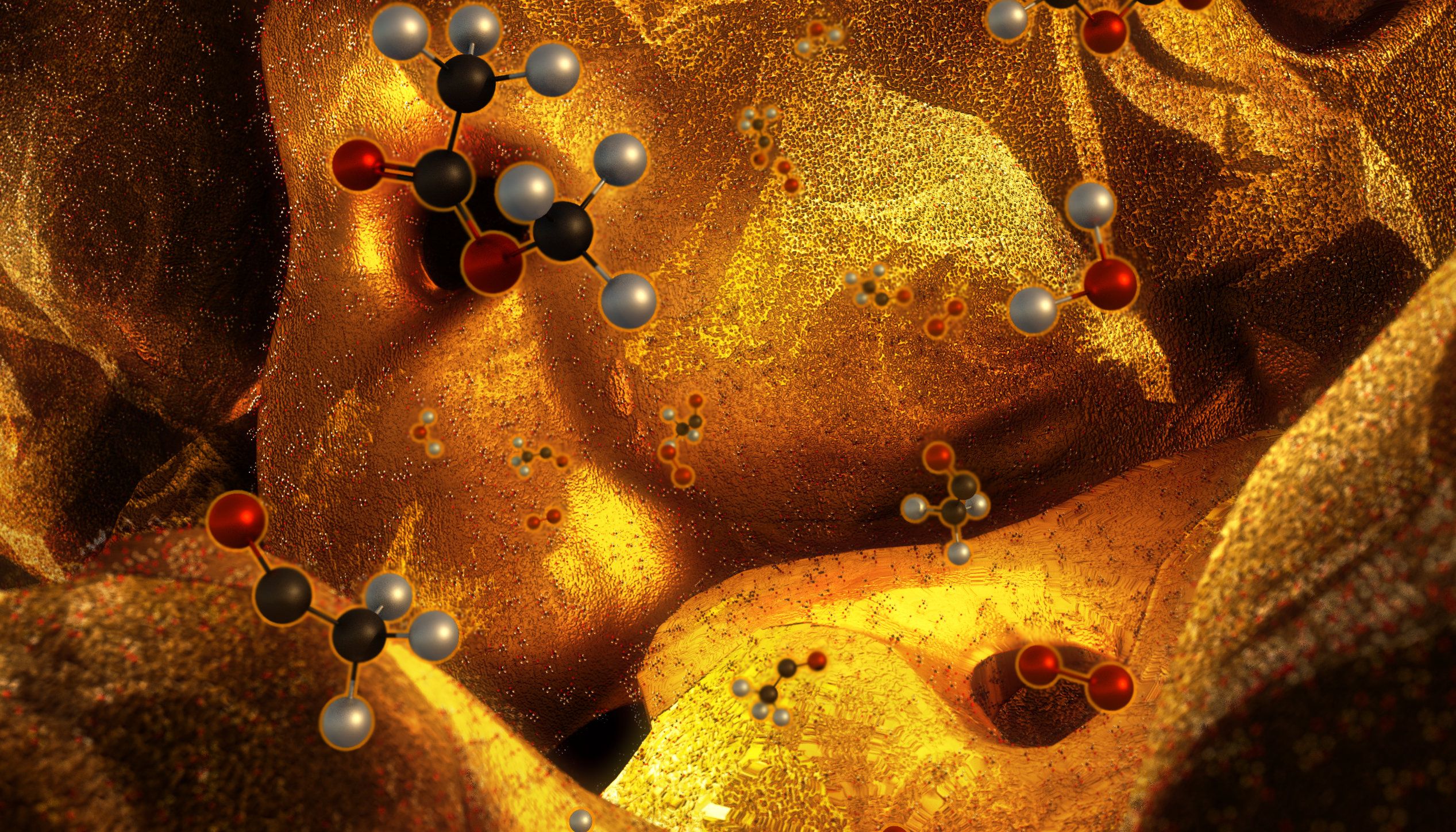
Nanoporous metals are superior catalysts for chemical reactions due to their large surface area and high electrical conductivity, making them perfect candidates for applications such as electrochemical reactors, sensors and actuators.
In a study published today in the journal Science Advances, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers, along with their counterparts at Harvard University, report on the hierarchical 3D printing of nanoporous gold, a proof of concept that researchers say could revolutionize the design of chemical reactors.
“If you consider traditional machining processes, it’s time consuming and you waste a lot of materials—also, you don’t have the capability to create complex structures,” said LLNL postdoctoral researcher Zhen Qi, a co-author on the paper. “By using 3D printing we can realize macroporous structures with application-specific flow patterns. By creating hierarchical structures, we provide pathways for fast mass transport to take full advantage of the large surface area of nanoporous materials. It’s also a way to save materials, especially precious metals.”
